Abstract
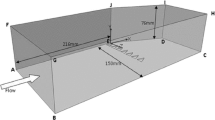
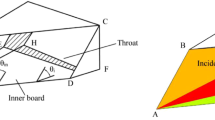
A numerical study to evaluate the critical height of microvortex generators in controlling swept shock wave boundary layer interactions is carried out. The planar shock wave is generated by placing a 20° sharp fin in a supersonic flow at Mach 4. The ramp and thick vane microvortex generator geometries were considered. The device heights were varied from 30 to 90 % of the incoming boundary layer thickness. The efficacy of the devices was observed to increase with increasing device height up to a height of 70 % of the incoming boundary layer thickness beyond which no further improvement was achieved.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, B.H., Tinapple, J., Surber, L.: Optimal control of shock wave turbulent boundary layer interactions using micro-array actuation. In: 3rd AIAA Flow Control Conference, San Francisco, CA, AIAA Paper 2006-3197, June, pp. 1–14 (2006)
Babinsky, H., Li, Y., Pitt Ford, C.: Microramp control of supersonic oblique shock wave/boundary layer interactions. AIAA J. 47(3), 6–13 (2009). doi:10.2514/1.38022
Barnhart, P.J., Greber, I., Hingst, W.R.: Glancing shock wave turbulent boundary layer interaction with boundary layer suction. In: AIAA Paper 88-0308 (1988)
Gaitonde, D., Knight, D.: Numerical investigation of some control methods for 3-d turbulent interactions due to sharp fins. In: 27th Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, Nevada, AIAA Paper 89-0360, January, pp. 1–20 (1989)
Gaitonde, D., Knight, D.: Numerical investigation of bleed on three-dimensional turbulent interactions due to sharp fins. AIAA J. 11(29), 1878–1885 (1991)
Ghosh, S., Choi, J.I., Edwards, J.R.: RANS and hybrid LES/RANS simulations of the effects of micro vortex generators using immersed boundary methods. In: 30th Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit, Seattle, Washington, AIAA Paper 2008-3728, June, pp. 1–27 (2008)
Herges, T., Kroeker, E., Elliott, G., Dutton, C.: Microramp flow control of normal shock/boundary-layer interactions . AIAA J. 48(11), 2529–2542 (2010). doi:10.2514/1.J050313
Holden, H., Babinsky, H.: Effects of microvortex generators on separated normal shock/boundary layer interactions. AIAA J. 1(44), 170–174 (2007)
Kim, K.S., Lee, Y., Alvi, F.S., Settles, G.S.: Skin-friction measurements and computational comparison of swept shock/boundary-layer interactions. AIAA J. 29(10), 1643–1650 (1991)
Koide, S., Griesel, C.J.W., Stollery, J.L.: Effects of strakes on a glancing shock wave/turbulent boundary-layer interaction. J. Aircr. 32(5), 985–992 (1995)
Korkegi, R.H.: Comparison on shock induced two- and three-dimensional incipient turbulent separation. AIAA J. 13(4), 534–535 (1975)
Launder, B.E., Sharma, B.L.: (1974) Application of the energy dissipation model of turbulence to the calculation of flow near a spinning disc. Lett. Heat Mass Transf. 1(2), 131–138
Lee, S., Loth, E.: Supersonic boundary-layer interactions with various micro-vortex generator geometries. Aeronaut. J. 113(1149), 683–697 (2009)
Lu, F.K., Li, Q., Liu, C.: Microvortex generators in high-speed flow. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 53, 30–45 (2012)
Martis, R.R., Misra, A., Singh, A.: Effect of microramps on separated swept shock wave/boundary layer interactions. under review
Mee, D., Stalker, R.: Investigation of weak shock-shock and shock-expansion intersection in the presence of a turbulent boundary layer. In: AIAA Paper 87-0549 (1987)
Rodi, W.: Experience with two-layer models combining the k-e model with a one-equation model near the wall. In: 29th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting, Reno, NV, AIAA Paper 1991-0216 (1991)
Settles, G.S., Teng, H.Y.: Cylindrical and conical flow regimes of three dimensional shock/boundary layer interactions. AIAA J. 22(2), 194–200 (1984)
Shih, T.H., Liou, W.W., Shabbir, A., Yang, Z., Zhu, J.: A new k-epsilon eddy viscosity model for high Reynolds number turbulent flows: Model development and validation. Comput. Fluids 24(3), 227–238 (1994)
Sun, Z., Schrijer, F.F.J., Scarano, F., van Oudheusen, B.W.: The three-dimensional flow organization past a micro-ramp in a supersonic boundary layer. Phys. Fluids 24, 055,105–1–22 (2012)
Weiss, J.M., Smith, W.A.: Preconditioning applied to variable and constant density flows. AIAA J. 11(33), 2050–2057 (1995)
Wolfstein, M.: The velocity and temperature distribution in one-dimensional flow with turbulence augmentation and pressure gradient. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 12, 301–318 (1969)
Yan, Y., Li, Q., Liu, C., Pierce, A., Lu, F., Lu, P.: Numerical discovery and experimental confirmation of vortex ring generation by microramp vortex generator. Appl. Math. Model. 36, 5700–5708 (2012)
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Vice Chancellor, Defence Institute of Advanced Technology (DIAT), Pune, India, for constant encouragement and support. The authors are also thankful to the Department of Computer Engineering and Department of Aerospace Engineering, DIAT, for the infrastructural support provided in conducting this study. The authors gratefully acknowledge Dr. Holger Babinsky of Cambridge University for providing results of his experiments and for several useful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martis, R.R., Misra, A. Effect of height of microvortex generators on swept shock wave boundary layer interactions. CEAS Aeronaut J 4, 315–326 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13272-013-0075-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13272-013-0075-y