Abstract
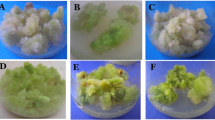
The effect of sodium azide (NaN3) was studied in Psoralea corylifolia L (2n = 22). Three distinct phenotypic variants one at 0.50 % and two at 0.75 % concentrations of NaN3 were selected for analysis. Besides morphological variations in the form of size, height, number of branches, number of flowers and seeds, cytological anomalies in the form of pollen fertility, univalents, multivalents, laggards, bridges, micronuclei, were also observed in all variants and the anomalies showed decreasing order at the final stages of both meiosis and mitosis. These variants were further analysed using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) technique, which differentiated the variants genotypically, on the basis of occurrence of polymorphic DNA bands. The percentage of polymorphism was found to be highest (70 %) using primer OPH-12 followed by OPC-02 having 66.66 % of polymorphism. Among 31 DNA bands 19 were found to be polymorphic which showed great variation created by NaN3 in the genome of the experimental plant. Therefore the above concentrations of sodium azide are best suited for the induction of genetic variations in Psoralea corylifolia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akihiko A, Ricardo M. Gamma-ray radiation and sodium azide (NaN3)mutagenic efficiency in rice. Crop Breeding Applied Biotechnology. 2001;1:339–46.
Al Qurainy F, Khan S. Mutagenic effects of Sodium azide and its application in crop improvement. W ApplSci J. 2009;6:1589–601.
Anand KK, Sharma ML, Singh B. Anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic properties of bavachinin. Flavones isolated from seeds of Psorelea corylifolia. Linn Ind J Exp Biol. 1978;16:1216–9.
Aras S, Duran A, Yenilmez G, Duman DC. Genetic relationships among some HesperisL. (Brassicaceae) species from Turkey assessed by RAPD analysis. African J Biotech. 2009;8:3128–34.
Bhat TA, Khan AH, Parveen S. Comparative analysis of meiotic abnormalities induced by gamma rays, EMS and MMS in Viciafaba L. J Ind Bot Soc. 2005;84:45–8.
Bhat TM, Kudesia R, Srivastav MK, Siddiqui S. Evaluation of variability in five linseed (LinumusitatissimumL.) genotypes using agromorphological characters and RAPD analysis. S Asian J Exp Biol. 2011;1:43–7.
Carovi C, Stanko K, Liber Z, Besendorfer V, Javornik B, Bohanec B, Kolak I, Satovic Z. Genetic relations among basil taxa (OcimumL.) based on molecular markers, nuclear DNA content, and chromosome number. Plant Syst Evol. 2010;285:13–22.
Chandhoke N, Ghatak BJ. Pharmacological investigations of angelicinAtranquillo sedativeand anticonvulsant agent. Ind J Med Resh. 1975;63:833–6.
Chopra RN, Nayar SL, Chopra IC. Glossary of Indian medicinal plants. New Delhi: Council of Scientific and Industrial Research; 1956. p. 206.
Draper J, Scott R. Plant genetic transformation and gene expression, Moscow: Mir Publ (in Russ). 1991.
Gaulden ME. Hypothesis: some mutagens directly alter specific chromosomal proteins thus produce chromosome stickiness. Mutagenesis. 1986;2:357–65.
Geda A, Jain PK, Bokadia MM. Antimicrobial activity of some Indian essential oils. Acta Ciencia Indica. 1978;4:248–51.
George M, Pandalai KM. Investigations on plant antibiotics. Part IV. Further research for antibiotic substances in Indian Medicinal Plants. Ind J Medl Resrh. 1949;37:169–71.
Grover GS, Rao JT. In vitro antimicrobial studies of the essential oil of Psoralea corylifolia. Indian Perfumer. 1979;23:135–9.
Gupta KC, Bhatia MC, Chopra CL, Amar N, Chopra IC. Ant staphylococcal activity of Psoralea corylifolia seed extracts. Bull Reg Res Lab Jammu. 1962;1:59–63.
Kakani KR, Singh SK, Pancholay A, Meena SR, Pathak RA. Assessment of genetic diversity in Trigonellafoenumgraecumbased on nuclear ribosomal DNA, InternaTranscribed Spacer and RAPD analysis. Plant molBiol Rep. 2011;29:315–23.
Khan MH, Tyagi SD. Cytological effects of different mutagens in Soybean (Glycine max). Frontiers Agriculture China. 2009;3:397–401.
Khan Z, Ansari MYK, Gupta H, Choudhary S. Dynamics of 2, 4-D in generation ofcytomorphological variants in an important anticancerous and antihepatotoxic herb-CichoriumintybusL. Turkish J Bot. 2009;33:383–7.
Kumar G, Tripathi A. Mutagenic response of caffeine in Capsicum annum L. J Indian Bot Soc. 2004;83:136–40.
Kumar G, Singh V. Comparative analysis of meiotic abnormalities induced by gamma raysand EMS in Barley. J Indian Bot Soc. 2003;82:19–22.
Kumar OA, Tata SS, Rao KGR. Cytogenetics of a spontaneous fasciated stem mutant of chilli pepper (Capsicum annuumL). Th Jpn Mndl Sty. 2006;71:321–4.
Lewis KR, John B. The meiotic consequences of spontaneous chromosome breakage. Chromosoma. 1966;18:287–304.
Narang GD, Garg LC, Mehta RK. Antibacterial activity of some indigenous drugs. J Veterinary Animal Husb Res. 1962;6:22–5.
Owais WM, Kleinhofs A. Metabolic action of the mutagen Sodium azide in biological systems. Mutation Res. 1988;197:313–22.
Rao GM, Rao VM. Mutagenic efficiency, effectiveness and factor effectiveness of physical and Chemical mutagens in Rice. Cytologia. 1983;48:427–36.
Saghai MA, Soliman KM, Jorgenson RA, Allard RW. Ribosomal DNA spacer lengthpolymorphism in barley. Mendelian Inheritance, chromosomal location and population dynamics. Proceedings of National Academy of Science. USA. 1984;81:8014–8018.
Satyavati GV, Ashok GK, Bhatla N. Medicinal plants of India. Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, 1987;2:519.
Saxena AP. In vitro antibiotic activity of components of remedy used for the treatmentof leprosy and leucoderma by the tribals of Central India, Abstr of papers presented at the Asian Conf., Trad Asian Med Bombay, 1983;(Abstr No. B-1).
Sheidai M, Mehdigholi K, Ahmad G, Attar F. Cytogenetic study of the genus Cousinia (Asteraceae, section Serratuloideae) in Iran. Gn Mol Bio. 2006;29:117–9.
Sidhu MC. Meiotic studies in the hybrids of wheat-rye additional lines and wheat (TriticumaestivumL) varieties. J Indian Bot Soc. 2008;12:86–91.
Zeerak NA. Cytogenetical effect of gamma rays and ethylmethane sulphonate in brinjal(SolanummelongenaL.). Cytologia. 1992;56:639–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhat, T.M., Ansari, M.Y.K., Alka et al. Sodium azide (NaN3) induced genetic variation of Psoralea corylifolia L. and analysis of variants using RAPD markers. Nucleus 55, 149–154 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-012-0069-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13237-012-0069-x