Abstract
Background
Tourette syndrome (TS) is a chronic neuropsychiatric disorder, also known as multiple tic syndrome. TS is associated with the serotonin (5-HT) system, of which 5-HT2A is a subtype. Xiaoyao San (XYS) comes from “Prescriptions of the Bureau of Taiping People’s Welfare”. It has the effect of harmonizing liver and spleen, relieving depression, nourishing blood, and invigorating spleen. However, the therapeutic mechanism of XYS for TS has not been evaluated. This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effect of XYS on the TS mouse model and its possible mechanism.
Methods
A mouse model of TS induced by DOI (selective 5-HT (2A/2C) receptor agonist, 10 ml/kg) was established. The mice were randomly divided into normal control group, DOI group, DOI + Tiapride Hydrochloride (Tia at 25 mg /kg) group, DOI + XYS low-dose (1.44 g/kg/d), medium-dose (2.88 g/kg/d) and high-dose (5.76 g/kg/d) groups, and the mice were given the corresponding drug intragastric administration for four consecutive weeks, and the stereotypic behavior was recorded weekly. The morphological characteristics of the cells were observed by hematoxylin–eosin staining. The content of 5-HT was determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Western blot and quantitative polymerase chain reaction were used to detect 5-HT2A.
Results
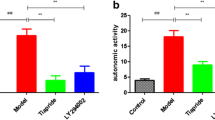
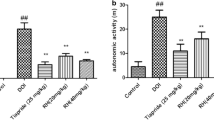
XYS could significantly improve the stereotypic behavior of TS mice, and the improvement effect increased with the increase of dose, the improvement effect of XYS high dose was similar to that of Tia. After Tia or XYS high-dose treatment, the prefrontal cortex cells and neuronal structure of TS mice gradually normal, cells arranged neatly. The prefrontal cortex cells recovered generally after XYS low-dose and medium-dose treatments. 5-HT in the serum of mice in all treatment groups was higher than that in the DOI group, and 5-HT in serum of XYS high-dose group and Tia group was the highest. 5-HT2A receptor protein and mRNA in the prefrontal cortex of mice in all treatment groups showed a downward trend, and the decrease degree was the largest in the XYS high-dose group and Tia group.
Conclusion
XYS has an improvement effect on TS in mice, and its mechanism is related to reducing 5-HT2A receptor expression, increasing 5-HT content, and enhancing 5-HT system activity. These results suggest that XYS is a therapeutic strategy for TS treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Anderson et al (1992) Postmortem analysis of subcortical monoamines and amino acids in Tourette syndrome. Adv Neurol 58:123–133
Barnes NM, Sharp T (1999) A review of central 5-HT receptors and their function. Neuropharmacology 38(8):1083–1152
Bishop C, Tessmer JL, Ullrich T, Rice KC, Walker PD (2004) Serotonin 5-HT2A receptors underlie increased motor behaviors induced in dopamine-depleted rats by intrastriatal 5-HT2A/2C agonism. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310(2):687–694
Buse J, Schoenefeld K, Münchau A, Roessner V (2013) Neuromodulation in Tourette syndrome: dopamine and beyond. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37(6):1069–1084
Comings DE (1990) Blood serotonin and tryptophan in Tourette syndrome. Am J Med Genet 36(4):418–430
Darmani NA, Martin BR, Glennon RA (1990) Withdrawal from chronic treatment with (+/-)-DOI causes super-sensitivity to 5-HT2 receptor-induced head-twitch behaviour in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 186(1):115–118
Diamond BI, Reyes MG, Borison R (1982) A new animal model for Tourette syndrome. Adv Neurol 35:221–225
González-Maeso J et al (2007) Hallucinogens recruit specific cortical 5-HT(2A) receptor-mediated signaling pathways to affect behavior. Neuron 53(3):439–452
Haugbøl S et al (2007) Cerebral 5-HT2A receptor binding is increased in patients with Tourette’s syndrome. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 10(2):245–252
Higgins GA, Enderlin M, Haman M, Fletcher PJ (2003) The 5-HT2A receptor antagonist M100,907 attenuates motor and “impulsive-type” behaviours produced by NMDA receptor antagonism. Psychopharmacology 170(3):309–319
Houeto JL, Giré P (2008) Tics and tourette syndrome: diagnosis, course and treatment principles. Presse Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lpm.2007.11.007
Jankovic J, Jimenez-Shahed J, Brown LW (2010) A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of topiramate in the treatment of Tourette syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 81(1):70–73
Lodge DJ, Grace AA (2006) The hippocampus modulates dopamine neuron responsivity by regulating the intensity of phasic neuron activation. Neuropsychopharmacology 31(7):1356–1361
Ninan I, Kulkarni SK (1998) 5-HT2A receptor antagonists block MK-801-induced stereotypy and hyperlocomotion. Eur J Pharmacol 358(2):111–116
Robertson MM, Eapen V, Cavanna AE (2009) The international prevalence, epidemiology, and clinical phenomenology of tourette syndrome: a cross-cultural perspective. J Psychosom Res 67(6):475–483
Scharf JM et al (2015) Population prevalence of tourette syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov Disord 30(2):221–228
Scharf JM, Miller LL, Mathews CA, Ben-Shlomo Y (2012) Prevalence of tourette syndrome and chronic tics in the population-based avon longitudinal study of parents and children cohort. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 51(2):192-201.e195
Schreiber R et al (1995) (1-(2,5-dimethoxy-4 iodophenyl)-2-aminopropane)-induced head-twitches in the rat are mediated by 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) 2A receptors: modulation by novel 5-HT2A/2C antagonists, D1 antagonists and 5-HT1A agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 273(1):101–112
Su GY et al (2014) Antidepressant-like effects of Xiaochaihutang in a rat model of chronic unpredictable mild stress. J Ethnopharmacol 152(1):217–226
Su H et al (2021) Simultaneous determination of multiple components in formula and preparations of Xiaoyaosan. Nat Prod Res 35(7):1207–1211
Wang D (2020) Effects of jian-pi-zhi-dong decoction on the expression of 5-ht and its receptor in a rat model of tourette syndrome and comorbid anxiety. Med Sci Monit 26:e924658
Wang Y et al (2016) Antidepressant-like effects of the radix bupleuri and radix paeoniae alba drug pair. Neurosci Lett 633:14–20
Willins DL, Meltzer HY (1997) Direct injection of 5-HT2A receptor agonists into the medial prefrontal cortex produces a head-twitch response in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 282(2):699–706
Wu XL (2023) Paeoniflorin inhibits pancreatitis-induced oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress through NF-κB/MAPK pathway. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 37(4):2043–2054
Xian YF, Fan D, Ip SP, Mao QQ, Lin ZX (2017) Antidepressant-like effect of isorhynchophylline in mice. Neurochem Res 42(2):678–685
Yael D, Israelashvili M, Bar-Gad I (2016) Animal models of tourette syndrome-from proliferation to standardization. Front Neurosci 10:132
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xingyue Liu designed the research study. Xingyue Liu and Guoyun Cao performed the research. Xingyue Liu and Guoyun Cao provided help and advice on the experiments. Guoyun Cao analyzed the data. Xingyue Liu wrote the manuscript. Xingyue Liu and Guoyun Cao reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors contributed to editorial changes in the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
Author Xingyue Liu declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Guoyun Cao declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The present study was approved by the Animal experiments were approved by Cangzhou Hospital of Integrated TCM-WM Hebei Animal Experimental Ethics Committee. And all procedures complied with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Use of Laboratory Animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Cao, G. A preliminary study on the effects of Xiaoyao San on neurological function and 5-HT2A mRNA expression in mice with Tourette syndrome. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-024-00460-8
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-024-00460-8