Abstract
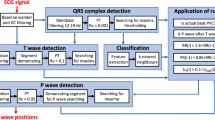
We present a novel wavelet-based ECG delineation method with robust classification of P wave and T wave. The work is aimed on an adaptation of the method to long-term experimental electrograms (EGs) measured on isolated rabbit heart and to evaluate the effect of global ischemia in experimental EGs on delineation performance. The algorithm was tested on a set of 263 rabbit EGs with established reference points and on human signals using standard Common Standards for Quantitative Electrocardiography Standard Database (CSEDB). On CSEDB, standard deviation (SD) of measured errors satisfies given criterions in each point and the results are comparable to other published works. In rabbit signals, our QRS detector reached sensitivity of 99.87% and positive predictivity of 99.89% despite an overlay of spectral components of QRS complex, P wave and power line noise. The algorithm shows great performance in suppressing J-point elevation and reached low overall error in both, QRS onset (SD = 2.8 ms) and QRS offset (SD = 4.3 ms) delineation. T wave offset is detected with acceptable error (SD = 12.9 ms) and sensitivity nearly 99%. Variance of the errors during global ischemia remains relatively stable, however more failures in detection of T wave and P wave occur. Due to differences in spectral and timing characteristics parameters of rabbit based algorithm have to be highly adaptable and set more precisely than in human ECG signals to reach acceptable performance.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addison, P. S. Wavelet transforms and the ECG: a review. Physiol. Meas. 26:155–199, 2005.
Alvarado, C., J. Arregui, J. Ramos, and R. Pallas-Areny. Automatic detection of ECG ventricular activity waves using continuous spline wavelet transform. In: 2005 2nd International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (Cie), 2005, pp. 189–192.
Bell, R. M., M. M. Mocanu, and D. M. Yellon. Retrograde heart perfusion: the Langendorff technique of isolated heart perfusion. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 50:940–950, 2011.
Bustamante, C. A., S. I. Duque, A. Orozco-Duque, and J. Bustamante. ECG delineation and ischemic ST-segment detection based in wavelet transform and support vector machines. In: 2013 Pan American Health Care Exchanges (PAHCE), 2013, pp. 1–7.
Chouhan, V. S., and S. S. Mehta. Detection of QRS complexes in 12-lead ECG using adaptive quantized threshold. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 8:155–163, 2008.
Chouhan, V. S., S. S. Mehta, and N. S. Lingayat. Delineation of QRS-complex, P and T-wave in 12-lead ECG. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 8:185–190, 2008.
Di Marco, L. Y., and L. Chiari. A wavelet-based ECG delineation algorithm for 32-bit integer online processing. Biomed. Eng. Online 10:23, 2011.
Ghaffari, A., M. R. Homaeinezhad, M. Akraminia, M. Atarod, and M. Daevaeiha. A robust wavelet-based multi-lead electrocardiogram delineation algorithm. Med. Eng. Phys. 31:1219–1227, 2009.
Go, A. S., D. Mozaffarian, and V. L. Roger. Heart disease and stroke statistics 2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 127:e6–e245, 2013.
Graja, S., and J. M. Boucher. Hidden Markov tree model applied to ECG delineation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 54:2163–2168, 2005.
Hamilton, P. Open source ECG analysis. Comput. Cardiol. 2002:101–104, 2002.
Kolarova, J., and M. Novakova. Isolated rabbit hearts—databases of EGs and MAP signals. Comput. Cardiol. 2013:551–554, 2013.
Laguna, P., R. G. Mark, A. Goldberg, and G. B. Moody. A database for evaluation of algorithms for measurement of QT and other waveform intervals in the ECG. Comput. Cardiol. 1997:673–676, 1997.
Laguna, P., D. Vigo, R. Jane, and P. Caminal. Automatic wave onset and offset determination in ECG signals: validation with the CSE database. In: Proceedings of Computers in Cardiology, 1992, pp. 167–170.
Langendorff, O. Untersuchungen am überlebenden Säugethierherzen. Arch für die gesamte Physiol des Menschen und der Tiere 61:291–332, 1895.
Li, C., C. Zheng, and C. Tai. Detection of ECG characteristic points using wavelet transforms. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 42:21–28, 1995.
Lin, C., C. Mailhes, and J.-Y. Tourneret. P- and T-wave delineation in ECG signals using a Bayesian approach and a partially collapsed Gibbs sampler. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 57:2840–2849, 2010.
Mallat, S. Zero-crossings of a wavelet transform. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 37:1019–1033, 1991.
Martinez, A., R. Alcaraz, and J. J. Rieta. Application of the phasor transform for automatic delineation of single-lead ECG fiducial points. Physiol. Meas. 31:1467–1485, 2010.
Martínez, J. P., R. Almeida, S. Olmos, A. P. Rocha, and P. Laguna. A wavelet-based ECG delineator: evaluation on standard databases. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 51:570–581, 2004.
Mehta, S. S. and N. S. Lingayat. Detection of P and T-waves in electrocardiogram. In: Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering and Computer Science, 2008, pp. 978–984.
Mehta, S. S., and N. S. Lingayat. Identification of QRS complexes in 12-lead electrocardiogram. Expert Syst. Appl. 36:820–828, 2009.
Moody GB, Mark RG. The MIT-BIH arrhythmia database on CD-ROM and software for use with it. In: Proceedings of Computers in Cardiology, 1990, pp. 185–188.
Pan, J., and W. J. Tompkins. A real-time QRS detection algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 32:230–236, 1985.
Sahambi, J. S., S. N. Tandon, and R. K. P. Bhatt. Using wavelet transforms for ECG characterization. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 16:77–83, 1997.
Soria, M. L., J. P. Martinez, and P. Laguna. A multilead wavelet-based ECG delineator based on the RMS signal. Comput. Cardiol. 2006:153–156, 2006.
Vitek, M., J. Hrubes, and J. Kozumplik. A wavelet-based ECG delineation with improved P wave offset detection accuracy. Anal. Biomed. Signals Images 20:1–6, 2010.
Vitek, M., J. Hrubes, and J. Kozumplik. A wavelet-based ECG delineation in multilead ECG signals: evaluation on the CSE database. IFBME Proc. 25:177–180, 2010.
Willems, J. L., P. Arnaud, J. H. Van Bemmel, P. J. Bourdillon, R. Degani, B. Denis, I. Graham, F. M. Harms, P. W. Macfarlane, G. Mazzocca, J. Meyer, and C. Zywietz. A reference data base for multilead electrocardiographic computer measurement programs. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 10:1313–1321, 1987.
Willems, J. L., P. Arnaud, J. H. van Bemmel, R. Degani, P. W. Macfarlane, and C. Zywietz. Common standards for quantitative electrocardiography: goals and main results. CSE Working Party. Methods Inf. Med. 29:263–271, 1990.
Acknowledgment
The work was supported by European Regional Development Fund-Project FNUSA-ICRC (No. CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0123), grant projects of the Grant Agency GACR 102/12/2034, and MUNI/A/0957/2013.
Conflict of interest
Author Hejc, author Vitek, author Ronzhina, author Novakova, and Author Kolarova declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of human studies
This manuscript does not contain any studies with human subjects performed by any of the authors.
Statement of animal studies
All animal experiments were carried out with respect to the recommendations of the European Community Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and followed the guidelines for animal treatment approved by local authorities. All animal experiments were approved by the appropriate institutional committees.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Ajit P. Yoganathan oversaw the review of this article.
Appendix
Appendix
In this section, we present some of important formulas which were stated, but not specifically defined, above in order to maintain clarity of the article. Constants that correspond to human-based algorithm are stated in parenthesis and vice versa. Main group contains formulas used to calculate various types of thresholds. Constants used in calculation of P wave and T wave detection time windows are listed in Table 3.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hejč, J., Vítek, M., Ronzhina, M. et al. A Wavelet-Based ECG Delineation Method: Adaptation to an Experimental Electrograms with Manifested Global Ischemia. Cardiovasc Eng Tech 6, 364–375 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13239-015-0224-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13239-015-0224-z