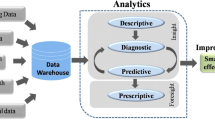
Abstract
Background
Exposure to harmful environmental substances influences lifelong health, but the molecular interpretation of how it affects human health is poorly understood. Therefore, a framework that can efficiently apply the major technologies and fields related to exposomes is needed, as it would provide an important tool for the identification of the environmental factors affecting human health.
Object
We aimed to develop a system that integrates multi-omics data and archives this information to ensure that omics analysis information can be utilised to understand the molecular phenotypical concerns associated with exposure to harmful environmental substances in humans.
Result
We established a data archive system called Online Resource of Environmental Omics (OREO) that standardises multi-omics cohort sample data of humans exposed to harmful environmental substances; integrates unstructured data; and can search, share, and store information. In addition, data profiling is provided to ensure that it can be applied to integrated omics analysis visualisation tools such as cBioportal. In the case of long-term exposure to low concentrations of harmful environmental substances, an integrated analysis of clinical observation and omics data could be performed.
Conclusion
We provide a brief account of multi-omics data repositories, the data processing method, and an analysis pipeline for the application of omics data. This data processing ability helps to comprehensively understand multi-omics data regarding harmful environmental substances.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarado-Cruz I et al (2018) Environmental epigenetic changes, as risk factors for the development of diseases in children: a systematic review. Ann Glob Health 84:212–224
Bailey T et al (2013) Practical guidelines for the comprehensive analysis of ChIP-seq data. PLOS Comput Biol 9:e1003326
Bantscheff M, Lemeer S, Savitski MM, Kuster B (2012) Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: critical review update from 2007 to the present. Anal Bioanal Chem 404:939–965
Bao R et al (2014) Review of current methods, applications, and data management for the bioinformatics analysis of whole exome sequencing. Cancer Inf 13:67–82
Bardet AF, He Q, Zeitlinger J, Stark A (2011) A computational pipeline for comparative ChIP-seq analyses analyses. Nat Protoc 7:45–61
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120
Cerami E et al (2012) The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2:401–404
Chen TW et al (2014) ChIPseek, a web-based analysis tool for ChIP data. BMC Genom 15:539
Corchete LA et al (2020) Systematic comparison and assessment of RNA-seq procedures for gene expression quantitative analysis. Sci Rep 10:19737
Dettmer K, Aronov PA, Hammock BD (2007) Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Mass Spectrom Rev 26:51–78
Feil R, Fraga MF (2012) Epigenetics and the environment: emerging patterns and implications. Nat Rev Genet 13:97–109
Furey TS (2012) ChIP-seq and beyond: new and improved methodologies to detect and characterize protein–DNA interactions. Nat Rev Genet 13:840–852
Ghosh S, Datta A, Choi H (2021) multiSLIDE is a web server for exploring connected elements of biological pathways in multi-omics data. Nat Commun 12:2279
Gomez-Cabrero D et al (2014) Data integration in the era of omics: current and future challenges. BMC Syst Biol 8(Supplement 2):I1
Hong JY et al (2016a) Environmental risk assessment of toxicity exposure: high-throughput expression profiling. BioChip J 10:74–80
Hong JY et al (2016b) Association analysis of toluene exposure time with high-throughput mRNA expressions and methylation patterns using in vivo samples. Environ Res 146:59–64
Huang S, Chaudhary K, Garmire LX (2017) More is better: recent progress in multi-omics data integration methods. Front Genet 8:84
Jirtle RL, Skinner MK (2007) Environmental epigenomics and disease susceptibility. Nat Rev Genet 8:253–262
Johnson DS, Mortazavi A, Myers RM, Wold B (2007) Genome-widemapping of in vivo protein–DNA interactions. Science 316:1497–1502
Juarez PD, Matthews-Juarez P (2018) Applying an exposome-wide (ExWAS) approach to cancer research. Front Oncol 8:313
Kalia V, Jones DP, Miller GW (2019) Networks at the nexus of systems biology and the exposome. Curr Opin Toxicol 16:25–31
Kim MK, Tagkopoulos I (2018) Data integration and predictive modeling methods for multi-omics datasets. Mol Omics 14:8–25
Koestler DC et al (2013) Differential DNA methylation in umbilical cord blood of infants exposed to low levels of arsenic in utero. Environ Health Perspect 121:971–977
Kvale MN et al (2015) Genotyping informatics and quality control for 100,000 subjects in the genetic epidemiology research on adult health and aging (GERA) cohort. Genetics 200:1051–1060
Langmead B, Salzberg SL (2012) Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 9:357–359
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760
Lockstone HE (2011) Exon array data analysis using Affymetrix power tools and R statistical software. Brief Bioinform 12:634–644
Maitre L et al (2018) Human Early Life Exposome (HELIX) study: a European population-based exposome cohort. BMJ Open 8:e021311
Manzoni C et al (2018) Genome, transcriptome and proteome: the rise of omics data and their integration in biomedical sciences. Brief Bioinform 19:286–302
Marioni RE et al (2018) Meta-analysis of epigenome-wide association studies of cognitive abilities. Mol Psychiatry 23:2133–2144
Matin M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. Embnet J 17:1–3
Mattick JS, Makunin IV (2006) Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet 15:R17–R29
Merino Martinez RM et al (2021) Human exposome assessment platform. Environ Epidemiol 5:e182
Nakato R, Sakata T (2021) Methods for ChIP-seq analysis: a practical workflow and advanced applications. Methods 187:44–53
Nicolazzi EL, Iamartino D, Williams JL (2014) AffyPipe: an open-source pipeline for Affymetrix Axiom genotyping workflow. Bioinformatics 30:3118–3119
Pedersen M et al (2013) Ambient air pollution and low birthweight: a European cohort study (ESCAPE). Lancet Respir Med 1:695–704
Purcell S et al (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81:559–575
Rappaport SM, Smith MT (2010) Epidemiology. Environment and disease risks. Science 330:460–461
Rhee HS, Pugh BF (2011) Comprehensive genome-wide protein–DNA interactions detected at single-nucleotide resolution. Cell 147:1408–1419
Robinson O, Vrijheid M (2015) The pregnancy exposome. Curr Envir Health Rpt 2:204–213
Subramanian I et al (2020) Multi-omics data integration, interpretation, and its application. Bioinform Biol Insights 14:1177932219899051
Taiwo O et al (2012) Methylome analysis using MeDIP-seq with low DNA concentrations. Nat Protoc 7:617–636
Vermeulen R, Schymanski EL, Barabási AL, Miller GW (2020) The exposome and health: where chemistry meets biology. Science 367:392–396
Vrijheid M (2014) Child health and the environment: where next with birth cohort research? Occup Environ Med 71:663–664
Want EJ, Cravatt BF, Siuzdak G (2005) The expanding role of mass spectrometry in metabolite profiling and characterization. ChemBioChem 6:1941–1951
Wild CP (2005) Complementing the genome with an “exposome”: the outstanding challenge of environmental exposure measurement in molecular epidemiology. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14:1847–1850
Wolters J et al (2018) Data on novel DNA methylation changes induced by valproic acid in human hepatocytes. Data Brief 16:161–171
Zhang Y et al (2008) Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol 9:R137
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Korea Environment Industry & Technology Institute through the Environmental Health Action Program funded by the Korea Ministry of Environment (2017001360005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GHS contributed to the conception of the study and wrote a section related to data archiving in the manuscript. JMH &SWP conceived and wrote the system-related part of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
G.H. Shin declares that he has no conflict of interest. J.M. Hong declares that he has no conflict of interest. S.W. Park declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, Gh., Hong, Jm. & Park, Sw. Novel data archival system for multi-omics data of human exposure to harmful substances. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 18, 277–283 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-022-00226-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-022-00226-0