Abstract
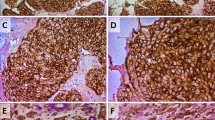
The expression status of CD74 in breast cancer stem cells and its clinical implications was evaluated in order to lay a foundation for managing breast cancer. Five hundred and eighty breast cancer specimens were enrolled in the study. The relationship between the CD74 protein and clinicopathological parameters as well as prognosis was subsequently determined. In total, 468 (80.69 %) of the 580 breast cases showed CD74-positive expression. After universal analysis, CD74 was observed to be related to lymph node metastasis and triple-negative breast cancer (P = 0.01 and 0.001). Moreover, CD74 expression has a line correlation with lymph node metastasis and triple-negative breast cancer (P = 0.02 and 0.001). Furthermore, periostin was shown to attain a significantly more distant liver metastasis and worse disease-specific survival than those with none or low-expressed CD74 protein (P = 0.001). In the Cox regression test, CD74 protein was detected as an independent prognostic factor (P = 0.001). CD74 is consistently expressed in triple-negative subgroups of breast cancer and might be a new potential marker for triple-negative breast cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Morales-Vasquez F, Hortobagyi GN. Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:1–22.
Kasami M, Uematsu T, Honda M, et al. Comparison of estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor and Her-2 status in breast cancer pre- and post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast. 2008;17:523–7.
Curado MP. Breast cancer in the world: incidence and mortality. Salud Publica Mex. 2011;53(5):372–84.
Liu C, Chen B, Zhu J, Zhang R, Yao F, Jin F, et al. Clinical implications for nestin protein expression in breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2010;101(3):815–9.
Krop IE, Lorusso P, Miller KD, Modi S, Yardley D, Rodriguez G, et al. A phase II study of trastuzumab emtansine in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive metastatic breast cancer who were previously treated with trastuzumab, lapatinib, an anthracycline, a taxane, and capecitabine. J Clin Oncol. 2012. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.40.5902
Chu QD, King T, Hurd T. Triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Breast Cancer. 2012;2012:671–84.
Liu C, Cao X, Zhang Y, Xu H, Zhang R, Wu Y, et al. Co-expression of Oct-4 and nestin in human breast cancers. Mol Biol Rep. 2011;39(5):5876–81.
Zeng Q, Li W, Lu D, Wu Z, Duan H, Luo Y, et al. CD146, an epithelial–mesenchymal transition inducer, is associated with triple-negative breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(4):1127–32.
Zheng YX, Yang M, Rong TT, Yuan XL, Ma YH, Wang ZH, et al. CD74 and macrophage migration inhibitory factor as therapeutic targets in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(18):2253–61.
Greenwood C, Metodieva G, Al-Janabi K, Lausen B, Alldridge L, Leng L, et al. Stat1 and CD74 overexpression is co-dependent and linked to increased invasion and lymph node metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. J Proteomics. 2012;75(10):3031–40.
Meyer P, Landgraf K, Högel B, Eiermann W, Ataseven B. BRCA2 mutations and triple-negative breast cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e38361.
Liu C, Lu Y, Wang B, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Lu Y, et al. Clinical implications of stem cell gene oct-4 expression in breast cancer. Annu Surg. 2011;253(6):1165–71.
Stove V, Verhasselt B. Modelling thymic HIV-1 Nef effects. Curr HIV Res. 2006;4(1):57–64.
Nagata S, Jin YF, Yoshizato K, Tomoeda M, Song M, Iizuka N, et al. CD74 is a novel prognostic factor for patients with pancreatic cancer receiving multimodal therapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(9):2531–8.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, B., Zhang, Y., Li, N. et al. CD74: a potential novel target for triple-negative breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 33, 2273–2277 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0489-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-012-0489-x