Abstract
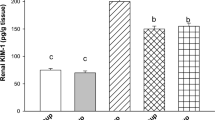
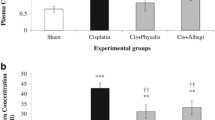
Taxilli Ramulus has been shown have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Cisplatin is the most active cytotoxic anti-cancer drugs. However, the nephrotoxicity of cisplatin limits its use as a therapeutic. In the present study, we examined whether Taxilli Ramulus could protect against cisplatin induced acute renal failure in mice. Taxilli Ramulus were administrated orally once a day for 3 days (150 or 300 mg/kg body wt). After 3 days, all groups of mice received a single dose of cisplatin (25 mg/kg (body wt)) intraperitoneally. Taxilli Ramulus treatment ameliorated renal dysfunction 72 h after cisplatin injection. Taxilli Ramulus treated group had significantly reduced levels of proinflammatory cytokines when compared to the control group. These results show that Taxilli Ramulus is a potent herbal medicine that can reduce cisplatin nephrotoxicity. It also demonstrates that Taxilli Ramulus can prevent the renal toxic effects caused by cisplatin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi, S. Z. et al. Triterpenes and phenolic constituents from Viscum album L. Yakhak Hoeji 45:591–598 (2001).
Zhang, Z. & Shi, L. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of cis-mulberroside A from Ramulus mori. Fitoterapia 81:214–218 (2010).
Kumar, A. et al. Protective effect of quercetin against ICV colchicine-induced cognitive dysfunctions and oxidative damage in rats. Phytother Res 22:1563–1569 (2008).
Reiter, M. et al. Antioxidant effects of quercetin and coenzyme Q10 in mini organ cultures of human nasal mucosa cells. Anticancer Res 29:33–39 (2009).
Rogerio, A. P. et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of quercetin and isoquercitrin in experimental murine allergic asthma. Inflamm Res 56:402–408 (2007).
Sadowska-Woda, I., Popowicz, D. & Karowicz-Bilinska, A. Bifenthrin-induced oxidative stress in human erythrocytes in vitro and protective effect of selected flavonols. Toxicol In Vitro 24:460–464 (2010).
Sohn, S. H. et al. Screening of herbal medicines for the recovery of cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Environ Toxicol Phar 28:206–212 (2009).
Wang, D. & Lippard, S. J. Cellular processing of platinum anticancer drugs. Nature Reviews 4:307–320 (2005).
Pabla, N. & Dong, Z. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney International 73:994–1007 (2008).
Ries, F. & Klastersky, J. Nephrotoxicity induced by cancer chemotherapy with special emphasis on cisplatin toxicity. Am J Kidney Dis 8:368–379 (1986).
Luke, D. R., Vadiei, K. & Lopez-Berestein, G. Role of vascular congestion in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in the rat. Nephrol Dial Transplant 7:1–7 (1992).
Ramesh, G. & Reeves, W. B. TNF-alpha mediates chemokine and cytokine expression and renal injury in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. J Clin Invest 110:835–842 (2002).
Davis, C. A., Nick, H. S & Agarwal, A. Manganese superoxide dismutase attenuates Cisplatin-induced renal injury: importance of superoxide. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:2683–2690 (2001).
Ramesh, G. & Reeves, W. B. Inflammatory cytokines in acute renal failure. Kidney Int Suppl 91:S56–61 (2004).
Faubel, S. et al. Cisplatin-induced acute renal failure is associated with an increase in the cytokines interleukin (IL)-1beta, IL-18, IL-6, and neutrophil infiltration in the kidney. J Pharm Exp Ther 322:8–15 (2007).
Ajith, T. A., Nivitha, V. & Usha, S. Zingiber officinale Roscoe alone and in combination with alpha-tocopherol protect the kidney against cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. Food Chem Toxicol 45:921–927 (2007).
Fatima, S., Arivarasu, N. A. & Mahmood, R. Vitamin C attenuates cisplatin-induced alterations in renal brush border membrane enzymes and phosphate transport. Human & Experimental Toxicology 26:419–426 (2007).
Kuhad, A. et al. Effect of curcumin on inflammation and oxidative stress in cisplatin-induced experimental nephrotoxicity. J Agric Food Chem 55:10150–10155 (2007).
Matsushima, H., Yonemura, K., Ohishi, K. & Hishida, A. The role of oxygen free radicals in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in rats. J Lab Clin Med 131:518–526 (1998).
Lau, A. H. Apoptosis induced by cisplatin nephrotoxic injury. Kidney International 56:1295–1298 (1999).
Sung, M. J. et al. Genistein protects the kidney from cisplatin-induced injury. Kidney International 74:1538–1547 (2008).
Negishi, K. et al. A role of liver fatty acid-binding protein in cisplatin-induced acute renal failure. Kidney International 72:348–358 (2007).
Ramesh, G. & Reeves, W. B. p38 MAP kinase inhibition ameliorates cisplatin nephrotoxicity in mice. American Journal of Physiology 289:166–174 (2005).
Simmons, E. M. et al. Plasma cytokine levels predict mortality in patients with acute renal failure. Kidney International 65:1357–1365 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, G., Lee, JH., Ham, K.K. et al. Cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity is inhibited by Taxilli Ramulus. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 8, 311–315 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-012-0038-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-012-0038-0