Abstract
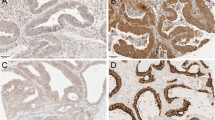
Toll-like receptor 4 belongs to the family of pattern recognition receptors and is therefore an important part of innate immunity. Since the last decade, Toll-like receptors (TLRs) have gained much interest in cancer research due to their role in tumor progression. However, there is scarcity of data evaluating TLR4 expression in different cell populations of tumor in relation to clinicopathological parameters of invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Therefore, we investigated TLR4 expression in 50 primary invasive ductal carcinoma and 17 lymph node sections through immunohistochemistry. Significant association of TLR4 expression with local metastasis and absence of necrosis was observed. The incidence of lymph node metastasis was higher in patients with high TLR4 expression in the tumor cells. We also observed an interesting inverse relationship of TLR4 with necrosis. In endothelial and lymphocytic population constituting breast tumors, a significant association of TLR4 expression was seen with the tumor grade. Therefore, we conclude that TLR4 expression is of biological interest both as a prognostic marker as well as a possible therapeutic target.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127(12):2893–917.
Li CI, Anderson BO, Daling JR, Moe RE. Trends in incidence rates of invasive lobular and ductal breast carcinoma. JAMA. 2003;289(11):1421–4.
Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357(9255):539–45.
Yu H, Kortylewski M, Pardoll D. Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: role of STAT3 in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(1):41–51.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell. 2000;100(1):57–70.
Mantovani A, Pierotti MA. Cancer and inflammation: a complex relationship. Cancer Lett. 2008;267(2):180–1.
Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2004;5(10):987–95.
Huang B, Zhao J, Shen S, Li H, He KL, Shen GX, Mayer L, Unkeless J, Li D, Yuan Y, et al. Listeria monocytogenes promotes tumor growth via tumor cell toll-like receptor 2 signaling. Cancer Res. 2007;67(9):4346–52.
Huang B, Zhao J, Li H, He KL, Chen Y, Chen SH, Mayer L, Unkeless JC, Xiong H. Toll-like receptors on tumor cells facilitate evasion of immune surveillance. Cancer Res. 2005;65(12):5009–14.
Kelly MG, Alvero AB, Chen R, Silasi DA, Abrahams VM, Chan S, Visintin I, Rutherford T, Mor G. TLR-4 signaling promotes tumor growth and paclitaxel chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66(7):3859–68.
Killeen SD, Wang JH, Andrews EJ, Redmond HP. Exploitation of the Toll-like receptor system in cancer: a doubled-edged sword? Br J Cancer. 2006;95(3):247–52.
Janeway Jr CA, Medzhitov R. Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:197–216.
Barton GM, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors and their ligands. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002;270:81–92.
Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2001;1(2):135–45.
Heine H, Lien E. Toll-like receptors and their function in innate and adaptive immunity. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2003;130(3):180–92.
Dunne A, O'Neill LA. The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: signal transduction during inflammation and host defense. Sci STKE. 2003;2003(171):re3.
Duesberg U, von dem Bussche A, Kirschning C, Miyake K, Sauerbruch T, Spengler U. Cell activation by synthetic lipopeptides of the hepatitis C virus (HCV)–core protein is mediated by toll like receptors (TLRs) 2 and 4. Immunol Lett. 2002;84(2):89–95.
Rassa JC, Meyers JL, Zhang Y, Kudaravalli R, Ross SR. Murine retroviruses activate B cells via interaction with toll-like receptor 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(4):2281–6.
Dong H, Zhu G, Tamada K, Chen L. B7-H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nat Med. 1999;5(12):1365–9.
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H, Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, et al. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 2002;8(8):793–800.
Brown JA, Dorfman DM, Ma FR, Sullivan EL, Munoz O, Wood CR, Greenfield EA, Freeman GJ. Blockade of programmed death-1 ligands on dendritic cells enhances T cell activation and cytokine production. J Immunol. 2003;170(3):1257–66.
Hua D, Liu MY, Cheng ZD, Qin XJ, Zhang HM, Chen Y, Qin GJ, Liang G, Li JN, Han XF, et al. Small interfering RNA-directed targeting of Toll-like receptor 4 inhibits human prostate cancer cell invasion, survival, and tumorigenicity. Mol Immunol. 2009;46(15):2876–84.
Hsu RY, Chan CH, Spicer JD, Rousseau MC, Giannias B, Rousseau S, Ferri LE. LPS-induced TLR4 signaling in human colorectal cancer cells increases beta1 integrin-mediated cell adhesion and liver metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011;71(5):1989–98.
Szczepanski MJ, Czystowska M, Szajnik M, Harasymczuk M, Boyiadzis M, Kruk-Zagajewska A, Szyfter W, Zeromski J, Whiteside TL. Triggering of Toll-like receptor 4 expressed on human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma promotes tumor development and protects the tumor from immune attack. Cancer Res. 2009;69(7):3105–13.
Gonzalez-Reyes S, Fernandez JM, Gonzalez LO, Aguirre A, Suarez A, Gonzalez JM, Escaff S, Vizoso FJ. Study of TLR3, TLR4, and TLR9 in prostate carcinomas and their association with biochemical recurrence. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011;60(2):217–26.
Szajnik M, Szczepanski MJ, Czystowska M, Elishaev E, Mandapathil M, Nowak-Markwitz E, Spaczynski M, Whiteside TL. TLR4 signaling induced by lipopolysaccharide or paclitaxel regulates tumor survival and chemoresistance in ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 2009;28(49):4353–63.
Fukata M, Chen A, Vamadevan AS, Cohen J, Breglio K, Krishnareddy S, Hsu D, Xu R, Harpaz N, Dannenberg AJ, et al. Toll-like receptor-4 promotes the development of colitis-associated colorectal tumors. Gastroenterology. 2007;133(6):1869–81.
Tsan MF, Gao B. Endogenous ligands of Toll-like receptors. J Leukoc Biol. 2004;76(3):514–9.
Gonzalez-Reyes S, Marin L, Gonzalez L, Gonzalez LO, del Casar JM, Lamelas ML, Gonzalez-Quintana JM, Vizoso FJ. Study of TLR3, TLR4 and TLR9 in breast carcinomas and their association with metastasis. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:665.
Yang H, Zhou H, Feng P, Zhou X, Wen H, Xie X, Shen H, Zhu X. Reduced expression of Toll-like receptor 4 inhibits human breast cancer cells proliferation and inflammatory cytokines secretion. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2010;29:92.
Yu L, Wang L, Li M, Zhong J, Wang Z, Chen S. Expression of toll-like receptor 4 is down-regulated during progression of cervical neoplasia. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010;59(7):1021–8.
DeNardo DG, Johansson M, Coussens LM. Immune cells as mediators of solid tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008;27(1):11–8.
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A, Balkwill F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 2008;454(7203):436–44.
Bhattacharya D, Yusuf N. Expression of toll-like receptors on breast tumors: taking a toll on tumor microenvironment. Int J Breast Cancer. 2012;2012:716564.
Aderem A, Ulevitch RJ. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature. 2000;406(6797):782–7.
Vamadevan AS, Fukata M, Arnold ET, Thomas LS, Hsu D, Abreu MT. Regulation of Toll-like receptor 4-associated MD-2 in intestinal epithelial cells: a comprehensive analysis. Innate Immun. 2010;16(2):93–103.
Faure E, Thomas L, Xu H, Medvedev A, Equils O, Arditi M. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide and IFN-gamma induce Toll-like receptor 2 and Toll-like receptor 4 expression in human endothelial cells: role of NF-kappa B activation. J Immunol. 2001;166(3):2018–24.
Cammarota R, Bertolini V, Pennesi G, Bucci EO, Gottardi O, Garlanda C, Laghi L, Barberis MC, Sessa F, Noonan DM, et al. The tumor microenvironment of colorectal cancer: stromal TLR-4 expression as a potential prognostic marker. J Transl Med. 2010;8:112.
Oblak A, Jerala R. Toll-like receptor 4 activation in cancer progression and therapy. Clin Dev Immunol. 2011;2011:609579.
Andrews EJ, Wang JH, Winter DC, Laug WE, Redmond HP. Tumor cell adhesion to endothelial cells is increased by endotoxin via an upregulation of beta-1 integrin expression. J Surg Res. 2001;97(1):14–9.
Wang JH, Manning BJ, Wu QD, Blankson S, Bouchier-Hayes D, Redmond HP. Endotoxin/lipopolysaccharide activates NF-kappa B and enhances tumor cell adhesion and invasion through a beta 1 integrin-dependent mechanism. J Immunol. 2003;170(2):795–804.
Cairns B, Maile R, Barnes CM, Frelinger JA, Meyer AA. Increased Toll-like receptor 4 expression on T cells may be a mechanism for enhanced T cell response late after burn injury. J Trauma. 2006;61(2):293–8. discussion 298–299.
Hayashi EA, Granato A, Paiva LS, Bertho AL, Bellio M, Nobrega A. TLR4 promotes B cell maturation: independence and cooperation with B lymphocyte-activating factor. J Immunol. 2010;184(9):4662–72.
Hwang IY, Park C, Harrison K, Kehrl JH. TLR4 signaling augments B lymphocyte migration and overcomes the restriction that limits access to germinal center dark zones. J Exp Med. 2009;206(12):2641–57.
Pober JS, Cotran RS. Cytokines and endothelial cell biology. Physiol Rev. 1990;70(2):427–51.
Mantovani A, Bussolino F, Dejana E. Cytokine regulation of endothelial cell function. FASEB J. 1992;6(8):2591–9.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan and the recurring budget of ASAB provided by NUST for the financial support of this project.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ehsan, N., Murad, S., Ashiq, T. et al. Significant correlation of TLR4 expression with the clinicopathological features of invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Tumor Biol. 34, 1053–1059 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0645-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-0645-y