Abstract
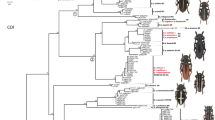
The systematics of Dorcus MacLeay has been a long-standing debate. Mitochondrial genomes were widely used to deeply understand the phylogeny of problematic taxa in virtue of their genetic importance and comprehensiveness. To provide more useful genetic data for resolving the systematic disputation of Dorcus stag beetles. The complete mitochondrial genomes of Dorcus hopei and Dorcus seguyi were obtained using the next generation sequencing. Characteristics of the two genomes are explicated through comparing their genome organization and base composition, protein-coding genes and codon usage, intergenic spacers and non-coding region, transfer and ribosomal RNA genes and control region. Phylogenetic relationships were reconstructed using Maximum likelihood and Bayesian inference analyses based on the concatenated nucleotide sequences of 13 PCGs from 9 stag beetles and 3 scarab beetles. The complete mitogenomes of D. hopei and D. seguyi was 16,026 bp/17,955 bp long, respectively. A tandem repeat with the length of 940 bp was presented in the A+T-rich region in D. hopei. An unexpected non-coding region of 332 bp was located between nad2 and trnW in D. seguyi. The phylogenetic analyses robustly supported that D. hopei formed a branch with the generic type of D. parallelipipedus. Whereas D. seguyi was not covered in the branch of (D. hopei + D. parallelipipedus), but was sister to them. The results indicated that D. hopei should be a good member of Dorcus MacLeay. The taxonomic status of D. seguyi remained to be studied furtherly.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araya K, Hosoya T (2005) Molecular phylogeny of the Dorcus velutinus species-group (Coleoptera, Lucanidae) Inferred from the mitochondrial 16S rRNA gene sequences, with the special reference to the taxonomic status of its Japanese and Taiwanese Members. Elytra 33:523–530
Araya K, Hosoya T (2007) Molecular phylogeny of Dorcus amanianus yaeyamaensis (Hori, 1991) (Coleoptera, Lucanidae). Gekkan-Mushi 438:2–7
Arrow GJ (1950) Coleoptera, Lamellicornia, Lucanidae and Passalidae: the fauna of India Including Pakistan, Ceylon, Burma and Malaya, vol IV. Taylor and Francis Ltd., London, pp 1–275
Balke M, Ribera I, Vogler AP (2004) MtDNA phylogeny and biogeography of Copelatinae, a highly diverse group of tropical diving beetles (Dytiscidae). Mol Phylogenet Evol 32:866–880
Bartolozzi L, Sprecher-Uebersax E (2006) Lucanidae. In: Lobl I, Smetana A (eds) Catalogue of Palaearctic Coleoptera, Scarabaeoidea—Scirtoidea—Dascilloidea—Buprestoidea—Byrrhoidea, vol III. Apollo Books, Vester Skerninge., Denmark, pp 63–76
Benesh B (1960) Lucanidae. Coleopterorum catalogus. Supplementa 8:1–178
Breeschoten T, Doorenweerd C, Tarasov S, Vogler AP (2016) Phylogenetics and biogeography of the dung beetle genus Onthophagus inferred from mitochondrial genomes. Mol Phylogenet Evol 105:86–95
Castresana J (2000) Selection of conserved blocks from multiple alignments for their use in phylogenetic analysis. Mol Biol Evol 17:540–552
Cheng XF, Zhang P, Yu DN, Storey KB, Zhang JY (2016) The complete mitochondrial genomes of four cockroaches (Insecta: Blattodea) and phylogenetic analyses within cockroaches. Gene 586:115–122
Crampton-Platt A, Timmermans MJTN., Gimmel ML, Kutty SN, Cockerill TD, Khen CV, Vogler AP (2015) Soup to tree: the phylogeny of beetles inferred by mitochondrial metagenomics of a Bornean rainforest sample. Mol Biol Evol 32:2302–2316
de Lisle M (1955) Description d’un Lucanide nouveau. Bulletin de la Société entomologique de France 60:6–8
Didier R, Se´guy E (1953) Catalogue illustre´ des lucanides du globe. Texte encyclope´die entomologique serie A, vol 27. Paul Lechevalier, Paris, pp 1–223
Drummond AJ, Ashton B, Buxton S, Cheung M, Cooper A (2011) Geneious v6.1.7. http://www.geneious.com/. Accessed 3 Sept 2017
Du C, Zhang L, Lu T, Ma J, Zeng C, Yue B, Zhang X (2017) Mitochondrial genomes of blister beetles (Coleoptera, Meloidae) and two large intergenic spacers in Hycleus genera. BMC Genomics 18:698
Fujita H (2010) The lucanid beetles of the world M. Mushi-Sha’s lconographic series of insects, vol 6. Mushisha, Tokyo, pp 1–472
Han TM, Jeong JC, Kang TH, Lee YB, Park HC (2010) Phylogenetic relationships of Dorcus koreanus Jang and Kawai (2008) (Coleoptera. Lucanidae): species or subspecies? Zool sci 27:362–368
Hosoya T, Araya K (2005) Phylogeny of Japanese stag beetles (Coleoptera: Lucanidae) inferred from 16S mtrRNA gene sequences, with reference to the evolution of sexual dimorphism of mandibles. Zool Sci 22:1305–1318
Hosoya T, Araya K (2007) Molecular phylogeny of Dorcus amanianus yaeyamaensis (Hori, 1991) (Coleoptera, Lucanidae). Gekkan-Mushi 438:2–7
Hosoya T, Honda M, Araya K (2001) Genetic variations of 16S rRNA gene observed in Ceruchus lignarius and Dorcus rectus rectus (Coleoptera: Lucanidae). Entomol Sci 4:335–344
Hosoya T, Araya K, Shirota Y (2002) Molecular phylogeny of Japanese and Taiwanese stag beetles of the genus Dorcus and allied genera (Coleoptera, Lucanidae) based on random amplified polymorphic DNA. Giornale Italiano di Entomologia 10:133–140
Hosoya T, Araya K, Shirota Y (2003) Molecular phylogeny of Japanese stag beetles of the genus Dorcus (Coleoptera, Lucanidae) and its allied genera inferred from mitochondrial COI gene sequences. Elytra 31:127–142
Huang H, Chen CC (2013) Stag beetles of China II. Formosa Ecological Company, Taiwan
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MrBayes: Bayesian inference of phylogenenetic trees. Biometrics 17:754–755
Kazutaka K, Daron M (2016) MAFFT versions 7.263. http://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/software/. Accessed 8 Sept 2017
Kikuta T (1986) On the higher taxa of the stag beetle family Lucanidae. Spe Bul Jap Soc Coleopter 2:131–138
Kim SI, Farrell BD (2015) Phylogeny of world stag beetles (Coleoptera: Lucanidae) reveals a Gondwanan origin of Darwin’s stag beetle. Mol Phylogenet Evol 86:35–48
Kim MJ, Wang AR, Park JS, Kim I (2014) Complete mitochondrial genomes of five skippers (Lepidoptera: Hesperiidae) and phylogenetic reconstruction of Lepidoptera. Gene 549:97–112
Kim MJ, Kim G, Kim SR, Kim I (2015) Complete mitochondrial genome of the two–spotted stag beetle, Metopodontus blanchardi (Coleoptera: Lucanidae). Mitochondr DNA 26:307–309
Krajcik M (2001) Lucanidae of the world. Catalogue - part I, checklist of the stag beetles of the world (Coleoptera: Lucanidae). M. Krajcik, Most
Lin ZQ, Song F, Li T, Wu YY, Wan X (2017) New mitogenomes of two chinese stag beetles (Coleoptera, Lucanidae) and their implications for systematics. J Insect Sci 63:1–9
Linard B, Arribas P, Andújar C, Crampton-Platt A, Vogler AP (2016) Lessons from genome skimming of arthropod-preserving ethanol. Mol Ecol Resour 16:1365–1377
Maes JM (1990) Notas diversas sobre la taxonomia de los Lucanidae. Revista Nicaraguense de Entomologia 11:1–34
Maes JM (1992) Lista de los Lucanidae del Mundo. Revista Nicaraguense de Entomologia 22B:61–121
Mizunuma T, Nagai S (1994) The lucanid beetles of the world: Mushi -shaIconograp -hic series of Insects. Mushisha, Tokyo
Perna NT, Kocher TD (1995) Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J Mol Evol 41:353–358
Posada D (2008) jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol 25:1253–1256. http://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/software/. Accessed 12 Sept 2017
Rambaut A (2016) FigTree: Tree Figure Drawing Tool, Version 1.4.3. Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh. http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/. Accessed 15 Sept 2017
Saunders WW (1854) Characters of undescribed Lucanidae, collected in China by R.Fortune, Esq. Trans Entomol Soc Lond 2:45–55
Sheffield NC, Song H, Cameron SL, Whiting MF (2008) A comparative analysis of mitochondrial genomes in Coleoptera (Arthropoda: Insecta) and genome descriptions of six new beetles. Mol Biol Evol 25:2499–2509
Sheffield NC, Song H, Cameron SL, Whiting MF (2009) Nonstationary evolution and compositional heterogeneity in beetle mitochondrial phylogenomics. Syst Biol 58:381–394
Simon C, Frati F, Beckenbach A, Crespi B, Liu H, Flook P (1994) Evolution, weighting, and phylogenetic utility of mitochondrial gene sequences and a compilation of conserved polymerase chain reaction primers. Ann Entomol Soc Am 87:651–701
Stamatakis A (2014) RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies. Bioinformatics 30:1312–1313
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Thomson J (1862) Catalogue des Lucanides de la collection de M. James Thomson, suivi d’un appendix renfermant la description des coupes génériques et spécifiques nouvelles. Annales de la Société Entomologique de France 2:389–436
Timmermans MJTN., Dodsworth S, Culverwell CL, Bocak L, Ahrens D, Littlewood DTJ, Pons J, Vogler AP (2010) Why barcode? Highhroughput multiplex sequencing of mitochondrial genomes for molecular systematics. Nucleic Acids Res 38:e197
Wan X, Yang XK (2006) Chinese names of “Lucanidae” and genera from China. Chin B Entomol 43:418–422
Wan X, Bai M, Cui JZ, Yang XK (2010) Six new record species of the Chinese Lucanidae. Zool Syst 35:247–250
Wu QL, Li Q, Gu Y, Shi BC, van Achterberg C, Wei SJ, Chen XX (2014) The complete mitochondrial genome of Taeniogonalos taihorina (Bischoff) (Hymenoptera: Trigonalyidae) reveals a novel gene rearrangement pattern in the Hymenoptera. Gene 543:76–84
Wu YY, Cao YY, Fang J, Wan X (2016) The first complete mitochondrial genome of stag beetle from China, Prosopocoilus gracilis (Coleoptera, Lucanidae). Mitochondr DNA 27:2633
Yang J, Ye F, Huang Y (2016) Mitochondrial genomes of four katydids (Orthoptera: Phaneropteridae): new gene rearrangements and their phylogenetic implications. Gene 575:702–7011
Yuan ML, Zhang QL, Zhang L, Guo ZL, Liu YJ, Shen YY. Shao R (2016) High-level phylogeny of the Coleoptera inferred with mitochondrial genome sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 104:99–111
Acknowledgements
We wish to extend our sincerest thanks to Dr. Hu Li and Dr. Fan Song (Department of Entomology, China Agricultural University, West Campus) who gave us invaluable advices about the data analysis during this study, We would like to thank Professor Alfried Vogler (Natural History Museum, London, UK). We would also like to express our gratitude to the lab colleagues, Qian Wang and Zi qi Lin for their kind help. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31201745, 31071954, and 31572311).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
YongJing Chen, Jing Liu, YuYan Cao, Shiju Zhou and Xia Wan declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving animal and human rights
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects by any of the authors. The animal experiment throughout the study was conducted according to the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology Guiding Directives for Humane Treatment of Laboratory Animals.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Liu, J., Cao, Y. et al. Two new complete mitochondrial genomes of Dorcus stag beetles (Coleoptera, Lucanidae). Genes Genom 40, 873–880 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0699-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-018-0699-8