Abstract
Background
Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2i) represent a new type of hypoglycemic medicine that can cause massive loss of glucose from the urine, which have several benefits of reducing body weight and improving the prognosis of cardiovascular and kidney diseases. Although they are oral medicated hypoglycemic agents, their effects on the gut microbiome and function have been unclear.
Objective
In order to describe the effects of canagliflozin on intestinal flora and metabolites, diabetic mice were randomized to receive canagliflozin or isoconcentration carboxymethylcellulose sodium by gavage for 8 weeks. Feces were collected for 16 S rRNA gene and LC-MS/MS analysis and enriched metabolic pathways through Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). Liver, muscle, intestinal, fat were collected for qRT-PCR according to KEGG enriched metabolic pathways.
Results
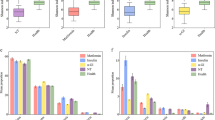
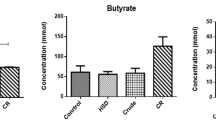
Our results showed that canagliflozin significantly increased GLP-1 level and impacted on the composition of gut microbiota and metabolites. It mainly increased Muribaculum, Ruminococcaceae_UCG_014, Lachnospiraceae-UCG-001, decreased ursodeoxycholic acids (UDCA) and hyodeoxycholic acids (HDCA), and increased fatty acids metabolites in feces.
Conclusion
In conclusion, we analyzed the changes of intestinal microbial composition and metabolites in diabetic mice after canagliflozin intervention and found that canagliflozin influenced intestinal fatty acid and bile acid (BA) metabolism. This study will provide reference for subsequent SGLT2i and intestinal related research.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Available on request.
References
Agus A, Clement K, Sokol H (2021) Gut microbiota-derived metabolites as central regulators in metabolic disorders. Gut 70:1174–1182. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323071
Ahmad TR, Haeusler RA (2019) Bile acids in glucose metabolism and insulin signalling - mechanisms and research needs. Nat Rev Endocrinol 15:701–712. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-019-0266-7
Bokulich NA, Kaehler BD, Rideout JR, Dillon M, Bolyen E, Knight R, Huttley GA, Gregory Caporaso J (2018) Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 6:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-018-0470-z
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJ, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13:581–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3869
Cani PD, Van Hul M, Lefort C, Depommier C, Rastelli M, Everard A (2019) Microbial regulation of organismal energy homeostasis. Nat Metab 1:34–46. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-018-0017-4
Chen Y, Zhou J, Wang L (2021) Role and mechanism of Gut Microbiota in Human Disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 11:625913. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2021.625913
De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Goncalves D, Vinera J, Zitoun C, Duchampt A, Bäckhed F, Mithieux G (2014) Microbiota-generated metabolites promote metabolic benefits via gut-brain neural circuits. Cell 156:84–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.016
de Vos WM, Tilg H, Van Hul M, Cani PD (2022) Gut microbiome and health: mechanistic insights. Gut 71:1020–1032. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2021-326789
Deng L, Yang Y, Xu G (2022) Empagliflozin ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus-related diabetic nephropathy via altering the gut microbiota. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids 1867:159234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2022.159234
Esgalhado M, Kemp JA, Damasceno NR, Fouque D, Mafra D (2017) Short-chain fatty acids: a link between prebiotics and microbiota in chronic kidney disease. Future Microbiol 12:1413–1425. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb-2017-0059
Fan Y, Pedersen O (2021) Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat Rev Microbiol 19:55–71. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-0433-9
Ferrannini E, Ramos SJ, Salsali A, Tang W, List JF (2010) Dapagliflozin monotherapy in type 2 diabetic patients with inadequate glycemic control by diet and exercise: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Diabetes Care 33:2217–2224. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc10-0612
Hata S, Okamura T, Kobayashi A, Bamba R, Miyoshi T, Nakajima H, Kitagawa N, Hashimoto Y, Majima S, Senmaru T et al (2022) Gut Microbiota Changes by an SGLT2 Inhibitor, Luseogliflozin, Alters Metabolites Compared with Those in a Low Carbohydrate Diet in db/db Mice. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14173531
Inagaki N, Kondo K, Yoshinari T, Maruyama N, Susuta Y, Kuki H (2013) Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 12-week study. Diabetes Obes Metab 15:1136–1145. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.12149
Koh A, De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Backhed F (2016) From Dietary Fiber to host physiology: short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 165:1332–1345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.041
Kovacs CS, Seshiah V, Swallow R, Jones R, Rattunde H, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC (2014) Empagliflozin improves glycaemic and weight control as add-on therapy to pioglitazone or pioglitazone plus metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Obes Metab 16:147–158. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.12188
Leonhardt J, Haider RS, Sponholz C, Leonhardt S, Drube J, Spengler K, Mihaylov D, Neugebauer S, Kiehntopf M, Lambert NA et al (2021) Circulating bile acids in liver failure activate TGR5 and induce Monocyte Dysfunction. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 12:25–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.01.011
Li YJ, Chen X, Kwan TK, Loh YW, Singer J, Liu Y, Ma J, Tan J, Macia L, Mackay CR et al (2020) Dietary Fiber protects against Diabetic Nephropathy through short-chain fatty acid-mediated activation of G protein-coupled receptors GPR43 and GPR109A. J Am Soc Nephrol 31:1267–1281. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2019101029
Marion S, Desharnais L, Studer N, Dong Y, Notter MD, Poudel S, Menin L, Janowczyk A, Hettich RL, Hapfelmeier S et al (2020) Biogeography of microbial bile acid transformations along the murine gut. J Lipid Res 61:1450–1463. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.RA120001021
Marron MM, Orwoll ES, Cawthon PM, Lane NE, Newman AB, Cauley JA (2022) Oxylipins Associated with D3-Creatine Muscle Mass/Weight and Physical Performance among Community-Dwelling Older Men. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232112857
Martin POS, Lawley JC, Browne TD, Harris HP, Bernalier-Donadille HMB, Duncan A, O’Toole SH PW, K PS, H JF (2016) Polysaccharide utilization loci and nutritional specialization in a dominant group of butyrate-producing human colonic Firmicutes. Microb Genom 2:e000043. https://doi.org/10.1099/mgen.0.000043
McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Køber L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, Ponikowski P, Sabatine MS, Anand IS, Bělohlávek J et al (2019) Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med 381:1995–2008. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1911303
Misheva M, Kotzamanis K, Davies LC, Tyrrell VJ, Rodrigues PRS, Benavides GA, Hinz C, Murphy RC, Kennedy P, Taylor PR et al (2022) Oxylipin metabolism is controlled by mitochondrial beta-oxidation during bacterial inflammation. Nat Commun 13:139. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27766-8
Mueller NT, Differding MK, Zhang M, Maruthur NM, Juraschek SP, Miller ER 3rd, Appel LJ, Yeh HC (2021) Metformin affects gut microbiome composition and function and circulating short-chain fatty acids: a Randomized Trial. Diabetes Care 44:1462–1471. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc20-2257
Nayeem MA (2018) Role of oxylipins in cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol Sin 39:1142–1154. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2018.24
Olivares M, Neyrinck AM, Pötgens SA, Beaumont M, Salazar N, Cani PD, Bindels LB, Delzenne NM (2018) The DPP-4 inhibitor vildagliptin impacts the gut microbiota and prevents disruption of intestinal homeostasis induced by a Western diet in mice. Diabetologia 61:1838–1848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-018-4647-6
Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Pocock SJ, Carson P, Januzzi J, Verma S, Tsutsui H, Brueckmann M et al (2020) Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart failure. N Engl J Med 383:1413–1424. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2022190
Pereira FC, Wasmund K, Cobankovic I, Jehmlich N, Herbold CW, Lee KS, Sziranyi B, Vesely C, Decker T, Stocker R et al (2020) Rational design of a microbial consortium of mucosal sugar utilizers reduces Clostridiodes difficile colonization. Nat Commun 11:5104. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18928-1
Perry RJ, Peng L, Barry NA, Cline GW, Zhang D, Cardone RL, Petersen KF, Kibbey RG, Goodman AL, Shulman GI (2016) Acetate mediates a microbiome-brain-β-cell axis to promote metabolic syndrome. Nature 534:213–217. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18309
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glockner FO (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D590–596. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1219
Rastelli M, Knauf C, Cani PD (2018) Gut microbes and health: a focus on the mechanisms linking microbes, obesity, and related disorders. Obes (Silver Spring) 26:792–800. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22175
Ridlon JM, Harris SC, Bhowmik S, Kang DJ, Hylemon PB (2016) Consequences of bile salt biotransformations by intestinal bacteria. Gut Microbes 7:22–39. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2015.1127483
Santos-Gallego CG, Requena-Ibanez JA, San Antonio R, Ishikawa K, Watanabe S, Picatoste B, Flores E, Garcia-Ropero A, Sanz J, Hajjar RJ et al (2019) Empagliflozin ameliorates adverse left ventricular remodeling in nondiabetic heart failure by enhancing myocardial energetics. J Am Coll Cardiol 73:1931–1944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2019.01.056
Silva YP, Bernardi A, Frozza RL (2020) The role of short-chain fatty acids from gut microbiota in Gut-Brain communication. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 11:25. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00025
Singh V, Chassaing B, Zhang L, San Yeoh B, Xiao X, Kumar M, Baker MT, Cai J, Walker R, Borkowski K et al (2015) Microbiota-dependent hepatic lipogenesis mediated by Stearoyl CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1) promotes metabolic syndrome in TLR5-Deficient mice. Cell Metab 22:983–996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.09.028
Song Z, Cai Y, Lao X, Wang X, Lin X, Cui Y, Kalavagunta PK, Liao J, Jin L, Shang J et al (2019) Taxonomic profiling and populational patterns of bacterial bile salt hydrolase (BSH) genes based on worldwide human gut microbiome. Microbiome 7:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-019-0628-3
Sorbara MT, Littmann ER, Fontana E, Moody TU, Kohout CE, Gjonbalaj M, Eaton V, Seok R, Leiner IM, Pamer EG (2020) Functional and genomic variation between human-derived isolates of Lachnospiraceae reveals Inter- and intra-species diversity. Cell Host Microbe 28:134–146e134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.005
Vacca M, Celano G, Calabrese FM, Portincasa P, Gobbetti M, De Angelis M (2020) The Controversial Role of Human Gut Lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040573
Wong J, Piceno YM, DeSantis TZ, Pahl M, Andersen GL, Vaziri ND (2014) Expansion of urease- and uricase-containing, indole- and p-cresol-forming and contraction of short-chain fatty acid-producing intestinal microbiota in ESRD. Am J Nephrol 39:230–237. https://doi.org/10.1159/000360010
Wu J, Wang K, Wang X, Pang Y, Jiang C (2021) The role of the gut microbiome and its metabolites in metabolic diseases. Protein Cell 12:360–373. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-020-00814-7
Zeng M, Cao H (2018) Fast quantification of short chain fatty acids and ketone bodies by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry after facile derivatization coupled with liquid-liquid extraction. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 1083:137–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.02.040
Zhang L, Feng Y, List J, Kasichayanula S, Pfister M (2010) Dapagliflozin treatment in patients with different stages of type 2 diabetes mellitus: effects on glycaemic control and body weight. Diabetes Obes Metab 12:510–516. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-1326.2010.01216.x
Zhang M, Feng R, Yang M, Qian C, Wang Z, Liu W, Ma J (2019) Effects of metformin, acarbose, and sitagliptin monotherapy on gut microbiota in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 7:e000717. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjdrc-2019-000717
Zheng X, Chen T, Jiang R, Zhao A, Wu Q, Kuang J, Sun D, Ren Z, Li M, Zhao M et al (2021) Hyocholic acid species improve glucose homeostasis through a distinct TGR5 and FXR signaling mechanism. Cell Metab 33:791–803e797. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.017
Funding
This study was supported by the Foundation of Sichuan Science and Technology (No. 2020YJ0461; granted to MZ) and the Foundation of Sichuan Provincial People’s Hospital (No. 2022QN14; granted to LZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: LZ, MZ, JM;Methodology: JM, TW, HW, GY, CH, TZ; Acquisition of data: JM, TW, HW, GY, CH, TZ ; Analysis and interpretation of data: LZ, HT, JM, TW; Writing of the manuscript: LZ; Writing and approval of the final draft: LZ, JM, HT, MZ ; Study supervision: HT, MZ. All authors read and approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, L., Ma, J., Wei, T. et al. The effect of canagliflozin on gut microbiota and metabolites in type 2 diabetic mice. Genes Genom 46, 541–555 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-024-01491-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-024-01491-0