Abstract
Background
Treating large-volume bone defects (LVBD) remains a challenge for orthopedics and maxillofacial surgeons globally.
Objective
The present study was to aimed investigate the role of Beta-naphthoflavone (BNF) a synthetic flavonoid on differentiation of osteoblast of human adipose derived stem cells.
Results
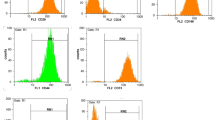
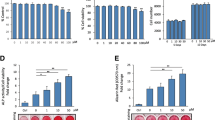
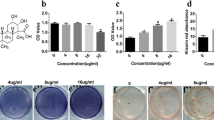
BNF at 1 μM showed a significantly increased ALP activity and rate of cell proliferation compared to control on the 3rd, 7th and 14th day. Also, it was observed that, BNF at 1 μM resulted in significantly increased expression of BSP. On the 14th day of treatment, BNF at all the three treatments resulted in increased levels of OCN. Also, extracellular matrix mineralization levels were recorded to be highest for BNF 1 μM. The levels of Runx2 were higher in 1 μM treated group on the 3rd day compared to other, whereas in contrast the levels were lower on the 7th and 14th day compared to control. BNF at all the three treatments caused a significant decrease in levels of pSTAT3, C/EBP-α and PPAR-γ levels.
Conclusion
BNF treatment resulted in increased differentiation of osteoblast of hASCs by targeting STAT3 pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn HH, Kim KS, Lee JH, Lee JY, Kim BS, Lee IW, Chun HJ, Kim JH, Lee HB, Kim MS (2009) in vivo osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells in an injectable in situ-forming gel scaffold. Tissue Eng Part A 15:1821–1832
Al-Salleeh F, Beatty MW, Reinhardt RA, Petro TM, Crouch L (2008) Human osteogenic protein-1 induces osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells harvested from mice. Arch Oral Biol 53(10):928–936
Behl S, Adem A, Hussain A, Singh J (2019) Effects of rilpivirine, 17β-estradiol and β-naphthoflavone on the inflammatory status of release of adipocytokines in 3T3-L1 adipocytes in vitro. Mol Biol Rep 46(3):2643–2655
Bianco P, Robey PG (2001) Stem cells in tissue engineering. Nature 414(6859):118–121
Calori GM, Albisetti W, Agus A, Iori S, Tagliabue L (2007) Risk factors contributing to fracture non-unions. Injury 38(Suppl 2):S11–S18
Canalis E (2008) Notch signaling in osteoblasts. Sci Signal 1(17):pe17
Chen CH, Ho ML, Chang JK, Hung SH, Wang GJ (2005) Green tea catechin enhances osteogenesis in a bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell line. Osteoporos Int 16(12):2039–2045
Cowan CM, Shi YY, Aalami OO, Chou YF, Mari C, Thomas R, Quarto N, Contag CH, Wu B, Longaker MT (2004) Adipose-derived adult stromal cells heal critical-size mouse calvarial defects. Nat Biotechnol 22:560–567
Darnell JE Jr (1997) STATs and gene regulation. Science 277(5332):1630–1635
Einhorn TA (1995) Enhancement of fracture-healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77(6):940–956
Farmer SR (2006) Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab 4(4):263–273
Fraser JK, Wulur I, Alfonso Z, Hedrick MH (2006) Fat tissue: an underappreciated source of stem cells for biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 24(4):150–154
Hsu SY, Liou JW, Cheng TL, Peng SY, Lin CC, Chu YY, Luo WC, Huang ZK, Jiang SJ (2015) beta-Naphthoflavone protects from peritonitis by reducing TNF-alpha-induced endothelial cell activation. Pharmacol Res 102:192–199
Jensen ED, Gopalakrishnan R, Westendorf JJ (2010) Regulation of gene expression in osteoblasts. BioFactors 36(1):25–32
Kaida K, Honda Y, Hashimoto Y, Tanaka M, Baba S (2015) Application of green tea catechin for inducing the osteogenic differentiation of human dedifferentiated fat cells in vitro. Int J Mol Sci 16(12):27988–28000
Knippenberg M, Helder MN, Zandieh Doulabi B, Wuisman PI, Klein-Nulend J (2006) Osteogenesis versus chondrogenesis by BMP-2 and BMP-7 in adipose stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 342(3):902–908
Komori T (2008) Regulation of bone development and maintenance by Runx2. Front Biosci 13:898–903
Kumar P, Vinitha B, Fathima G (2013) Bone grafts in dentistry. J Pharm Bioallied Sci 5(Suppl 1):S125–S127
Lee KS, Kim HJ, Li QL, Chi XZ, Ueta C, Komori T, Wozney JM, Kim EG, Choi JY, Ryoo HM, Bae SC (2000) Runx2 is a common target of transforming growth factor beta1 and bone morphogenetic protein 2, and cooperation between Runx2 and Smad5 induces osteoblast-specific gene expression in the pluripotent mesenchymal precursor cell line C2C12. Mol Cell Biol 20(23):8783–8792
Levi B, Hyun JS, Nelson ER, Li S, Montoro DT, Wan DC, Jia FJ, Glotzbach JC, James AW, Lee M, Huang M, Quarto N, Gurtner GC, Wu JC, Longaker MT (2011) Nonintegrating knockdown and customized scaffold design enhances human adipose-derived stem cells in skeletal repair. Stem Cells 29(12):2018–2029
Levy DE, Lee CK (2002) What does Stat3 do? J Clin Invest 109(9):1143–1148
Lin L, Shen Q, Wei X, Hou Y, Xue T, Fu X, Duan X, Yu C (2009) Comparison of osteogenic potentials of BMP4 transduced stem cells from autologous bone marrow and fat tissue in a rabbit model of calvarial defects. Calcif Tissue Int 85(1):55–65
Linhart HG, Ishimura-Oka K, DeMayo F, Kibe T, Repka D, Poindexter B, Bick RJ, Darlington GJ (2001) C/EBPalpha is required for differentiation of white, but not brown, adipose tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(22):12532–12537
Liu Y, Wu G, de Groot K (2010) Biomimetic coatings for bone tissue engineering of critical-sized defects. J R Soc Interface 7(Suppl 5):S631–S647
Long F (2012) Building strong bones: Molecular regulation of the osteoblast lineage. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 13(1):27–38
Maruyama Z, Yoshida CA, Furuichi T, Amizuka N, Ito M, Fukuyama R, Miyazaki T, Kitaura H, Nakamura K, Fujita T, Kanatani N, Moriishi T, Yamana K, Liu W, Kawaguchi H, Nakamura K, Komori T (2007) Runx2 determines bone maturity and turnover rate in postnatal bone development and is involved in bone loss in estrogen deficiency. Dev Dyn 236(7):1876–1890
Mehrkens A, Saxer F, Güven S, Hoffmann W, Müller AM, Jakob M, Weber FE, Martin I, Scherberich A (2012) Intraoperative engineering of osteogenic grafts combining freshly harvested, human adipose-derived cells and physiological doses of bone morphogenetic protein-2. Eur Cell Mater 24:308–319
Morel G, Ban M, Bonnet P, Zissu D, Brondeau MT (2005) Effect of beta-naphthoflavone and phenobarbital on the nephrotoxicity of chlorotrifluoroethylene and 1,1-dichloro-2,2-difluoroethylene in the rat. J Appl Toxicol 25(2):153–165
Murray TJ, Yang X, Sherr DH (2006) Growth of a human mammary tumor cell line is blocked by galangin, a naturally occurring bioflavonoid, and is accompanied by down-regulation of cyclins D3, E, and A. Breast Cancer Res 8(2):R17
Nakanishi C, Nagaya N, Ohnishi S, Yamahara K, Takabatake S, Konno T, Hayashi K, Kawashiri MA, Tsubokawa T, Yamagishi M (2011) Gene and protein expression analysis of mesenchymal stem cells derived from rat adipose tissue and bone marrow. Circ J 75(9):2260–2268
Nicolaidou V, Wong MM, Redpath AN, Ersek A, Baban DF, Williams LM, Cope AP, Horwood NJ (2012) Monocytes induce STAT3 activation in human mesenchymal stem cells to promote osteoblast formation. PLoS ONE 7(7):e39871
O’Brien FJ (2011) Biomaterials & scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater Today 14(3):88–95
Otto F, Thornell AP, Crompton T, Denzel A, Gilmour KC, Rosewell IR, Stamp GW, Beddington RS, Mundlos S, Olsen BR, Selby PB, Owen MJ (1997) Cbfa1, a candidate gene for cleidocranial dysplasia syndrome, is essential for osteoblast differentiation and bone development. Cell 89(5):765–771
Panetta NJ, Gupta DM, Lee JK, Wan DC, Commons GW, Longaker MT (2010) Human adipose-derived stromal cells respond to and elaborate bone morphogenetic protein-2 during in vitro osteogenic differentiation. Plast Reconstr Surg 125(2):483–493
Quarto R, Mastrogiacomo M, Cancedda R et al (2001) Repair of large bone defects with the use of autologous bone marrow stromal cells. N Engl J Med 344(5):385–386
Rosen ED, Hsu CH, Wang X, Sakai S, Freeman MW, Gonzalez FJ, Spiegelman BM (2002) C/EBPalpha induces adipogenesis through PPARgamma: a unified pathway. Genes Dev 16(1):22–26
Sheyn D, Pelled G, Zilberman Y, Talasazan F, Frank JM, Gazit D, Gazit Z (2008) Nonvirally engineered porcine adipose tissue-derived stem cells: use in posterior spinal fusion. Stem Cells 26(4):1056–1064
Shiraishi T, Sumita Y, Wakamastu Y, Nagai K, Asahina I (2012) Formation of engineered bone with adipose stromal cells from buccal fat pad. J Dent Res 91(6):592–597
Siersbaek R, Nielsen R, Mandrup S (2010) PPARgamma in adipocyte differentiation and metabolism—novel insights from genome-wide studies. FEBS Lett 584(15):3242–3249
Takanaga H, Yoshitake T, Yatabe E, Hara S, Kunimoto M (2004) Beta-naphthoflavone disturbs astrocytic differentiation of C6 glioma cells by inhibiting autocrine interleukin-6. J Neurochem 90(3):750–757
Tzioupis C, Giannoudis PV (2007) Prevalence of long-bone non-unions. Injury 38(Suppl 2):S3–S9
Wang C, Xu CX, Bu Y, Bottum KM, Tischkau SA (2014) Beta-naphthoflavone (DB06732) mediates estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cell cycle arrest through AhR-dependent regulation of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK signaling. Carcinogenesis 35(3):703–713
Wang Z, Zhang D, Hu Z, Cheng J, Zhuo C, Fang X, Xing Y (2015) MicroRNA-26a-modified adipose-derived stem cells incorporated with a porous hydroxyapatite scaffold improve the repair of bone defects. Mol Med Rep 12(3):3345–3350
Wei YJ, Tsai KS, Lin LC, Lee YT, Chi CW, Chang MC, Tsai TH, Hung SC (2011) Catechin stimulates osteogenesis by enhancing PP2A activity in human mesenchymal stem cells. Osteoporos Int 22(5):1469–1479
Yochum L, Kushi LH, Meyer K, Folsom AR (1999) Dietary flavonoid intake and risk of cardiovascular disease in postmenopausal women. Am J Epidemiol 149(10):943–949
Zatloukalová J, Svihálková-Sindlerová L, Kozubík A, Krcmár P, Machala M, Vondrácek J (2007) beta-Naphthoflavone and 3′-methoxy-4′-nitroflavone exert ambiguous effects on Ah receptor-dependent cell proliferation and gene expression in rat liver “stem-like” cells. Biochem Pharmacol 73(10):1622–1634
Zeng Q, Li X, Beck G, Balian G, Shen FH (2007) Growth and differentiation factor-5 (GDF-5) stimulates osteogenic differentiation and increases vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels in fat-derived stromal cells in vitro. Bone 40(2):374–381
Zhang X, Guo J, Zhou Y, Wu G (2014) The roles of bone morphogenetic proteins and their signaling in the osteogenesis of adipose-derived stem cells. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 20(1):84–92
Zhang X, Jiang W, Liu Y, Zhang P, Wang L, Li W, Wu G, Ge Y, Zhou Y (2018) Human adipose-derived stem cells and simvastatin-functionalized biomimetic calcium phosphate to construct a novel tissue-engineered bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 495(1):1264–1270
Zhou X, Li D, Xu W, Zhang H, Wang H, Perdew GH (2020) β-Naphthoflavone activation of the Ah receptor alleviates irradiation-induced intestinal injury in mice. Antioxidants 9(12):1264
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, Huang J, Futrell JW, Katz AJ, Benhaim P, Lorenz HP, Hedrick MH (2001a) Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng 7:211–228
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H et al (2001b) Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng 7(2):211–228
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the staff and management of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center, Shanghai, Shanghai Yuanxi Medical Technology Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China and College of Biomedical Science, Zhejiang University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QC, ML and ML built the concept and designed the work; TL, YL, MW, HX, MZ along with QC, ML and ML planed the experiments and performed them as a team. All the authors prepared and verified the manuscript. ML and QC designed the study. ML, TL, YL, MW, HX, MZ along with ML and WC performed all the experiments. All the authors prepared the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Ming Lu declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Min Li declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Tao Luo declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Yongsui Li declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Mingxin Wang declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Huashi Xue declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Mengchen Zhang declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. Qiu Chen declares that he/she has no conflict of interest. We all the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The human study was approved by the ethical review board of College of Biomedical Science, Zhejiang University, China. The study protocol was in accordance to Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, M., Li, M., Luo, T. et al. Beta-naphthoflavone increases the differentiation of osteoblasts and suppresses adipogenesis in human adipose derived stem cells involving STAT3 pathway. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 19, 539–549 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-022-00283-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-022-00283-5