Abstract
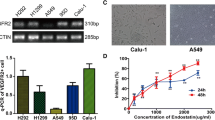
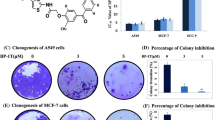
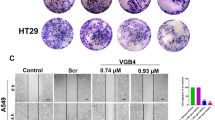
Recombinant human endostatin (rh-endostatin), a potential antiangiogenic agent, is used in non-small cell lung carcinoma treatment and represses vascular endothelial cell growth factor (VEGF) levels in tumor cell. However, precise affection of rh-endostatin on the proangiogenic VEGF isoforms (VEGF165) or antiangiogenic VEGF isoforms (VEGF165b) is not clear. We therefore tested the hypothesis that rh-endostatin could alter expression of these isoforms to regulate tumor growth. A549 cells were exposed to rh-endostatin, and the expression of VEGF165 and VEGF165b was detected. The role of SP1 as a regulator of isoform expression was investigated. We then examined the anticancer and antiangiogenic efficacy of rh-endostatin in combination with exogenous VEGF165b against A549 cells, EA.HY 926 cells and xenograft model of human lung cancer. rh-Endostatin reduced VEGF165 and induced VEGF165b as well as inhibited SP1 in A549 cells. SP1 inhibitor (betulinic acid) also developed those changes. VEGF165b–rh-endostatin combination was highly synergistic and inhibited growth, survival, and migration of A549 cells, VEGF-mediated VEGFR2 phosphorylation in EA.HY 926 cells, and tumor growth in xenograft model of human lung cancer. rh-Endostatin downregulates proangiogenic vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) isoform and upregulates antiangiogenic VEGFA isoform, possibly through inhibition of SP1. Furthermore, VEGF165b sensitizes A549 to rh-endostatin treatment and enhances the anticancer effect of rh-endostatin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J. What is the evidence that tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 1990;82:4–6.
Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett N, Phillips HS, et al. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature. 1993;362:841–4.
O’Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, et al. Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell. 1997;88:277–85.
O’Reilly MS, Holmgren L, Shing Y, Chen C, Rosenthal RA, Moses M, et al. Angiostatin: a novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the suppression of metastases by a lewis lung carcinoma. Cell. 1994;79:315–28.
Bates DO, Cui TG, Doughty JM, Winkler M, Sugiono M, Shields JD, et al. Vegf165b, an inhibitory splice variant of vascular endothelial growth factor, is down-regulated in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2002;62:4123–31.
Nowak DG, Woolard J, Amin EM, Konopatskaya O, Saleem MA, Churchill AJ, et al. Expression of pro- and anti-angiogenic isoforms of vegf is differentially regulated by splicing and growth factors. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:3487–95.
Perrin RM, Konopatskaya O, Qiu Y, Harper S, Bates DO, Churchill AJ. Diabetic retinopathy is associated with a switch in splicing from anti- to pro-angiogenic isoforms of vascular endothelial growth factor. Diabetologia. 2005;48:2422–7.
Woolard J, Wang WY, Bevan HS, Qiu Y, Morbidelli L, Pritchard-Jones RO, et al. Vegf165b, an inhibitory vascular endothelial growth factor splice variant: mechanism of action, in vivo effect on angiogenesis and endogenous protein expression. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7822–35.
Varey AH, Rennel ES, Qiu Y, Bevan HS, Perrin RM, Raffy S, et al. Vegf 165 b, an antiangiogenic vegf-a isoform, binds and inhibits bevacizumab treatment in experimental colorectal carcinoma: balance of pro- and antiangiogenic vegf-a isoforms has implications for therapy. Br J Cancer. 2008;98:1366–79.
Pritchard-Jones RO, Dunn DB, Qiu Y, Varey AH, Orlando A, Rigby H, et al. Expression of vegf(xxx)b, the inhibitory isoforms of vegf, in malignant melanoma. Br J Cancer. 2007;97:223–30.
Diaz R, Pena C, Silva J, Lorenzo Y, Garcia V, Garcia JM, et al. P73 isoforms affect vegf, vegf165b and pedf expression in human colorectal tumors: Vegf165b downregulation as a marker of poor prognosis. Int J Cancer. 2008;123:1060–7.
Rennel ES, Hamdollah-Zadeh MA, Wheatley ER, Magnussen A, Schuler Y, Kelly SP, et al. Recombinant human vegf165b protein is an effective anti-cancer agent in mice. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44:1883–94.
Rennel E, Waine E, Guan H, Schuler Y, Leenders W, Woolard J, et al. The endogenous anti-angiogenic vegf isoform, vegf165b inhibits human tumour growth in mice. Br J Cancer. 2008;98:1250–7.
Kim HS, Lim SJ, Park YK. Anti-angiogenic factor endostatin in osteosarcoma. APMIS. 2009;117:716–23.
Sim BK, MacDonald NJ, Gubish ER. Angiostatin and endostatin: endogenous inhibitors of tumor growth. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2000;19:181–90.
Dhanabal M, Ramchandran R, Waterman MJ, Lu H, Knebelmann B, Segal M, et al. Endostatin induces endothelial cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:11721–6.
Yamaguchi N, Anand-Apte B, Lee M, Sasaki T, Fukai N, Shapiro R, et al. Endostatin inhibits vegf-induced endothelial cell migration and tumor growth independently of zinc binding. EMBO J. 1999;18:4414–23.
Kim YM, Hwang S, Kim YM, Pyun BJ, Kim TY, Lee ST, et al. Endostatin blocks vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated signaling via direct interaction with kdr/flk-1. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:27872–9.
Boehm T, Folkman J, Browder T, O’Reilly MS. Antiangiogenic therapy of experimental cancer does not induce acquired drug resistance. Nature. 1997;390:404–7.
Ling Y, Yang Y, Lu N, You QD, Wang S, Gao Y, et al. Endostar, a novel recombinant human endostatin, exerts antiangiogenic effect via blocking vegf-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of kdr/flk-1 of endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;361:79–84.
Song HF, Liu XW, Zhang HN, Zhu BZ, Yuan SJ, Liu SY, et al. Pharmacokinetics of his-tag recombinant human endostatin in rhesus monkeys. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005;26:124–8.
Hajitou A, Grignet C, Devy L, Berndt S, Blacher S, Deroanne CF, et al. The antitumoral effect of endostatin and angiostatin is associated with a down-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in tumor cells. FASEB J. 2002;16:1802–4.
Ryuto M, Ono M, Izumi H, Yoshida S, Weich HA, Kohno K, et al. Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor by tumor necrosis factor alpha in human glioma cells. Possible roles of sp-1. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:28220–8.
Tekle C, Giovannetti E, Sigmond J, Graff JR, Smid K, Peters GJ. Molecular pathways involved in the synergistic interaction of the pkc beta inhibitor enzastaurin with the antifolate pemetrexed in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2008;99:750–9.
Chen WC, McBride WH, Iwamoto KS, Barber CL, Wang CC, Oh YT, et al. Induction of radioprotective peroxiredoxin-i by ionizing irradiation. J Neurosci Res. 2002;70:794–8.
Jeong HW, Nam JO, Kim IS. The cooh-terminal end of r-ras alters the motility and morphology of breast epithelial cells through rho/rho-kinase. Cancer Res. 2005;65:507–15.
Xu L, Deng X. Protein kinase ciota promotes nicotine-induced migration and invasion of cancer cells via phosphorylation of micro- and m-calpains. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:4457–66.
Chintharlapalli S, Papineni S, Ramaiah SK, Safe S. Betulinic acid inhibits prostate cancer growth through inhibition of specificity protein transcription factors. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2816–23.
Eremeeva ME, Silverman DJ. Rickettsia rickettsii infection of the ea.Hy 926 endothelial cell line: morphological response to infection and evidence for oxidative injury. Microbiology. 1998;144:2037–48.
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the key program of the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (no. 2009CDA061) and Simcere Pharmaceutical Research Co., Ltd., Jiangsu Province, P.R.China.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Zy., Zhu, F., Hu, Jl. et al. Sp1 inhibition-mediated upregulation of VEGF165b induced by rh-endostatin enhances antiangiogenic and anticancer effect of rh-endostatin in A549. Tumor Biol. 32, 677–687 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-011-0168-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-011-0168-3