Abstract
Background
Sepsis is a condition of severe septicemia and septic shock caused by infection, accompanied by multiple organ dysfunction often leading to patients’ admission to the intensive care unit (ICU) and death.
Objective
This study aims to investigate the efficacy of urinary trypsin inhibitor in the treatment of rats with severe sepsis, and to analyze its effects on coagulation and immunity. Sixty Sprague Dawley rats were randomly divided into a model control group (MCG), an ulinastatin group (UG), and a normal control group (n = 20 each). Rats in the model CG and UG were modeled for severe sepsis through cecal ligation and puncture, and the 72 h survival of the rats in the three groups was recorded. The expression of IL-18 and TNF-α before urinary trypsin inhibitor administration and 72 h after administration was detected by an ELISA. Activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), prothrombin time (PT), thrombin time (TT), and fibrinogen (FIB) were determined using a fully automatic coagulation analyzer. CD4 + , CD8 + , and CD4 + /CD8 + levels were quantitated by flow cytometry.
Results
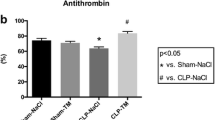
After administration, compared with those in the MCG, rats in the UG showed higher survival rates (P < 0.05), lower IL-18 and TNF-α expression (P < 0.05), lower APTT, PT, and TT (P < 0.05), higher FIB (P < 0.05), higher CD4 + and CD4 +/CD8 + levels (P < 0.05), and significantly lower CD8 + levels (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Urinary trypsin inhibitor can increase the survival rate of rats with severe sepsis, reduce their inflammatory responses, and ameliorate coagulation disorders and immune dysfunction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamik B, Gozdzik W, Jakubczyk D, Welna M, Kubler A (2017) Coagulation abnormalities identified by thromboelastometry in patients with severe sepsis: the relationship to endotoxemia and mortality. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 28:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1097/MBC.0000000000000572
Atal SS, Atal S (2016) Ulinastatin–a newer potential therapeutic option for multiple organ dysfunction syndrome. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 27:91–99
Cao Y-Z et al (2012) Protective effect of Ulinastatin against murine models of sepsis: inhibition of TNF-α and IL-6 and augmentation of IL-10 and IL-13. Exp Toxicol Pathol 64:543–547
Cao C et al (2018) Ulinastatin mediates suppression of regulatory T cells through TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in murine sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol 64:411–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.09.025
Chen Q et al (2017) Safety and tolerability of high-dose ulinastatin after 2-hour intravenous infusion in adult healthy chinese volunteers: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, ascending-dose study. PloS one. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0177425)
Delano MJ, Ward PA (2016) Sepsis-induced immune dysfunction: can immune therapies reduce mortality? J Clin Invest 126:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI82224
Eidt MV et al (2016) Biochemical and inflammatory aspects in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: the predictive role of IL-18 in mortality. Clin Chim Acta 453:100–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2015.12.009
Fatani SH et al (2018) Assessment of tumor necrosis factor alpha polymorphism TNF-alpha-238 (rs 361525) as a risk factor for development of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. Mol Biol Rep 45:839–847. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-018-4230-8
Fu Y et al (2014) Correlation of coagulation indicators with inflammatory markers for sepsis in the patients with hematological malignancies. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 22:1381–1385. https://doi.org/10.7534/j.issn.1009-2137.2014.05.038
Jiang W et al (2018) ADJunctive ulinastatin in sepsis treatment in china (ADJUST study): study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 19:133. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-018-2513-y
Koizumi R et al (2000) Therapeutic effects of ulinastatin on experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis in rats. Nephron 84:347–353
Li D et al (2018) Evaluation of a novel prognostic score based on thrombosis and inflammation in patients with sepsis: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Chem Lab Med 56:1182–1192. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2017-0863
Li ST et al (2018) Ulinastatin attenuates LPS-induced inflammation in mouse macrophage RAW264 7 cells by inhibiting the JNK/NF-kappaB signaling pathway and activating the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2017.143
Liu Y et al (2010) Effect of ulinastatin preconditioning on gene expression profile of kidney tissue in a rat sepsis model. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 22:547–552
Niu R, Gao H, Zhou Y, Zhang J (2018) Ouabain attenuates sepsis-induced immunosuppression in mice by activation and anti-apoptosis of T cells. Med Sci Monit 24:2720–2727. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.906889
Pan Y et al (2017) Ulinastatin ameliorates tissue damage of severe acute pancreatitis through modulating regulatory T cells. J Inflamm (Lond). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12950-017-0154-7
Rimmelé T et al (2016) Immune cell phenotype and function in sepsis. Shock 45:282–291
Schmutzhard E, Pfausler B (2017) Neurologic complications of sepsis. Handb Clin Neurol 141:675–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63599-0.00036-3
Stoller J et al (2016) Epidemiology of severe sepsis: 2008–2012. J Crit Care 31:58–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.09.034
De La Rica AS, Gilsanz F, Maseda E (2016) Epidemiologic trends of sepsis in western countries. Annals of translational medicine. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2016.08.59
Torio CM, Moore BJ (2006) Healthcare cost and utilization project (HCUP) statistical briefs [Internet]. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US), Rockville (MD). PMID: 21413206
Wada H (2004) Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Clin Chim Acta 344(1–2):13–21
Wang J et al (2015a) Analyses prognostic factors relevant to sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 50:448–452
Wang S, Li Z, Wang X, Li W, Lin Z (2015b) Effect of ulinastatin on HMGB1 expression in rats with acute lung injury induced by sepsis. Genet Mol Res 14:4344–4353
Wang FY et al (2016) The efficacy and immunomodulatory effects of ulinastatin and thymosin alpha1 for sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int 2016:9508493. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9508493
Wang Y, Yin X, Yang F (2018) Comprehensive analysis of gene expression profiles of sepsis-induced multiorgan failure identified its valuable biomarkers. DNA Cell Biol 37:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2017.3944
Whittaker SA et al (2015) Epidemiology and outcomes in patients with severe sepsis admitted to the hospital wards. J Crit Care 30:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrc.2014.07.012
Wu Y, Qin C, Lu X, Marchiori J, Feng Q (2016) North American ginseng inhibits myocardial NOX2-ERK1/2 signaling and tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in endotoxemia. Pharmacol Res 111:217–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2016.06.010
Wynn JL et al (2016) Targeting IL-17A attenuates neonatal sepsis mortality induced by IL-18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113:E2627–E2635. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1515793113
Ye Q, Shao WX, Wang QQ, Mao JH (2019) An imbalance of T cell subgroups exists in children with sepsis. Microbes Infect. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micinf.2019.04.002
Zhong S, Zhang C, Hu J, Tang Z (2016) Evaluation of coagulation disorders with thrombelastography in patients with sepsis. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 28:153–158. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2016.02.013
Zhou J et al (2017) Population-based epidemiology of sepsis in a subdistrict of Beijing. Crit Care Med 45:1168–1176. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCM.0000000000002414
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
In this work, BT and ZL conceived the study and designed the experiments. JY, SW and HZ contributed to the data collection, performed the data analysis and interpreted the results. BT wrote the manuscript; ZL contributed to the critical revision of article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
Author Biao Tang, Jiemin Yao, Shengtian Wu, Haibin Zhu, Zhiheng Li declares that have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. This study was approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of The Second Nanning People’s Hospital.
Informed consent
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, B., Yao, J., Wu, S. et al. Efficacy of urinary trypsin inhibitor in the treatment of rats with severe sepsis and its effects on coagulation and immunity. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 19, 753–765 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-022-00303-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-022-00303-4