Abstract
Background
Baicalin has been proven to have the potential to reduce apoptosis and diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM). However, the mechanism behind this effect still needs to be fully understood.
Objectives
To explore the potential therapeutic properties of Baicalin in managing DCM and controlling glycemic levels.
Results
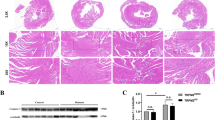
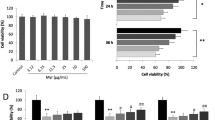
In this study, Baicalin (at doses of 20, 60, or 120 mg/kg/d) were used to treat diabetic rats. At the end of treatment, the heart function of the rats was assessed. Furthermore, their serum levels of TG, TC, and LDL were measured using the ELISA method. Cell viability was evaluated using the CCK8 assay and apoptosis was assessed using flow cytometry or TUNEL assay. Primary cardiomyocytes were infected with NRF2 siRNA and then treated with Baicalin while incubating with high glucose (25 mmol/L). Protein and mRNA variations were analyzed using Western blot and qRT-PCR, respectively. The study found that when given Baicalin, diabetic rats demonstrated improved heart function. Without treatment, the hearts of diabetic rats displayed elevated levels of apoptotic cell death and cardiomyocyte autophagy, as well as decreased expressions of NRF2, HO-1, and KEAP1. However, Baicalin was able to reverse all of these diabetes-induced biochemical changes. Treatment enhanced NRF2 nuclear transfer, reduced hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis and autophagy in primary cardiomyocytes, and improved cellular viability in in vitro experiments. It must be noted that the protective effects of Baicalin were only observed when the Nrf2 gene expression was present in primary cardiomyocytes.
Conclusion
Baicalin may reduce the effects of DCM by activating NRF2 through KEAP1 suppression and regulating autophagy activation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author by reasonable request.
References
Alnahdi A, John A, Raza H (2019) Augmentation of glucotoxicity, oxidative stress, apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction in Hepg2 cells by palmitic acid. Nutrients 11(9):1979
Armstrong AC, Ambale-Venkatesh B, Turkbey E, Donekal S, Chamera E, Backlund JY, Cleary P, Lachin J, Bluemke DA, Lima JA (2017) Association of cardiovascular risk factors and myocardial fibrosis with early cardiac dysfunction in Type 1 diabetes: the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications study. Diabetes Care 40(3):405–411
Asbun J, Villarreal FJ (2006) The pathogenesis of myocardial fibrosis in the setting of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 47(4):693–700
Bai J, Wang Q, Qi J, Yu H, Wang C, Wang X, Ren Y, Yang F (2019) Promoting effect of baicalin on nitric oxide production in cmecs via activating the Pi3k-Akt-Enos pathway attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Phytomedicine 63:153035
Cao G, Yang C, Jin Z, Wei H, Xin C, Zheng C, Xu J, Huang Q, Zhang Z, Hu T (2022) Fndc5/Irisin reduces ferroptosis and improves mitochondrial dysfunction in hypoxic cardiomyocytes by Nrf2/Ho-1 Axis. Cell Biol Int 46(5):723–736
Chen X, Wan W, Guo Y, Ye T, Fo Y, Sun Y, Qu C, Yang B, Zhang C (2021) Pinocembrin ameliorates post-infarct heart failure through activation of Nrf2/Ho-1 signaling pathway. Mol Med 27(1):100
Despa S, Margulies KB, Chen L, Knowlton AA, Havel PJ, Taegtmeyer H, Bers DM, Despa F (2012) Hyperamylinemia contributes to cardiac dysfunction in obesity and diabetes: a study in humans and rats. Circ Res 110(4):598–608
Dhakshinamoorthy S, Long DJ 2nd, Jaiswal AK (2000) Antioxidant regulation of genes encoding enzymes that detoxify xenobiotics and carcinogens. Curr Top Cell Regul 36:201–216
Dillmann WH (2019) Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res 124(8):1160–1162
Fiordaliso F, Bianchi R, Staszewsky L, Cuccovillo I, Doni M, Laragione T, Salio M, Savino C, Melucci S, Santangelo F et al (2004) Antioxidant treatment attenuates hyperglycemia-induced cardiomyocyte death in rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol 37(5):959–968
Gao G, Chen W, Yan M, Liu J, Luo H, Wang C, Yang P (2020) Rapamycin regulates the balance between cardiomyocyte apoptosis and autophagy in chronic heart failure by inhibiting mtor signaling. Int J Mol Med 45(1):195–209
Guo F, Wang Y, Wang J, Liu Z, Lai Y, Zhou Z, Liu Z, Zhou Y, Xu X, Li Z et al (2022) Choline protects the heart from doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity through vagal activation and Nrf2/Ho-1 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:4740931
Hu X, Rajesh M, Zhang J, Zhou S, Wang S, Sun J, Tan Y, Zheng Y, Cai L (2018) Protection by dimethyl fumarate against diabetic cardiomyopathy in type 1 diabetic mice likely via activation of nuclear factor erythroid-2 related factor 2. Toxicol Lett 287:131–141
Huang DD, Shi G, Jiang Y, Yao C, Zhu C (2020) A review on the potential of resveratrol in prevention and therapy of diabetes and diabetic complications. Biomed Pharmacother 125:109767
Ichimura Y, Waguri S, Sou YS, Kageyama S, Hasegawa J, Ishimura R, Saito T, Yang Y, Kouno T, Fukutomi T et al (2013) Phosphorylation of P62 activates the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway during selective autophagy. Mol Cell 51(5):618–631
Jain A, Lamark T, Sjøttem E, Larsen KB, Awuh JA, Øvervatn A, McMahon M, Hayes JD, Johansen T (2010) P62/Sqstm1 is a target gene for transcription factor nrf2 and creates a positive feedback loop by inducing antioxidant response element-driven gene transcription. J Biol Chem 285(29):22576–22591
Jiang T, Harder B, Rojo de la Vega M, Wong PK, Chapman E, Zhang DD (2015) P62 links autophagy and Nrf2 signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 88(Pt B):199–204
Jiang T, Peng D, Shi W, Guo J, Huo S, Men L, Zhang C, Li S, Lv J, Lin L (2021) Il-6/Stat3 signaling promotes cardiac dysfunction by upregulating Fundc1-dependent mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes formation in sepsis mice. Front Cardiovasc Med 8:790612
Kong F, Luan Y, Zhang ZH, Cheng GH, Qi TG, Sun C (2014) Baicalin protects the myocardium from reperfusion-induced damage in isolated rat hearts via the antioxidant and paracrine effect. Exp Ther Med 7(1):254–259
Lacombe VA, Viatchenko-Karpinski S, Terentyev D, Sridhar A, Emani S, Bonagura JD, Feldman DS, Györke S, Carnes CA (2007) Mechanisms of impaired calcium handling underlying subclinical diastolic dysfunction in diabetes. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293(5):R1787–R1797
Li K, Deng Y, Deng G, Chen P, Wang Y, Wu H, Ji Z, Yao Z, Zhang X, Yu B et al (2020a) High cholesterol induces apoptosis and autophagy through the Ros-Activated Akt/Foxo1 pathway in tendon-derived stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 11(1):131
Li Z, Cheng J, Liu J (2020b) Baicalin protects human Oa chondrocytes against Il-1β-induced apoptosis and Ecm degradation by activating autophagy via Mir-766-3p/Aifm1 axis. Drug Des Devel Ther 14:2645–2655
Liao HH, Zhang N, Meng YY, Feng H, Yang JJ, Li WJ, Chen S, Wu HM, Deng W, Tang QZ (2019) Myricetin alleviates pathological cardiac hypertrophy via Traf6/Tak1/Mapk and Nrf2 signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:6304058
Lin L, Wu XD, Davey AK, Wang J (2010) The Anti-Inflammatory effect of baicalin on hypoxia/reoxygenation and Tnf-alpha induced injury in cultural rat cardiomyocytes. Phytother Res 24(3):429–437
Liu P, Li J, Liu M, Zhang M, Xue Y, Zhang Y, Han X, Jing X, Chu L (2021) Hesperetin modulates the Sirt1/Nrf2 signaling pathway in counteracting myocardial ischemia through suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother 139:111552
Lorenzo-Almorós A, Cepeda-Rodrigo JM, Lorenzo Ó (2022) Diabetic cardiomyopathy. Rev Clin Esp (barc) 222(2):100–111
Lovic D, Piperidou A, Zografou I, Grassos H, Pittaras A, Manolis A (2020) The growing epidemic of diabetes mellitus. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 18(2):104–109
Luo J, Yan D, Li S, Liu S, Zeng F, Cheung CW, Liu H, Irwin MG, Huang H, Xia Z (2020) Allopurinol reduces oxidative stress and activates Nrf2/P62 to attenuate diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats. J Cell Mol Med 24(2):1760–1773
Ma Q (2013) Role of Nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:401–426
Ma L, Wu F, Shao Q, Chen G, Xu L, Lu F (2021) Baicalin alleviates oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic nephropathy via Nrf2 and Mapk signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther 15:3207–3221
Maack C, Lehrke M, Backs J, Heinzel FR, Hulot JS, Marx N, Paulus WJ, Rossignol P, Taegtmeyer H, Bauersachs J et al (2018) Heart failure and diabetes: metabolic alterations and therapeutic interventions: a state-of-the-art review from the translational research committee of the heart failure association-European society of cardiology. Eur Heart J 39(48):4243–4254
Marwick TH, Ritchie R, Shaw JE, Kaye D (2018) Implications of underlying mechanisms for the recognition and management of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 71(3):339–351
Murtaza G, Virk HUH, Khalid M, Lavie CJ, Ventura H, Mukherjee D, Ramu V, Bhogal S, Kumar G, Shanmugasundaram M et al (2019) Diabetic cardiomyopathy - a comprehensive updated review. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 62(4):315–326
Nie P, Bai X, Lou Y, Zhu Y, Jiang S, Zhang L, Tian N, Luo P, Li B (2021) Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce oxidative damage and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy by activating Nrf2. Stem Cell Res Ther 12(1):450
Ogurtsova K, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Huang Y, Linnenkamp U, Guariguata L, Cho NH, Cavan D, Shaw JE, Makaroff LE (2017) Idf diabetes atlas: global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 128:40–50
Paolillo S, Marsico F, Prastaro M, Renga F, Esposito L, De Martino F, Di Napoli P, Esposito I, Ambrosio A, Ianniruberto M et al (2019) Diabetic cardiomyopathy: definition, diagnosis, and therapeutic implications. Heart Fail Clin 15(3):341–347
Papatheodorou K, Banach M, Bekiari E, Rizzo M, Edmonds M (2018) Complications of diabetes 2017. J Diabetes Res 2018:3086167
Perry BD, Caldow MK, Brennan-Speranza TC, Sbaraglia M, Jerums G, Garnham A, Wong C, Levinger P et al (2016) Muscle atrophy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: roles of inflammatory pathways, physical activity and exercise. Exerc Immunol Rev 22:94–109
Rawshani A, Rawshani A, Franzén S, Eliasson B, Svensson AM, Miftaraj M, McGuire DK, Sattar N, Rosengren A, Gudbjörnsdottir S (2017) Mortality and cardiovascular disease in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 376(15):1407–1418
Ren BC, Zhang YF, Liu SS, Cheng XJ, Yang X, Cui XG, Zhao XR, Zhao H, Hao MF, Li MD et al (2020) Curcumin alleviates oxidative stress and inhibits apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy via Sirt1-Foxo1 and Pi3k-Akt signalling pathways. J Cell Mol Med 24(21):12355–12367
Rushmore TH, Morton MR, Pickett CB (1991) The antioxidant responsive element. activation by Oxidative Stress and Identification of the DNA consensus sequence required for functional activity. J Biol Chem 266(18):11632–11639
Russo I, Frangogiannis NG (2016) Diabetes-associated cardiac fibrosis: cellular effectors, molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J Mol Cell Cardiol 90:84–93
Ryter SW, Choi AM (2013) Autophagy: an integral component of the mammalian stress response. J Biochem Pharmacol Res 1(3):176–188
Shen K, Feng X, Pan H, Zhang F, Xie H, Zheng S (2017) Baicalin ameliorates experimental liver cholestasis in mice by modulation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and Nrf2 transcription factor. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:6169128
Singh S, Meena A, Luqman S (2021) Baicalin mediated regulation of key signaling pathways in cancer. Pharmacol Res 164:105387
Su H, Ji L, Xing W, Zhang W, Zhou H, Qian X, Wang X, Gao F, Sun X, Zhang H (2013) Acute hyperglycaemia enhances oxidative stress and aggravates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury: role of thioredoxin-interacting protein. J Cell Mol Med 17(1):181–191
Tan Y, Ichikawa T, Li J, Si Q, Yang H, Chen X, Goldblatt CS, Meyer CJ, Li X, Cai L et al (2011) Diabetic downregulation of Nrf2 activity via Erk contributes to oxidative stress-induced insulin resistance in cardiac cells in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes 60(2):625–633
Ti Y, Xie GL, Wang ZH, Bi XL, Ding WY, Wang J, Jiang GH, Bu PL, Zhang Y, Zhong M et al (2011) Trb3 gene silencing alleviates diabetic cardiomyopathy in a type 2 diabetic rat model. Diabetes 60(11):2963–2974
Tian C, Gao L, Zimmerman MC, Zucker IH (2018) Myocardial infarction-induced microrna-enriched exosomes contribute to cardiac Nrf2 dysregulation in chronic heart failure. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 314(5):H928–H939
Tian H, Xiong Y, Zhang Y, Leng Y, Tao J, Li L, Qiu Z, Xia Z (2021) Activation of Nrf2/Fpn1 pathway attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in diabetic rats by regulating iron homeostasis and ferroptosis. Cell Stress Chaperones 27(2):149–164
Ungvari Z, Bailey-Downs L, Gautam T, Jimenez R, Losonczy G, Zhang C, Ballabh P, Recchia FA, Wilkerson DC, Sonntag WE et al (2011) Adaptive induction of Nf-E2-related factor-2-driven antioxidant genes in endothelial cells in response to hyperglycemia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 300(4):H1133–H1140
Varga ZV, Giricz Z, Liaudet L, Haskó G, Ferdinandy P, Pacher P (2015) Interplay of oxidative, nitrosative/nitrative stress, inflammation, cell death and autophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1852(2):232–242
Vashi R, Patel BM (2021) Nrf2 in cardiovascular diseases: a ray of hope! J Cardiovasc Transl Res 14(3):573–586
Wang G, Song X, Zhao L, Li Z, Liu B (2018) Resveratrol prevents diabetic cardiomyopathy by increasing Nrf2 expression and transcriptional activity. Biomed Res Int 2018:2150218
Wang Y, Xue J, Li Y, Zhou X, Qiao S, Han D (2019) Telmisartan protects against high glucose/high lipid-induced apoptosis and insulin secretion by reducing the oxidative and Er stress. Cell Biochem Funct 37(3):161–168
Wang J, Chen P, Cao Q, Wang W, Chang X (2022) Traditional Chinese medicine ginseng Dingzhi decoction ameliorates myocardial fibrosis and high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte injury by regulating intestinal flora and mitochondrial dysfunction. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:9205908
Wei L, Zhou Q, Tian H, Su Y, Fu GH, Sun T (2020) Integrin Β3 promotes cardiomyocyte proliferation and attenuates hypoxia-induced apoptosis via regulating the Pten/Akt/Mtor and Erk1/2 pathways. Int J Biol Sci 16(4):644–654
Woo AY, Cheng CH, Waye MM (2005) Baicalein protects rat cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation damage via a prooxidant mechanism. Cardiovasc Res 65(1):244–253
Wu T, Yao H, Zhang B, Zhou S, Hou P, Chen K (2021) Κ Opioid receptor agonist inhibits myocardial injury in heart failure rats through activating Nrf2/Ho-1 pathway and regulating Ca(2+)-Serca2a. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:7328437
Yamada S, Ding Y, Tanimoto A, Wang KY, Guo X, Li Z, Tasaki T, Nabesima A, Murata Y, Shimajiri S et al (2011) Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 deficiency accelerates hyperlipidemia-induced atheromatous plaques via suppression of macrophage apoptosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 31(7):1555–1564
Yu H, Chen B, Ren Q (2019) Baicalin relieves hypoxia-aroused h9c2 cell apoptosis by activating Nrf2/Ho-1-Mediated Hif1α/Bnip3 pathway. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47(1):3657–3663
Zhang Y, Hu M, Jia W, Liu G, Zhang J, Wang B, Li J, Cui P, Li X, Lager S et al (2020) Hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance modulate gravid uterine and placental ferroptosis in Pcos-like rats. J Endocrinol 246(3):247–263
Zhao S, Huang M, Yan L, Zhang H, Shi C, Liu J, Zhao S, Liu H, Wang B (2022) Exosomes derived from baicalin-pretreated mesenchymal stem cells alleviate hepatocyte ferroptosis after acute liver injury via the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:8287227
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
We are very grateful to the Chongqing Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine for its financial support for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Research study design: XZ, Experiment conduction: WW, Data acquisition: RH, Data analysis: LL, Manuscript writing: XZ.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Wanling Wang declares that she has no conflict of interest, Rui Han declares that she has no conflict of interest, Li Lai declares that she has no conflict of interest, Xia Zhang declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All the experimental procedures were performed in accordance with the ethical standards stipulated by the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Han, R., Lai, L. et al. Unlocking the potential: Baicalin's apoptosis-reducing power and activation of NRF2/P62 for alleviating diabetic cardiomyopathy in rats. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-024-00434-w
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-024-00434-w