Abstract
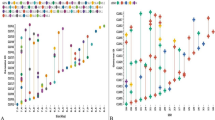
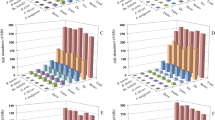
Microsatellites are small repetitive sequences found in all kingdoms of life including viruses. Members of the Tombusviridae family severely affect growth of wide range of plants and reduce economic yield in diverse cropping systems worldwide. Here, we analyzed the nature and distribution of both simple and complex microsatellites present in complete genome of 47 species of Tombusviridae family. Our results showed, in all analyzed genomes, genome size and GC content had a weak influence on number, relative abundance and relative density of microsatellites, respectively. For each genome, dinucleotide repeats followed by mononucleotide repeats were found to be highly predominant. Mononucleotide repeats were found to be underrepresented in majority of Tombusviridae genomes. Poly G and Poly C repeats were more abundant as compared to poly A or poly T nucleotides. TG/GT and AG/CA was the most abundant dinucleotide repeat motif observed in Tombusviridae genomes. Repeats larger than trinucleotide were never found in these viral genomes. Comparative study of relative abundance and density of microsatellite among available RNA and DNA viral genomes indicated that simple repeats were lower than many RNA virus genomes. To our knowledge, this is the first analysis of microsatellites occurring in Tombusviridae genomes. Characterization of such variations in repeat sequences would be important in deciphering the origin, mutational processes, and role of repeat sequences in viral genomes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam CM, George B, Sharfuddin C, Jain SK, Chakraborty S (2013) Occurrence and analysis of imperfect microsatellites in diverse potyvirus genomes. Gene 521:238–244
Benet A, Mollà G, Azorín F (2000) Microsatellite DNA sequences enhance homologous DNA recombination in SV40 minichromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28:4617–4622
Boyko A, Kathiria P, Zemp FJ, Yao Y, Pogribny I, Kovalchuk I (2007) Transgenerational changes in the genome stability and methylation in pathogen-infected plants: (virus-induced plant genome instability). Nucleic Acids Res 35:1714–1725
Chen M, Tan Z, Jiang J, Li M, Chen H, Shen G, Yu R (2009) Similar distribution of simple sequence repeats in diverse completed Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 genomes. FEBS Lett 583:2959–2963
Chen M, Zeng G, Tan Z, Jiang M, Zhang J, Zhang C, Lu L, Lin Y, Peng J (2011) Compound microsatellites in complete Escherichia coli genomes. FEBS Lett 585:1072–1076
Chen M, Tan Z, Zeng G, Zhuotong Z (2012) Differential distribution of compound microsatellites in various Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 complete genomes. Infect Genet Evol 12:1452–1457
Coenye T, Vandamme P (2005) Characterization of mononucleotide repeats in sequenced prokaryotic genomes. DNA Res 12:221–233
Davis CL, Field D, Metzgar D, Saiz R, Morin PA, Smith IL, Spector SA, Wills C (1999) Numerous length polymorphisms at short tandem repeats in human cytomegalovirus. J Virol 73:6265–6270
De wachter R (1981) The number of repeats expected in random nucleic acid sequences and found in genes. J Theor Biol 91:71–98
Deback C, Boutolleau D, Depienne C, Luyt CE, Bonnafous P, Gautheret-Dejean A, Garrigue I, Agut H (2009) Utilization of microsatellite polymorphism for differentiating herpes simplex virus type 1 strains. J Clin Microbiol 47:533–540
Dieringer D, Schlotterer C (2003) Two distinct modes of microsatellite mutation processes: evidence from the complete genomic sequences of nine species. Genome Res 13:2242–2251
Duffy S, Holmes EC (2008) Phylogenetic evidence for rapid rates of molecular evolution in the single-stranded DNA begomovirus tomato yellow leaf curl virus. J Virol 82:957–965
Ellegren H (2004) Microsatellites: simple sequences with complex evolution. Nat Rev Genet 5:435–445
George B, Mashhood AC, Jain SK, Sharfuddin C, Chakraborty S (2012) Differential distribution and occurrence of simple sequence repeats in diverse geminivirus genomes. Virus Genes 45:556–566
George B, Gnanasekaran P, Jain SK, Chakraborty S (2014) Genome wide survey and analysis of small repetitive sequences in caulimoviruses. Infect Genet Evol 27:15–24
Groisman EA, Casadesu´s J (2005) The origin and evolution of human pathogens. Mol Microbiol 56:1–7
Gur-Arie R, Cohen CJ, Eitan Y (2000) Simple sequence repeats in Escherichia coli: abundance, distribution, composition, and polymorphism. Genome Res 10:62–71
Hull R (2002) Matthews’ plant virology. Academic Press, San Diego
Jiwan SD, White KA (2011) Subgenomic mRNA transcription in Tombusviridae RNA Biol 8:287–294
Karaoglu H, Lee CM, Meyer W (2005) Survey of simple sequence repeats in completed fungal genomes. Mol Biol Evol 22:639–649
Kashi Y, King DG (2006) Simple sequence repeats as advantageous mutators in evolution. Trends Genet 22:253–259
Kashi Y, King D, Soller M (1997) Simple sequence repeats as a source of quantitative genetic variation. Trends Genet 13:74–78
Kathiria P, Golubov A, Sidler C, Kalischuk M, Kawchuk LM, Kovalchuk I (2010) Tobacco mosaic virus infection results in an increase in recombination frequency and resistance to viral, bacterial and fungal pathogens in the progeny of infected tobacco plants. Plant Physiol 153:1859–1870
Kelkar YD, Tyekucheva S, Chiaromonte F, Makova KD (2008) The genome-wide determinants of human and chimpanzee microsatellite evolution. Genome Res 18:30–38
Kofler R, Schlotterer C, Luschutzky E, Lelley T (2008) Survey of microsatellite clustering in eight fully sequenced species sheds light on the origin of compound microsatellites. BMC Genom 9:612
Kovalchuk I, Kovalchuk O, Kalck V, Boyko V, Filkowski J, Heinlein M, Hohn B (2003) Pathogen-induced systemic plant signal triggers DNA rearrangements. Nature 423:760–762
Kumari P, Singh AK, Chattopadhyay B, Chakraborty S (2011) A new begomovirus species and betasatellite causing severe tomato leaf curl disease in Ranchi, India. New Dis Rep 23:11
Li YC, Korol AB, Fahima T, Nevo E (2004) Microsatellites within genes: structure, function, and evolution. Mol Biol Evol 21:991–1007
Metzgar D, Bytof J, Wills C (2000) Selection against frame shift mutations limits microsatellite expansion in coding DNA. Genome Res 10:72–80
Morgante M, Hanafey M, Powell W (2002) Microsatellites are preferentially associated with nonrepetitive DNA in plant genomes. Nat Genet 30:194–200
Mrazek J (2006) Analysis of distribution indicates diverse functions of simple sequence repeats in Mycoplasma genomes. Mol Biol Evol 23:1370–1385
Mudunuri SB, Nagarajaram HA (2007) IMEx: imperfect microsatellite extractor. Bioinformatics 23:1181–1187
Murphy KE, Stringer JR (1986) RecA independent recombination of poly[d(GT)-d(CA)] in pBR322. Nucleic Acids Res 14:7325–7340
Napierala M, Parniewski P, Pluciennik A, Wells RD (2002) Long CTG.CAG repeat sequences markedly stimulate intramolecular recombination. J Biol Chem 277:34087–34100
Napierala M, Dere R, Vetcher A, Wells RD (2004) Structure-dependent recombination hot spot activity of GAA.TTC sequences from intron 1 of the Friedreich’s ataxia gene. J Biol Chem 279:6444–6454
Padidam M, Sawyer S, Fauquet CM (1999) Possible emergence of new geminiviruses by frequent recombination. Virology 265:218–225
Pauli S, Rothnie HM, Chen G, He X, Hohn T (2004) The cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter extends into the transcribed region. J Virol 78:12120–12128
Sawaya SM, Bagshaw AT, Buschiazzo E, Gemmell NJ (2012) Promoter microsatellites as modulators of human gene expression. Adv Exp Med Biol 769:41–54
Alam CM, Singh, AK, Sharfuddin C, Ali S (2014) Genome-wide scan for extraction and analysis of simple and imperfect microsatellites in diverse carlaviruses. Infect Genet Evol 21:287–294 (ISSN: 1567–1348)
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
Toth G, Gáspári X, Jurka J (2000) Microsatellites in different eukaryotic genomes: survey and analysis. Genome Res 10:967–981
Usdin K (2008) The biological effects of simple tandem repeats: lessons from the repeat expansion diseases. Genome Res 18:1011–1019
Vinces MD, Legendre M, Caldara M, Hagihara M, Verstrepen KJ (2009) Unstable tandem repeats in promoters confer transcriptional resolvability. Science 324:1213–1216
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Blessy software solution for support.
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest regarding this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
George, B., George, B., awasthi, M. et al. Genome wide survey and analysis of microsatellites in Tombusviridae family. Genes Genom 37, 657–667 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-015-0295-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-015-0295-0