Abstract
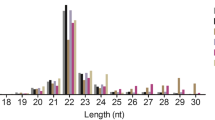
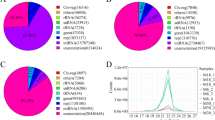
microRNAs (miRNAs) and PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) execute important regulatory roles in testis development and spermatogenesis, while previous studies mainly focus on the expression profiles in immature and mature porcine testes, which may cause a bottleneck for further understanding their complex physiological processes in porcine testes development and spermatogenesis. Thus, we presented the expression and characterization of miRNAs and piRNAs in DS (60-day-old), DN (90-day-old), DT (120-day-old) and DF (150-day-old) pig testes. In total, 12,834,628, 13,359,726, 12,851,249 and 12,938,601 clean reads were generated from these libraries, respectively. 293 mature and 36 novel miRNAs as well as 4923 piRNA clusters were identified from pig testes, and they showed an age-dependent manner. GO enrichment analysis of miRNA target genes and piRNA generated genes showed that they participated widely in regulating the pig spermatogenesis process. In addition, 12 differentially expressed miRNAs were randomly selected to validate using qRT-PCR. Our results provided novel comprehensive expression profiles of miRNAs and piRNAs in pig testes at different stages of sexual maturity, which will promote our knowledge of them in regulating the pig testes development and spermatogenesis process.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aravin A, Gaidatzis D, Pfeffer S, Lagos-Quintana M, Landgraf P, Iovino N, Morris P, Brownstein MJ, Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Nakano T et al (2006) A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature 442:203–207
Beyret E, Liu N, Lin H (2012) piRNA biogenesis during adult spermatogenesis in mice is independent of the ping-pong mechanism. Cell Res 22:1429–1439
Busk PK (2014) A tool for design of primers for microRNA-specific quantitative RT-qPCR. BMC Bioinform 15:29
Cora E, Pandey RR, Xiol J, Taylor J, Sachidanandam R, McCarthy AA, Pillai RS (2014) The MID-PIWI module of Piwi proteins specifies nucleotide- and strand-biases of piRNAs. RNA 20:773–781
Cui L, Fang L, Shi B, Qiu S, Ye Y (2015) Spermatozoa micro ribonucleic acid-34c level is correlated with intracytoplasmic sperm injection outcomes. Fertil Steril 104(312–7):e1
de Mateo S, Sassone-Corsi P (2014) Regulation of spermatogenesis by small non-coding RNAs: role of the germ granule. Semin Cell Dev Biol 29:84–92
Eisenberg I, Kotaja N, Goldman-Wohl D, Imbar T (2015) microRNA in human reproduction. Adv Exp Med Biol 888:353–387
Fu Q, Wang PJ (2014) Mammalian piRNAs: biogenesis, function, and mysteries. Spermatogenesis 4:e27889
Girard A, Sachidanandam R, Hannon GJ, Carmell MA (2006) A germline-specific class of small RNAs binds mammalian Piwi proteins. Nature 442:199–202
Grivna ST, Beyret E, Wang Z, Lin H (2006) A novel class of small RNAs in mouse spermatogenic cells. Genes Dev 20:1709–1714
He Z, Jiang J, Kokkinaki M, Tang L, Zeng W, Gallicano I, Dobrinski I, Dym M (2013) MiRNA-20 and mirna-106a regulate spermatogonial stem cell renewal at the post-transcriptional level via targeting STAT3 and Ccnd1. Stem Cells 31:2205–2217
Holt JE, Stanger SJ, Nixon B, McLaughlin EA (2016) Non-coding RNA in spermatogenesis and epididymal maturation. Adv Exp Med Biol 886:95–120
Jan SZ, Hamer G, Repping S, de Rooij DG, van Pelt AM, Vormer TL (2012) Molecular control of rodent spermatogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:1838–1850
Kawaoka S, Izumi N, Katsuma S, Tomari Y (2011) 3′ end formation of PIWI-interacting RNAs in vitro. Mol Cell 43:1015–1022
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M, Salzberg SL (2009) Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol 10:R25
Le Thomas A, Stuwe E, Li S, Du J, Marinov G, Rozhkov N, Chen YC, Luo Y, Sachidanandam R, Toth KF et al (2014) Transgenerationally inherited piRNAs trigger piRNA biogenesis by changing the chromatin of piRNA clusters and inducing precursor processing. Genes Dev 28:1667–1680
Li M, Yu M, Liu C, Zhu H, He X, Peng S, Hua J (2013a) miR-34c works downstream of p53 leading to dairy goat male germline stem-cell (mGSCs) apoptosis. Cell Prolif 46:223–231
Li M, Yu M, Liu C, Zhu H, Hua J (2013b) Expression of miR-34c in response to overexpression of Boule and Stra8 in dairy goat male germ line stem cells (mGSCs). Cell Biochem Funct 31:281–288
Li Y, Li J, Fang C, Shi L, Tan J, Xiong Y, Bin F, Li C (2016) Genome-wide differential expression of genes and small RNAs in testis of two different porcine breeds and at two different ages. Sci Rep 6:26852
Lian C, Sun B, Niu S, Yang R, Liu B, Lu C, Meng J, Qiu Z, Zhang L, Zhao Z (2012) A comparative profile of the microRNA transcriptome in immature and mature porcine testes using Solexa deep sequencing. FEBS J 279:964–975
Liang X, Zhou D, Wei C, Luo H, Liu J, Fu R, Cui S (2012) MicroRNA-34c enhances murine male germ cell apoptosis through targeting ATF1. PLoS ONE 7:e33861
Liu G, Lei B, Li Y, Tong K, Ding Y, Luo L, Xia X, Jiang S, Deng C, Xiong Y et al (2012a) Discovery of potential piRNAs from next generation sequences of the sexually mature porcine testes. PLoS ONE 7:e34770
Liu WM, Pang RT, Chiu PC, Wong BP, Lao K, Lee KF, Yeung WS (2012b) Sperm-borne microRNA-34c is required for the first cleavage division in mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:490–494
Luo LF, Hou CC, Yang WX (2016) Small non-coding RNAs and their associated proteins in spermatogenesis. Gene 578:141–157
Niu Z, Goodyear SM, Rao S, Wu X, Tobias JW, Avarbock MR, Brinster RL (2011) MicroRNA-21 regulates the self-renewal of mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:12740–12745
Niu B, Wu J, Mu H, Li B, Wu C, He X, Bai C, Li G, Hua J (2016) miR-204 Regulates the proliferation of dairy goat spermatogonial stem cells via targeting to Sirt1. Rejuvenation Res 19:120–130
Quenerch’du E, Anand A, Kai T (2016) The piRNA pathway is developmentally regulated during spermatogenesis in Drosophila. RNA 22:1044–1054
Ran ML, Chen B, Wu MS, Liu XC, He CQ, Yang AQ, Li Z, Xiang YJ, Li ZH, Zhang SW (2015) Integrated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in development of porcine testes. RSC Adv 5: 63439–63449
Ran M, Chen B, Li Z, Wu M, Liu X, He C, Zhang S, Li Z (2016) Systematic identification of long noncoding RNAs in immature and mature porcine testes. Biol Reprod 94:77
Tong MH, Mitchell D, Evanoff R, Griswold MD (2011) Expression of Mirlet7 family microRNAs in response to retinoic acid-induced spermatogonial differentiation in mice. Biol Reprod 85:189–197
Wang L, Feng Z, Wang X, Wang X, Zhang X (2010) DEGseq: an R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 26:136–138
Watanabe T, Lin H (2014) Posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression by Piwi proteins and piRNAs. Mol Cell 56:18–27
Wu J, Bao J, Wang L, Hu Y, Xu C (2011) MicroRNA-184 downregulates nuclear receptor corepressor 2 in mouse spermatogenesis. BMC Dev Biol 11:64
Yamtich J, Heo SJ, Dhahbi J, Martin DI, Boffelli D (2015) piRNA-like small RNAs mark extended 3′UTRs present in germ and somatic cells. BMC Genomics 16:462
Yang Q, Hua J, Wang L, Xu B, Zhang H, Ye N, Zhang Z, Yu D, Cooke HJ, Zhang Y et al (2013a) MicroRNA and piRNA profiles in normal human testis detected by next generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 8:e66809
Yang QE, Racicot KE, Kaucher AV, Oatley MJ, Oatley JM (2013b) MicroRNAs 221 and 222 regulate the undifferentiated state in mammalian male germ cells. Development 140: 280–290
Yu M, Mu H, Niu Z, Chu Z, Zhu H, Hua J (2014) miR-34c enhances mouse spermatogonial stem cells differentiation by targeting Nanos2. J Cell Biochem 115:232–242
Zhang Y, Wang X, Kang L (2011) A k-mer scheme to predict piRNAs and characterize locust piRNAs. Bioinformatics 27:771–776
Zhang S, Yu M, Liu C, Wang L, Hu Y, Bai Y, Hua J (2012) MIR-34c regulates mouse embryonic stem cells differentiation into male germ-like cells through RARg. Cell Biochem Funct 30:623–632
Zhang S, Zhang Y, Yang C, Zhang W, Ju Z, Wang X, Jiang Q, Sun Y, Huang J, Zhong J et al (2015a) TNP1 functional SNPs in bta-miR-532 and bta-miR-204 target sites are associated with semen quality traits in Chinese holstein bulls. Biol Reprod 92:139
Zhang X, Li C, Liu X, Lu C, Bai C, Zhao Z, Sun B (2015b) Differential expression of miR-499 and validation of predicted target genes in the testicular tissue of swine at different developmental stages. DNA Cell Biol 34:464–469
Zhou L, Chen J, Li Z, Li X, Hu X, Huang Y, Zhao X, Liang C, Wang Y, Sun L et al (2010) Integrated profiling of microRNAs and mRNAs: microRNAs located on Xq27.3 associate with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 5:e15224
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by China Agriculture Research System (CARS-36), Hunan Provincial Innovation Foundation for Postgraduate (CX2015B251) and Excellent Doctoral Dissertation Cultivating Fund of Hunan Agricultural University (YB2015001).
Author contributions
BW, MR and BC conceived and designed the experiments. BW, MR, BC, MW, FP, LD, CH, SZ, ZL performed the experiments. BW and MR analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript. Authors would like to thank JY for critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Bo Weng declares that he/she does not have conflict of interest. Maoliang Ran declares that he/she does not have conflict of interest. Bin Chen declares that he/she does not have conflict of interest. Maisheng Wu declares that he/she does not have conflict of interest. Fuzhi Peng declares that he/she does not have conflict of interest. Lianhua Dong declares that he/she does not have conflict of interest. Changqing He declares that he/she does not have conflict of interest. Shanwen Zhang declares that he/she does not have conflict of interest. Zhaohui Li declares that he/she does not have conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Animals care was performed in accordance with the guidelines of the declaration of Helsinki. All experimental protocols were approved by the animal welfare committee of College of Animal Science and Technology, Hunan Agriculture University, Changsha city, Hunan province, P. R. China.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weng, B., Ran, M., Chen, B. et al. Systematic identification and characterization of miRNAs and piRNAs from porcine testes. Genes Genom 39, 1047–1057 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-017-0573-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-017-0573-0