Abstract
Background
Cancer-induced bone pain (CIBP) is the pain caused by bone metastasis from malignant tumors, and the largest source of pain for cancer patients. miR-300 is an important miRNA in cancer. It has been shown that miR-300 regulates tumorigenesis of various tumors.
Purpose
This study aims to investigate the role of miR-300 in CIBP and its underlying molecular mechanisms in vitro and in vivo.
Methods
We constructed CIBP model in rats and investigated the mechanism through which miR-300 affects CIBP. We first examined expression level of miR-300 in CIBP rats and then tested the effect of its overexpression. Next, we identified the target of miR-300 using TargetScan analysis and double luciferase assay. Finally, we studied genetic interactions between miR-300 and its target and their roles in CIBP.
Results
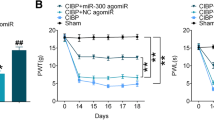
We found that miR-300 was downregulated in CIBP rats. Overexpression of miR-300 significantly attenuated cancer-induced neuropathic pain (p < 0.01). Furthermore, TargetScan analysis and double luciferase assay show High Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) is a target of miR-300. Notably, HMGB1 is overexpressed in CIBP rats, while up-regulation of miR-300 significantly suppresses expression of HMGB1 (p < 0.01). Moreover, knockdown of HMGB1 by siRNA significantly relieves cancer-induced neuropathic pain in rats (p < 0.01). On the other hand, HMGB1 overexpression partially blocked the effect of miR-300 on cancer-induced nerve pain.
Conclusion
miR-300 relieves cancer-induced neuropathic pain by inhibiting HMGB1 expression. These results may be beneficial for the treatment of CIBP in clinical practice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernardino L, Xapelli S, Silva AP, Jakobsen B, Poulsen FR, Oliveira CR, Vezzani A, Malva JO, Zimmer J (2005) Modulator effects of interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on AMPA-induced excitotoxicity in mouse organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. J Neurosci 25(29):6734–6744. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.1510-05.2005 (PMID: 16033883)
Chen G, Gong M, Yan M, Zhang X (2013) Sevoflurane induces endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated apoptosis in hippocampal neurons of aging rats. PLoS ONE 8(2):e57870. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057870 (PMID: 23469093)
Chen L, Xie W, Xie W, Zhuang W, Jiang C, Liu N (2017) Apigenin attenuates isoflurane-induced cognitive dysfunction via epigenetic regulation and neuroinflammation in aged rats. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 73:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archger.2017.07.004 (PMID: 28743056)
Del Rosario A, McDermott MM, Panee J (2012) Effects of a high-fat diet and bamboo extract supplement on anxiety- and depression-like neurobehaviours in mice. Br J Nutr 108(7):1143–1149. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0007114511006738 (PMID: 22313665)
Feng X, Valdearcos M, Uchida Y, Lutrin D, Maze M, Koliwad SK (2017) Microglia mediate postoperative hippocampal inflammation and cognitive decline in mice. JCI Insight 2(7):e91229. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.91229 (PMID: 28405620)
Hobin JA, Goosens KA, Maren S (2003) Context-dependent neuronal activity in the lateral amygdala represents fear memories after extinction. J Neurosci 23(23):8410–8416 (PMID: 12968003)
Hou X, Zhang J, Ahmad H, Zhang H, Xu Z, Wang T (2014) Evaluation of antioxidant activities of ampelopsin and its protective effect in lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress piglets. PLoS ONE 9(9):e108314. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108314 (PMID: 25268121)
Hovens IB, Schoemaker RG, van der Zee EA, Absalom AR, Heineman E, van Leeuwen BL (2014) Postoperative cognitive dysfunction: involvement of neuroinflammation and neuronal functioning. Brain Behav Immun 38:202–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2014.02.002 (PMID: 24517920)
Jungwirth B, Zieglgansberger W, Kochs E, Rammes G (2009) Anesthesia and postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). Mini Rev Med Chem 9(14):1568–1579 (PMID: 20088778)
Kou X, Shen K, An Y, Qi S, Dai WX, Yin Z (2012) Ampelopsin inhibits H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis by ERK and Akt signaling pathways and up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1. Phytother Res 26(7):988–994. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.3671 (PMID: 22144097)
Kou X, Jie L, Jing B, Yi Y, Yang X, Fan J, Jia S, Ning C (2015) Ampelopsin attenuates 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity by regulating GSK-3β/NRF2/ARE signalling. J Funct Foods 19:765–774
Kou X, Liu X, Chen X, Li J, Yang X, Fan J, Yang Y, Chen N (2016) Ampelopsin attenuates brain aging of D-gal-induced rats through miR-34a-mediated SIRT1/mTOR signal pathway. Oncotarget 7(46):74484–74495. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12811 (PMID: 27780933)
Li ZQ, Rong XY, Liu YJ, Ni C, Tian XS, Mo N, Chui DH, Guo XY (2013) Activation of the canonical nuclear factor-κB pathway is involved in isoflurane-induced hippocampal interleukin-1beta elevation and the resultant cognitive deficits in aged rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 438(4):628–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.08.003 (PMID: 23933318)
Liu Y, Yin Y (2018) Emerging roles of immune cells in postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Med Inflamm 2018:6215350. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6215350 (PMID: 29670465)
Ma H, Yao L, Pang L, Li X, Yao Q (2016) Tetrandrine ameliorates sevofluraneinduced cognitive impairment via the suppression of inflammation and apoptosis in aged rats. Mol Med Rep 13(6):4814–4820. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5132 (PMID: 27082007)
Qi S, Xin Y, Guo Y, Diao Y, Kou X, Luo L, Yin Z (2012) Ampelopsin reduces endotoxic inflammation via repressing ROS-mediated activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 12(1):278–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2011.12.001 (PMID: 22193240)
Rosczyk HA, Sparkman NL, Johnson RW (2008) Neuroinflammation and cognitive function in aged mice following minor surgery. Exp Gerontol 43(9):840–846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2008.06.004 (PMID: 18602982)
Safavynia SA, Goldstein PA (2018) The role of neuroinflammation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction: moving from hypothesis to treatment. Front Psychiatry 9:752. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00752 (PMID: 30705643)
Shalini S, Dorstyn L, Dawar S, Kumar S (2015) Old, new and emerging functions of caspases. Cell Death Differ 22(4):526–539. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2014.216 (PMID: 25526085)
Tan H, Cao J, Zhang J, Zuo Z (2014) Critical role of inflammatory cytokines in impairing biochemical processes for learning and memory after surgery in rats. J Neuroinflammation 11:93. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-11-93 (PMID: 24884762)
Tang N, Ou C, Liu Y, Zuo Y, Bai Y (2014) Effect of inhalational anaesthetic on postoperative cognitive dysfunction following radical rectal resection in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment. J Int Med Res 42(6):1252–1261. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060514549781 (PMID: 25339455)
Tian Y, Guo S, Wu X, Ma L, Zhao X (2015) Minocycline alleviates sevoflurane-induced cognitive impairment in aged rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 35(4):585–594. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0154-6 (PMID: 25585814)
Vacas S, Degos V, Feng X, Maze M (2013) The neuroinflammatory response of postoperative cognitive decline. Br Med Bull 106:161–178. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldt006 (PMID: 23558082)
Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M (2009) Regulation and function of NF-κB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 27:693–733. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132641 (PMID: 19302050)
Wan Y, Xu J, Ma D, Zeng Y, Cibelli M, Maze M (2007) Postoperative impairment of cognitive function in rats: a possible role for cytokine-mediated inflammation in the hippocampus. Anesthesiology 106(3):436–443. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200703000-00007 (PMID: 17325501)
Wang Y, Zuo M (2015) Nicotinamide improves sevoflurane-induced cognitive impairment through suppression of inflammation and anti-apoptosis in rat. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8(11):20079–20085 (PMID: 26884920)
Weng L, Zhang H, Li X, Zhan H, Chen F, Han L, Xu Y, Cao X (2017) Ampelopsin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response through the inhibition of the NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways in microglia. Int Immunopharmacol 44:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.12.018 (PMID: 27998743)
Whyte M, Evan G (1995) Apoptosis. The last cut is the deepest. Nature 376(6535):17–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/376017a0 (PMID: 7596422)
Wooten MW (1999) Function for NF-kB in neuronal survival: regulation by atypical protein kinase C. J Neurosci Res 58(5):607–611 (PMID: 10561688)
Yang ZY, Yuan CX (2018) IL-17A promotes the neuroinflammation and cognitive function in sevoflurane anesthetized aged rats via activation of NF-κB signaling pathway. BMC Anesthesiol 18(1):147. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-018-0607-4 (PMID: 30342469)
Zhang J, Jiang W, Zuo Z (2014) Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuates surgery-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive dysfunction possibly via inhibition of nuclear factor κB. Neuroscience 261:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.12.034 (PMID: 24365462)
Zhang Z, Li X, Li F, An L (2016) Berberine alleviates postoperative cognitive dysfunction by suppressing neuroinflammation in aged mice. Int Immunopharmacol 38:426–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.06.031 (PMID: 27376853)
Zhou Y, Liang X, Chang H, Shu F, Wu Y, Zhang T, Fu Y, Zhang Q, Zhu JD, Mi M (2014) Ampelopsin-induced autophagy protects breast cancer cells from apoptosis through Akt-mTOR pathway via endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cancer Sci 105(10):1279–1287. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12494 (PMID: 25088800)
Zhu G, Tao L, Wang R, Xue Y, Wang X, Yang S, Sun X, Gao G, Mao Z, Yang Q (2017) Endoplasmic reticulum stress mediates distinct impacts of sevoflurane on different subfields of immature hippocampus. J Neurochem 142(2):272–285. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.14057 (PMID: 28444766)
Funding
This work was supported by the Yangzhou’s 13th Five-Year plan for “Ke Jiao Qiang Wei” (Grant No. ZDRC39) and Science and Technology Development Fundation of Clinical Medicine of Jiangsu University (Grant No. JLY20180167).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CLL and XJZ conceived and designed the experiments, HHL and FW analyzed and interpreted the results of the experiments, FZ performed the experiments
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests, and all authors should confirm its accuracy.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animal use peotocol listed below has been reviewde and approved by the Animal Ethical and Welfaer Committee (Approval No. 20190004).
Patient consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from a legally authorized representative(s) for anonymized patient information to be published in this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Zha, X., Liu, H. et al. Ampelopsin alleviates sevoflurane-induced cognitive dysfunction by mediating NF-κB pathway in aged rats. Genes Genom 42, 361–369 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00897-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00897-5