Abstract
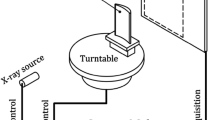
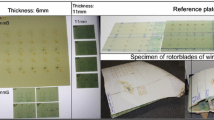
In this paper a new method for an experimental determination of the mass distribution of rotor blades is presented. This mass distribution measurement method is developed for the testing of on active twist blades, but it is applicable to the mass property determination of any type of rotating blade. Usually X-ray computer tomography (CT) is used for non-destructive inspection, such as to find voids in composite components. In this research CT is used to get information regarding the spatial distribution of mass in a rotor blade. The CT-analysis of an active twist rotor blade and the implemented determination of the mass distribution are presented in this paper. Image reconstruction due to X-ray computer tomography makes possible to obtain a cross-section image of the rotor blade. Each pixel of this image has a CT-Number which is proportional to the attenuation coefficient of the material forming the blade. Due to the fact that the attenuation of X-ray is characteristic for each material, it is theoretically possible to correlate CT-Numbers with material properties. This method is “quasi”-experimental because the attenuation coefficient for each pixel is experimentally determined and then densities are assigned to these pixels. Once that correlation is done, calculating mass properties such as total mass, mass per length, local center of mass and local moment of inertia for each cross section is possible.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Voxel is an artificial word composed of volume (x) element. It is used to discretize a volume and is represented as a unit cube with a single value. This is analogous to a pixel in two-dimensional.
References
Opitz, S., Riemenschneider, J., Monner, H.P.: Modal investigation of an active twist helicopter rotor blade. In: ICAST—International Conference on adaptive Structures and Technologies. Hong Kong, China (2009)
Riemenschneider, J., Opitz, S., Wierach, P., des Rochettes, H.M., Buchaniek, L., Joly, D.: Structural design and testing of active twist blades—a comparison. In: ERF—European Rotorcraft Forum. Hamburg, Germany (2009)
Hoffmann, F., Opitz, S., Riemenschneider, J.: Validation of active twist modeling based on whirl tower tests. In: AHS—American Helicopter Society. Texas, USA (2009)
Monner, H.P., Opitz, S., Riemenschneider, J., Wierach, P.: Evolution of active twist rotor designs at dlr. In: AIAA/ASME/AHS Adaptive Structures Conference. Schaumburg, IL, USA (2008)
Wierach, P., Riemenschneider, J., Opitz, S., Hoffmann, F.: Experimental investigation of an active twist rotor under centrifugal loads. In: ERF—European Rotorcraft Forum. Kazan, Russia (2007)
Riemenschneider, J., Keye, S., Wierach, P., des Rochettes, H.M.: Overview of the common dlr/onera project ’active twist blade’. In: 30th European Rotorcraft Forum, Marseille (2004)
Shin, S., Cesnik, C., Wilkie, W., Wilbur, M.: Design and manufacturing of a model-scale active twist rotor prototype blade. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 19(12), 1443–1456 (2008)
Herman, G.T.: Fundamentals of Computerized Tomography: Image Reconstruction from Projections. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Buzug, T.M.: Computed Tomography: From Photon Statistics to Modern Cone-Beam CT. Springer, Berlin (2008)
Herman, G.T., Kuba, A., et al.: Advances in Discrete Tomography and its Applications: Applied and Numerical Harmonic Analysis. Birkhäuser, Boston (2007)
Sonka, M., Hlavac, V., Boyle, H.: Image Processing, Analysis and Machine Vision. Chapman & Hall, London (1993)
Cheung, K.W., Yeung, D.Y., Chin, R.T.: On deformable models for visual pattern recognition. Pattern Recognit. 35(7), 1507–1526 (2002)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dipl.-Ing. Raouf Jemmali and the Institute of Structures and Design, German Aerospace Center, for their great support during the computer tomography analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulz, M., Opitz, S. & Riemenschneider, J. A new concept to determine the mass distribution of an active twist rotor blade. CEAS Aeronaut J 3, 117–123 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13272-012-0046-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13272-012-0046-8