Abstract
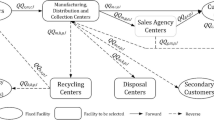
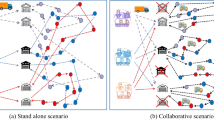
The current paper aims to design a closed-loop supply chain network which maximizes the productivity and the asset recovery by focusing on the location-routing decisions. A practical network is presented using quality-based routing and segmentation policies. Moreover, a novel social index is provided based on the sustainability reporting guidelines. The forward chain includes the manufacturers, the depots, the distributors and the customers. In the backward chain, the distributers collect and sort the returns into three groups to be sent out either to the emerging markets, the decomposition centre or the secondary chain facility. The resultant model is then validated and tested via a numerical example under the different scenarios from single-objective and multiple-objective approaches. A comprehensive analysis is presented to test the impacts of the return rates, the location of the receiver facility, and the transport fleet. The results show the effectiveness of the model under different scenarios.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amirian H, Sahraeian R (2015) Augmented ε-constraint method in multi-objective flowshop problem with past sequence set-up times and a modified learning effect. Int J Prod Res 53:5962–5976
Banasik A, Kanellopoulos A, Claassen GDH, Bloemhof-Ruwaard JM, van der Vorst JGAJ (2017) Closing loops in agricultural supply chains using multi-objective optimization: A case study of an industrial mushroom supply chain. Int J Prod Econ 183:409–420
Bhattacharjee S, Cruz J (2015) Economic sustainability of closed loop supply chains: A holistic model for decision and policy analysis. Decis Support Syst 77:67–86
Dempsey N, Bramley G, Power S, Brown C (2011) The social dimension of sustainable development: Defining urban social sustainability. Sustain Dev 19:289–300
Deng S, Li Y, Guo H, Liu B (2016) Solving a closed-loop location-inventory-routing problem with mixed quality defects returns in E-commerce by hybrid ant colony optimization algorithm. Discret Dyn Nat Soc 2016:1–12
Flapper SD, Van Nunen J, Van Wassenhove LN (2006) Managing closed-loop supply chains. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg
Garg K, Kannan D, Diabat A, Jha PC (2015) A multi-criteria optimization approach to manage environmental issues in closed loop supply chain network design. J Clean Prod 100:297–314
Giri BC, Sharma S (2015) Optimizing a closed-loop supply chain with manufacturing defects and quality dependent return rate. J Manuf Syst 35:92–111
Govindan K, Jafarian A, Khodaverdi R, Devika K (2014) Two-echelon multiple-vehicle location–routing problem with time windows for optimization of sustainable supply chain network of perishable food. Int J Prod Econ 152:9–28
Govindan K, Soleimani H (2017) A review of reverse logistics and closed-loop supply chains: A Journal of Clean Production focus. J Clean Prod 142:371–384
Kaya O, Urek B (2016) A mixed integer nonlinear programming model and heuristic solutions for location, inventory and pricing decisions in a closed loop supply chain. Comput Oper Res 65:93–103
Li X, Wang D, Li K, Gao Z (2013) A green train scheduling model and fuzzy multi-objective optimization algorithm. Appl Math Model 37:2063–2073
Li Y, Guo H, Wang L, FU J (2013) A hybrid genetic-simulated annealing algorithm for the location-inventory-routing problem considering returns under E-supply chain environment. ScientificWorldJournal 2013:1–10
Martínez-Salazar IA, Molina J, Ángel-Bello F, Gómez T, Caballero R (2014) Solving a bi-objective transportation location routing problem by metaheuristic algorithms. Eur J Oper Res 234:25–36
Masoudipour E, Amirian H, Sahraeian R (2017) A novel closed-loop supply chain based on the quality of returned products. J Clean Prod 151:344–355
Mavrotas G (2009) Effective implementation of the ε-constraint method in multi-objective mathematical programming problems. Appl Math Comput 213:455–465
Moshtagh MS, Taleizadeh AA (2017) Stochastic integrated manufacturing and remanufacturing model with shortage, rework and quality based return rate in a closed loop supply chain. J Clean Prod 141:1548–1573
Pedram A, Yusoff NB, Udoncy OE, Mahat AB, Pedram P, Babalola A (2017) Integrated forward and reverse supply chain: A tire case study. Waste Manag 60:460–470
Pishvaee MS, Farahani RZ, Dullaert W (2010) A memetic algorithm for bi-objective integrated forward/reverse logistics network design. Comput Oper Res 37:1100–1112
Prodhon C, Prins C (2014) A survey of recent research on location-routing problems. Eur J Oper Res 238:1–17
Shaharudin MR, Govindan K, Zailani S, Tan KC, Iranmanesh M (2017) Product return management: Linking product returns, closed-loop supply chain activities and the effectiveness of the reverse supply chains. J Clean Prod 149:1144–1156
Soysal M (2016) Closed-loop inventory routing problem for returnable transport items. Transport Res D-TR E 48:31–45
Strozzilaan B (2017) G4 sustainability reporting guidelines. https://www.globalreporting.org/information/g4/Pages/default.aspx. Accessed 3 September 2017
Sundin E, Bras B (2005) Making Functional Sales Environmentally and Economically Beneficial through Product Remanufacturing. J Clean Prod 13:913–925
Wei S, Tang O, Sundin E (2015) Core (product) Acquisition Management for remanufacturing: a review. J Remanuf 5:4
Wong CWY, Lai K, Lun YHV, Cheng TCE (2015) Environmental management: The supply chain perspective. Springer International Publishing, Cham
Yadegari E, Najmi H, Ghomi-Avili M, Zandieh M (2015) A flexible integrated forward/reverse logistics model with random path-based memetic algorithm. Iranian J Manag Studies 8:287–313
Zhalechian M, Tavakkoli-Moghaddam R, Zahiri B, Mohammadi M (2016) Sustainable design of a closed-loop location-routing-inventory supply chain network under mixed uncertainty. Transport Res E-Log 89:182–214
Acknowledgements
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
In this section, the optimal solutions of the numerical example in section “Single-objective scenarios” are summarized in Tables 14 and 15.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masoudipour, E., Jafari, A., Amirian, H. et al. A novel transportation location routing network for the sustainable closed-loop supply chain considering the quality of returns. Jnl Remanufactur 10, 79–106 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13243-019-00075-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13243-019-00075-6