Abstract
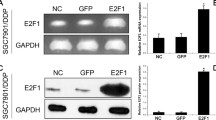
The aim of this study was to examine the effects of esophageal cancer-related gene 4 (ECRG4) expression levels on chemotherapeutic sensitivity of gastric cancer cells. A SGC-7901 cell system with tetracycline-inducible ECRG4 expression (SGC-7901/ECRG4) was successfully established. ECRG4 mRNA and protein expression levels were detected using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting, respectively. Chemosensitivity to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) was examined by cell proliferation assay and cell apoptosis assay. ECRG4 mRNA and protein expression levels were significantly upregulated in SGC-7901/ECRG4 cells induced with tetracycline. Compared with control cells, the growth inhibition rate of cells with ECRG4 overexpression was significantly increased when treated with 5-FU. Treatment with 5 μmol/l 5-FU resulted in 15.2 % apoptotic cells, whereas such treatment after overexpression of ECRG4 resulted in 44.5 % apoptotic cells. In conclusion, overexpression of ECRG4 enhanced the chemosensitivity of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells to 5-FU through induction of apoptosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leung WK, Wu MS, Kakugawa Y, Kim JJ, Yeoh KG, Goh KL, et al. Asia Pacific Working Group on Gastric Cancer. Screening for gastric cancer in Asia: current evidence and practice. Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:279–87. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(08)70072-X.
Kamangar F, Dores GM, Anderson WF. Patterns of cancer incidence, mortality, and prevalence across five continents: defining priorities to reduce cancer disparities in different geographic regions of the world. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2137–50. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.05.2308.
Macdonald JS. Treatment of localized gastric cancer. Semin Oncol. 2004;31:566–73. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2004.04.022.
Carrato A, Gallego-Plazas J, Guillen-Ponce C. Adjuvant therapy of resected gastric cancer is necessary. Semin Oncol. 2005;32:S105–8. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2005.06.005.
Su T, Liu H, Lu S. Cloning and identification of cDNA fragments related to human esophageal cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 1998;20:254–7.
Mirabeau O, Perlas E, Severini C, Audero E, Gascuel O, Possenti R, et al. Identification of novel peptide hormones in the human proteome by hidden Markov model screening. Genome Res. 2007;17:320–7. doi:10.1101/gr.5755407.
Gonzalez AM, Podvin S, Lin SY, Miller MC, Botfield H, Leadbeater WE, et al. Ecrg4 expression and its product augurin in the choroid plexus: impact on fetal brain development, cerebrospinal fluid homeostasis and neuroprogenitor cell response to CNS injury. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2011;8:6. doi:10.1186/2045-8118-8-6.
Kujuro Y, Suzuki N, Kondo T. Esophageal cancer-related gene 4 is a secreted inducer of cell senescence expressed by aged CNS precursor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:8259–64. doi:10.1073/pnas.0911446107.
Yue CM, Deng DJ, Bi MX, Guo LP, Lu SH. Expression of ECRG4, a novel esophageal cancer-related gene, downregulated by CpG island hypermethylation in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9:1174–8.
Mori Y, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, Kimura M, Mitsui A, Kurehara H, et al. Expression of ECRG4 is an independent prognostic factor for poor survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2007;18:981–5.
Li LW, Yu XY, Yang Y, Zhang CP, Guo LP, Lu SH. Expression of esophageal cancer related gene 4 (ECRG4), a novel tumor suppressor gene, in esophageal cancer and its inhibitory effect on the tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer. 2009;125:1505–13. doi:10.1002/ijc.24513.
Li W, Liu X, Zhang B, Qi D, Zhang L, Jin Y, et al. Overexpression of candidate tumor suppressor ECRG4 inhibits glioma proliferation and invasion. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010;29:89. doi:10.1186/1756-9966-29-89.
Li LW, Li YY, Li XY, Zhang CP, Zhou Y, Lu SH. A novel tumor suppressor gene ECRG4 interacts directly with TMPRSS11A (ECRG1) to inhibit cancer cell growth in esophageal carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:52. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-11-52.
Vanaja DK, Ehrich M, Van den Boom D, Cheville JC, Karnes RJ, Tindall DJ, et al. Hypermethylation of genes for diagnosis and risk stratification of prostate cancer. Cancer Invest. 2009;27:549–60. doi:10.1080/07357900802620794.
Götze S, Feldhaus V, Traska T, Wolter M, Reifenberger G, Tannapfel A, et al. ECRG4 is a candidate tumor suppressor gene frequently hypermethylated in colorectal carcinoma and glioma. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:447. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-9-447.
Ozawa A, Lick AN, Lindberg I. Processing of proaugurin is required to suppress proliferation of tumor cell lines. Mol Endocrinol. 2011;25:776–84. doi:10.1210/me.2010-0389.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, CP., Wu, BH., Wang, BQ. et al. Overexpression of ECRG4 enhances chemosensitivity to 5-fluorouracil in the human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell line. Tumor Biol. 34, 2269–2273 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0768-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0768-1