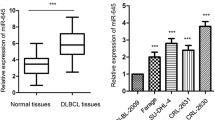
Abstract
Background
Previous studies have shown that the copy number of microRNA (miR)-124 is decreased in diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and that miR-124 is a tumor suppressor by targeting NF-κB p65 in B-cell lymphoma. In turn, miR-124 expression is regulated by transcription factors such as HNF4α, ETS2, and p53. However, whether and how miR-124 transcription is modulated by NF-κB transcription factors remain unknown in DLBCL.
Objective
To investigate whether the activation of NF-κB signaling could inhibit the expression of miR-124, possibly contributing to the pathogenesis of DLBCL.
Methods
Potential transcription factors regulating miR-124 transcription were predicted using the Transfac software. The cellular effects of NF-κB p65 on miR-124 were examined by MTS assay, Western blot assay, qPCR, and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays using DLBCL cell lines.
Results
Inhibition of NF-κB signals using Bay11-7085 increased miR-124 expression whereas exposure to TNF-α decreased it. Ectopic expression of p65 suppressed miR-124 expression, suggesting that p65 may be a transcriptional repressor of miRNA-124. Pharmacological analyses showed that phosphorylated/activated p65 downregulates miR-124 via two signaling pathways: (1) TAK1/IKKα-IKKβ/IκBα and (2) MAPK/p65. Moreover, ChIP assay demonstrated that p65 directly regulates miR-124 by binding to the NF-κB consensus sequence in its promoter region. Finally, we also confirmed that stable ectopic expression of miR-124 suppresses cell proliferation and survival.
Conclusion
Taken together, our study uncovered a mechanism by which active NF-κB signaling disrupts the function of miR-124 as a tumor suppressor in DLBCL.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardekani AM, Naeini MM (2010) The role of microRNAs in human diseases Avicenna. J Med Biotechnol 2(4):161–179
Ashburner BP, Westerheide SD, Baldwin AS Jr (2001) The p65 (RelA) subunit of NF-kappaB interacts with the histone deacetylase (HDAC) corepressors HDAC1 and HDAC2 to negatively regulate gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 21(20):7065–7077
Chalbatani GM, Dana H, Gharagozlou E, Mahmoodzadeh H, Zeinalinia E, Rezaeian O, Pilvar P, Ardaneh M, Meghdadi S, Memari F (2017) Microrna a new gate in cancer and human disease: a review. J Biol Sci 17(6):247–254
Cheng Y, Li Y, Nian Y, Liu D, Dai F, Zhang J (2015) STAT3 is involved in miR-124-mediated suppressive effects on esophageal cancer cells. BMC Cancer 15(1):306
Gambari R, Brognara E, Spandidos DA, Fabbri E (2016) Targeting oncomiRNAs and mimicking tumor suppressor miRNAs: Nuew trends in the development of miRNA therapeutic strategies in oncology (review). Int J Oncol 49(1):5–32
Getaneh Z, Asrie F, Melku M (2019) MicroRNA profiles in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. EJIFCC 30(2):195
Hartmann EM, Ott G, Rosenwald A (2008) Molecular biology and genetics of lymphomas. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am 22(5):807–823
Hirata Y, Takahashi M, Morishita T, Noguchi T, Matsuzawa A (2017) Post-translational modifications of the TAK1–TAB complex. Int J Mol Sci 18(1):205
Hoesel B, Schmid JA (2013) The complexity of NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol Cancer 12:86
Jeong D, Kim J, Nam J, Sun H, Lee YH, Lee TJ, Aguiar RC, Kim SW (2015) MicroRNA-124 links p53 to the NF-kappaB pathway in B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 29(9):1868–1874
Jost PJ, Ruland J (2007) Aberrant NF-kappaB signaling in lymphoma: mechanisms, consequences, and therapeutic implications. Blood 109(7):2700–2707
Kim J, Jeong D, Nam J, Aung TN, Gim JA, Park KU, Kim SW (2015) MicroRNA-124 regulates glucocorticoid sensitivity by targeting phosphodiesterase 4B in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Gene 558(1):173–180
Lim SG, Kim JK, Suk K, Lee WH (2017) Crosstalk between signals initiated from TLR4 and cell surface BAFF results in synergistic induction of proinflammatory mediators in THP-1 cells. Sci Rep 7:45826
Lujambio A, Ropero S, Ballestar E, Fraga MF, Cerrato C, Setien F, Casado S, Suarez-Gauthier A, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Git A, Spiteri I, Das PP, Caldas C, Miska E, Esteller M (2007) Genetic unmasking of an epigenetically silenced microRNA in human cancer cells. Cancer Res 67(4):1424–1429
Ma X, Becker Buscaglia LE, Barker JR, Li Y (2011) MicroRNAs in NF-κB signaling. J Mol Cell Biol 3(3):159–166
Pasqualucci L, Dalla-Favera R (2015) The genetic landscape of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Semin Hematol 52(2):67–76
Perkins ND (2007) Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(1):49–62
Sandhu SK, Croce CM, Garzon R (2011) Micro-RNA expression and function in lymphomas. Adv Hematol 2011:347137
Sehn LH, Gascoyne RD (2015) Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: optimizing outcome in the context of clinical and biologic heterogeneity. Blood 125(1):22–32
Simeonidis S, Castagliuolo I, Pan A, Liu J, Wang CC, Mykoniatis A, Pasha A, Valenick L, Sougioultzis S, Zhao D, Pothoulakis C (2003) Regulation of the NK-1 receptor gene expression in human macrophage cells via an NF-kappa B site on its promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(5):2957–2962
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S (2009) Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol 11(3):228–234
Wong KY, So CC, Loong F, Chung LP, Lam WWL, Liang R, Li GKH, Jin D-Y, Chim CS (2011) Epigenetic inactivation of the miR-124-1 in haematological malignancies. PLoS ONE 6(4):e19027
Yang L, Zhu Y, Kong D, Gong J, Yu W, Liang Y, Nie Y, Teng C-B (2019) EGF suppresses the expression of miR-124a in pancreatic β cell lines via ETS2 activation through the MEK and PI3K signaling pathways. Int J Biol Sci 15(12):2561
Zhang W, Liu HT (2002) MAPK signal pathways in the regulation of cell proliferation in mammalian cells. Cell Res 12(1):9–18
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a two-year Research Grant to Pusan National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Hyein Shim, Jehyun Nam and Sang-Woo Kim. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Hyein Shim and Sang-Woo Kim. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Hyein Shim, Jehyun Nam and Sang-Woo Kim declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shim, H., Nam, J. & Kim, SW. NF-κB p65 represses microRNA-124 transcription in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Genes Genom 42, 543–551 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-020-00922-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-020-00922-y