Abstract
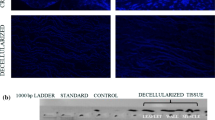
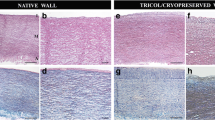
Decellularized allografts are promising options for pediatric valve replacement due to reduced immunogenicity and the potential for in vivo autologous recellularization, extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling and re-endothelialization, which may be enhanced with post-decellularization processing steps. This study investigated the performance and morphology of decellularized and ECM conditioned pulmonary valves implanted in the right ventricular outflow tracts (RVOT) of juvenile sheep. RVOT reconstructions in juvenile sheep using cryopreserved pulmonary allografts (Cryo; n = 2), porcine aortic root bioprostheses (Biopros; n = 2) or decellularized/ECM conditioned pulmonary allografts (Conditioned; n = 4) were performed. Valve performance and morphology were evaluated at 20 weeks after implant. Uniaxial tensile testing was performed on a subset of unimplanted valves from each group. At explant, Biopros had significantly higher peak/mean gradients vs. Conditioned and Cryo, which were similar. No cusp calcification occurred in any valve; arterial wall calcification was present only in Cryo (mild/moderate) and Biopros (severe). No autologous recellularization or inflammation occurred in Biopros; cellularity was decreased in Cryo. Autologous recellularization was present in Conditioned arterial walls and variably extending into the cusps, with consistent cusp re-endothelialization. Conditioned valves had reduced cusp extensibility, increased stiffness and similar tensile strength vs. Cryo. Although Conditioned valves were slightly stiffer and less extensible than Cryo valves, their hemodynamic performance was comparable, indicating they behave as functional heart valves immediately following implant. Because both autologous recellularization and re-endothelialization were seen, ECM conditioning shows promise for encouraging renewal of the cellularity of decellularized allograft valves without the need for pre-implant endothelial cell seeding.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almond, A. Hyaluronin. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 64:1591–1596, 2007.
Bader, A., T. Schilling, O. E. Teebken, G. Brandes, T. Herden, G. Steinhoff, and A. Haverich. Tissue engineering of heart valves—human endothelial cell seeding of detergent acellularized porcine valves. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 14(3):279–284, 1998.
Baraki, H., I. Tudorache, M. Braun, K. Hoffler, A. Gorler, A. Lichtenberg, C. Bara, A. Calistru, A. Brandeis, M. Hewicker-Trautwein, A. Hilfiker, A. Haverich, and S. Cebotari. Orthotopic replacement of the aortic valve with decellularized allograft in a sheep mode. Biomaterials 30:6240–6246, 2009.
Bechtel, J. F. M., M. Muller-Steinhardt, C. Schmidtke, A. Brunswik, U. Stierle, and H. H. Sievers. Evaluation of the decellularized pulmonary homograft (SynerGraft). J. Heart Valve Dis. 12:734–740, 2003.
Bertipaglia, B., F. Ortolani, L. Petrelli, G. Gerosa, M. Spina, P. Pauletto, D. Casarotto, M. Marchini, and S. Sartore. Cell characterization of porcine aortic valve and decellularized leaflets repopulated with aortic valve interstitial cells: the VESALIO Project (Vitalitate Exornatum Succedaneum Aorticum Labore Ingenioso Obtenibitur). Ann. Thorac. Surg. 75:1274–1282, 2003.
Dohmen, P. M., F. da Costa, S. V. Lopes, S. Yoshi, F. P. da Souza, R. Vilani, M. B. da Costa, and W. Konertz. Results of a decellularized porcine heart valve implanted into the juvenile sheep model. Heart Surg. Forum 8(2):E100–E104, 2005.
Dohmen, P. M., F. da Costa, S. Yoshi, S. V. Lopes, F. P. da Souza, R. Vilani, A. F. Wouk, M. da Costa, and W. Konertz. Histological evaluation of tissue-engineered heart valves implanted in the juvenile sheep model: is there a need for in vitro seeding? J Heart Valve Dis. 15:823–829, 2006.
Donati, A., A. Magnani, C. Bonechi, R. Barbucci, and C. Rossi. Solution structure of hyaluronic acid oligomers by experimental and theoretical NMR and molecular dynamics simulation. Biopolymers 59:434–445, 2001.
Elkins, R. C., P. E. Dawson, S. Goldstein, S. P. Walsh, and K. S. Black. Decellularized human valve allografts. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 71:S428–S432, 2001.
Elkins, R. C., S. Goldstein, C. W. Hewett, S. P. Walsh, P. E. Dawson, J. D. Ollerenshaw, K. S. Black, D. R. Clarke, and M. O’Brien. Recellularization of heart valve grafts by a process of adaptive remodeling. Sem. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 13:87–92, 2001.
Erdbrugger, W., W. Konertz, P. M. Dohmen, S. Posner, H. Ellerbrok, O. Brodde, H. Robenek, D. Modersohn, A. Pruss, S. Holinski, M. Stein-Konertz, and G. Pauli. Decellularized xenogenic heart valves reveal remodeling and growth potential in vivo. Tissue Eng. 12:2059–2068, 2006.
Fischlein, T., G. Lehner, W. Lante, M. Fittkau, J. G. Murphy, C. H. Weinhold, and B. Reichart. Endothelialization of cardiac valve bioprostheses. Int. J. Artif. Organs. 17(6):345–352, 1994.
Gilbert, T. W., T. L. Sellaro, and S. F. Badylak. 2006. Decellularization of tissues and organs. Biomaterials 27:3675–3683, 2006.
Gui, L., S. A. Chan, C. K. Breuer, and L. E. Niklason. Novel utilization of serum in tissue decellularization. Tissue Eng. 16(2):173–184, 2010.
Gulbins, H., A. Goldemund, A. Uhlig, A. Pritisanac, B. Meiser, and B. Reichart. Implantation of an autologously endothelialized homograft. J. Thorasc. Cardiovasc. Surg. 126(3):890–891, 2003.
Hawkins, J. A., J. P. Breinholt, L. M. Lambert, et al. Class I and class II anti-HLA antibodies after implantation of cryopreserved allograft material in pediatric patients. J. Thorasc. Cardiovasc. Surg. 119(2):324–330, 2000.
Haycock, G. B., G. J. Schwartz, and D. H. Wisotsky. Geometric method for measuring body surface area: a height-weight formula validated in infants, children and adults. J. Pediatr. 93:62–66, 1978.
Hilbert, S. L., R. Yanagida, J. Souza, L. Wolfinbarger, A. L. Jones, P. Kreuger, G. Stearns, A. A. Bert, and R. A. Hopkins. Prototype anionic detergent technique used to decellularize allograft valve conduits evaluated in the right ventricular outflow tract in sheep. J. Heart Valve Dis. 13:831–840, 2004.
Hoerstrup, S. P., A. Kadner, S. Melnitchouk, A. Trojan, K. Eid, J. Tracy, R. Sodian, J. F. Visjager, S. A. Kolb, J. Grunenfelder, G. Zund, and M. I. Turina. Tissue engineering of functional trileaflet heart valves from human marrow stromal cells. Circulation 106(12 Suppl 1):143–150, 2002.
Hoerstrup, S. P., R. Sodian, S. Daebritz, J. Wang, E. A. Bacha, D. P. Martin, A. M. Moran, K. J. Guleserian, J. S. Sperling, S. Kaushal, J. P. Vacanti, F. J. Schoen, and J. E. Mayer Jr. Functional living trileaflet heart valves grown in vitro. Circulation 102(19 Suppl 3):44–49, 2000.
Honge, J. L., J. Funder, E. Hansen, P. M. Dohmen, W. Konertz, and J. M. Hasenkam. Recellularization of aortic valves in pigs. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 39:829–834, 2011.
Hopkins, R. A., A. L. Jones, L. Wolfinbarger, M. A. Moore, A. A. Bert, and G. K. Lofland. Decellularization reduces calcification while improving both durability and 1-year functional results of pulmonary homograft valves in juvenile sheep. J. Thorasc. Cardiovasc. Surg. 137:907–913, 2009.
Knight, R. L., C. Booth, H. E. Wilcox, J. Fisher, and E. Ingham. Tissue engineering of cardiac valves: re-seeding of acellular porcine aortic valve matrices with human mesenchymal progenitor cells. J. Heart Valve Dis. 14:806–813, 2005.
Knight, R. L., H. E. Wilcox, S. A. Korossis, J. Fisher, and E. Ingham. The use of acellular matrices for the tissue engineering of cardiac valves. Proc. IMechE Part H: J. Eng. Med. 222:129–143, 2008.
Korossis, S. A., C. Booth, H. E. Wilcox, K. G. Watterson, J. N. Kearney, J. Fisher, and E. Ingham. Tissue engineering of cardiac valve prostheses II: biomechanical characterization of decellularized porcine aortic valves. J. Heart Valve Dis. 11:463–471, 2002.
Liao, J., E. M. Joyce, and M. S. Sacks. Effects of decellularization on the mechanical and structural properties of the porcine aortic valve leaflet. Biomaterials 29:1065–1074, 2008.
Meyer, S. R., B. Chiu, T. A. Churchill, L. Zhu, J. R. T. Lakey, and D. B. Ross. Comparison of aortic valve allograft decellularization techniques in the rat. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 79A:254–262, 2006.
Meyer, S. R., J. Nagendran, L. S. Desai, G. R. Rayat, T. A. Churchill, C. C. Anderson, R. V. Rajotte, J. R. T. Lakey, and D. B. Ross. Decellularization reduces the immune response to aortic valve allografts in the rat. J. Thorasc. Cardiovasc. Surg. 130:469–476, 2005.
Nimni, M. E., D. Cheung, B. Strates, M. Kodama, and K. Sheikh. Chemically modified collagen: a natural biomaterial for tissue replacement. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 21(6):741–771, 1987.
O’Brien, M. F., S. Goldstein, S. Walsh, K. S. Black, R. Elkins, and D. Clarke. The SynerGraft valve: a new acellular (nonglutaraldehyde-fixed) tissue heart valve for autologous recellularization first experimental studies before clinical implantation. Sem. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 11(4):194–200, 1999.
Quinn, R. W., S. L. Hilbert, A. A. Bert, B. W. Drake, J. A. Bustamante, J. E. Fenton, S. J. Moriarty, S. L. Neighbors, G. K. Lofland, and R. A. Hopkins. Performance and morphology of decellularized pulmonary valves implanted in juvenile sheep. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 92:131–137, 2011.
Rajani, B., R. B. Mee, and N. B. Ratliff. Evidence for rejection of homograft cardiac valves in infants. J. Thorasc. Cardiovasc. Surg. 115:111–117, 1998.
Rieder, E., M. T. Kasimir, G. Silberhumer, G. Seebacher, E. Wolner, P. Simon, and G. Weigel. Decellularization protocols of porcine heart valves differ importantly in efficiency of cell removal and susceptibility of the matrix to recellularization with human vascular cells. J. Thorasc. Cardiovasc. Surg. 127:399–405, 2004.
Sales, V. L., B. A. Mettler, G. C. Engelmayr, E. Aikawa, J. Bischoff, D. P. Martin, A. Exarhopoulos, M. A. Moses, F. Schoen, M. S. Sacks, and J. E. Mayer. Endothelial progenitor cells as a sole source for ex vivo seeding of tissue-engineered heart valves. Tissue Eng. A. 16(1):257–267, 2010.
Schenke-Layland, K., O. Vasilevski, F. Opitz, K. Konig, I. Riemann, K. J. Halbhuber, T. Whalers, and U. A. Stock. Impact of decellularization of xenogenic tissue on extracellular matrix integrity for tissue engineering of heart valves. J. Struct. Biol. 143:201–208, 2003.
Seebacher, G., C. Grasl, M. Stoiber, E. Rieder, M. Kasimir, D. Dunkler, P. Simon, G. Weigel, and H. Schima. Biomechanical properties of decellularized porcine pulmonary valve conduits. Artif. Organs. 32:28–35, 2008.
Shinoka, T. Tissue engineered heart valves: autologous cell seeding on biodegradable polymer scaffold. Artif. Organs. 26(5):402–406, 2002.
Spina, M., F. Ortolani, A. El Messelemani, A. Gandaglia, J. Bujan, N. Garcia-Honduvilla, I. Vesely, G. Gerosa, D. Casarotto, L. Petrelli, and M. Marchini. Isolation of intact aortic valve scaffolds for heart-valve bioprostheses: extracellular matrix structure, prevention from calcification and cell repopulation features. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 67A:1338–1350, 2003.
Steinhoff, G., U. Stock, N. Karim, H. Mertsching, A. Timke, R. R. Meliss, K. Pethig, A. Haverich, and A. Bader. Tissue engineering of pulmonary heart valves on allogenic acellular matrix conduits: in vivo restoration of valve tissue. Circulation 102(19 Suppl 3):50–55, 2000.
Tavakkol, Z., S. Gelehrter, C. S. Goldberg, E. L. Bove, E. J. Devaney, and R. G. Ohye. Superior durability of SynerGraft pulmonary allografts compared with standard cryopreserved allografts. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 80:1610–1614, 2005.
Tudorache, I., S. Cebotari, G. Sturtz, L. Kirsch, C. Hurschler, A. Hilfiker, A. Haverich, and A. Lichtenberg. Tissue engineering of heart valves: biomechanical and morphological properties of decellularized heart valves. J. Heart Valve Dis. 16:567–574, 2007.
Vincentelli, A., F. Wautot, F. Juthier, O. Fouquet, D. Corseaux, S. Marechaux, T. Le Tourneau, O. Fabre, S. Susen, E. Van Belle, F. Mouquet, C. Decoene, A. Prat, and B. Jude. In vivo autologous recellularization of a tissue-engineered heart valve: are bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells the best candidates? J. Thorasc. Cardiovasc. Surg. 134(2):424–432, 2007.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the exemplary teamwork and professionalism of the Experimental Cardiac Surgery Team of The Ward Family Center for Congenital Heart Disease: Stacy L. Neighbors, RNFA; Julie Bustamante, RN, CNOR; Jason E. Fenton, RN, MS, CCP; Kellie Merrigan, MPS, CCP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Adrian Chester oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quinn, R.W., Hilbert, S.L., Converse, G.L. et al. Enhanced Autologous Re-endothelialization of Decellularized and Extracellular Matrix Conditioned Allografts Implanted Into the Right Ventricular Outflow Tracts of Juvenile Sheep. Cardiovasc Eng Tech 3, 217–227 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13239-011-0078-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13239-011-0078-y