Abstract
Systemic toxicity, poor aqueous solubility, and poorly cell permeable ability hindered the clinical application of Celastrol. In this study, we aimed to design and synthesize an amphiphilic conjugate to encapsulate Celastrol into micelles to improve its water solubility, cellular membrane penetration, improving the clinic translation potential of Celastrol for the treatment of psoriasis. For this purpose, we first synthesized gelatin and oleic acid conjugate (GOC-1), and then covalently bonded 4-(3-boronophenylamino)-4-oxobutanoic acid (BPOA) with GOC-1 to form a stable GOC-2 conjugate which can self-assemble into micelles in aqueous solution. Celastrol (Cel) was physically encapsulated into the core of GOCs micelles. The dynamic stability, particle size, drug release, zeta potential, drug-loading efficiency, and surface morphology of Cel/loaded GOCs nano-micelles were determined. In addition, cell viability, cellular uptake of Cel/loaded GOC-2, and skin permeation and in vivo anti-psoriasis effect of Cel-loaded GOC-2 were investigated. Our results have shown that Cel/loaded GOC-1 and Cel/loaded GOC-2 have spherical shapes with diameters of around 200–300 nm. Compared to GOC-1, GOC-2 micelles showed higher drug-loading efficiency and excellent permeation ability in vitro. Moreover, Cel/GOC-2 micelles reduced erythema and white scales on the dorsal skin of psoriatic mice. In conclusion, BPOA attached GOC nanoparticles as a Celastrol carrier not only increase its water solubility but also improve drug-loading efficiency and cell permeation ability, exhibiting superior anti-psoriatic effect than the commercially available tacrolimus. Our work is expected to provide a facile approach to prepare nanocarrier for Celastrol to improve the clinic translation potential of Celastrol.
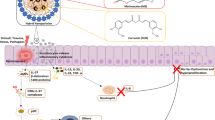
Graphical abstract
Fabrication of Celastrol containing micelles and its Anti-psoriasis activity against IMQ induced mice model. Amphiphilic BPOA-modified gelatin–oleic conjugates (GOC-2) was synthesized and used as backbone to encapsulate Celastrol into self-assembled micelles. The synthesized Cel/GOC-2 micelles can completely dissolve in water as well biologically more effective. IMQ was used to induce psoriasis mouse models and then the Cel/GOC-2 micelles treatment carried out. GOC-2 micelles as a Celastrol improve drug-loading efficiency and cell permeation ability, exhibiting superior anti-psoriatic effect than the commercially available tacrolimus which improve therapeutic outcomes of Celastrol.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.E. Greb, A.M. Goldminz, J.T. Elder, M.G. Lebwohl, D.D. Gladman, J.J. Wu, N.N. Mehta, A.Y. Finlay, A.B. Gottlieb, Psoriasis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2, 16082 (2016)
A. Rendon, K. Schäkel, Psoriasis pathogenesis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 20(6), 1475 (2019)
M. Pradhan, D. Singh, M.R. Singh, Novel colloidal carriers for psoriasis: current issues, mechanistic insight and novel delivery approaches. J Control Release. 170(3), 380–395 (2013)
P.K. Suresh, P. Singh, S.K. Saraf, Novel topical drug carriers as a tool for treatment of psoriasis: progress and advances. J Afr J Pharm Pharmacol. 7(5), 138–147 (2013)
O.P. Katare, K. Raza, B. Singh, S. Dogra, Novel drug delivery systems in topical treatment of psoriasis: rigors and vigors. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 76(6), 612–621 (2010)
S. Meng, Z. Lin, Y. Wang, Z. Wang, P. Li, Y. Zheng, Psoriasis therapy by Chinese medicine and modern agents. Chin Med. 13(1), 16 (2018)
X.Q. Li, Y. Chen, H.M. Zhou, H.L. Shi, X.N. Yan, L.P. Lin, R.X. Tan, Anti-psoriasis effect of water-processed rosin in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 242(18), 1–8 (2019)
W.J. Cheng, C.C. Chiang, C.Y. Lin, Y.L. Chen, Y.L. Leu, J.Y. Sie, W.L. Chen, C.Y. Hsu, J.J. Kuo, T.L. Hwang, Astragalus mongholicus bunge water extract exhibits anti-inflammatory effects in human neutrophils and alleviates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice. Front Pharmacol. 12, 1–20 (2021)
X. Zhang, X. Li, Y. Chen, B. Li, C. Guo, P. Xu, Z. Yu, Y. Ding, Y. Shi, J. Gu, Therapy alleviates psoriasis-like skin inflammation through suppressing γδT17 cell polarization. Front Pharmacol 12, 1–15 (2021)
S.R. Chen, Y. Dai, J. Zhao, L. Lin, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, A mechanistic overview of triptolide and celastrol, natural products from tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. Front Pharmacol. 9(104), 1–13 (2018)
X. Song, Y. Zhang, E. Dai, H. Du, L. Wang, Mechanism of action of celastrol against rheumatoid arthritis: a network pharmacology analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 74(10055), 105725 (2019)
B. Astry, S.H. Venkatesha, A. Laurence, A. Christensen-Quick, A. Garzino-Demo, M.B. Frieman, J.J. O’Shea, K.D. Moudgil, Celastrol, a Chinese herbal compound, controls autoimmune inflammation by altering the balance of pathogenic and regulatory T cells in the target organ. Clin Immunol. 157(2), 228–238 (2015)
G.F. Pinna, M. Fiorucci, J.M. Reimund, N. Taquet, Y. Arondel, C.D. Muller, Celastrol inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion in Crohn’s disease biopsies. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 322(3), 778–786 (2004)
L.L. Zhou, Z.X. Lin, K.P. Fung, C.H. Cheng, C.T. Che, M. Zhao, S.H. Wu, Z. Zuo, Celastrol-induced apoptosis in human HaCaT keratinocytes involves the inhibition of NF-κB activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 670(2–3), 399–408 (2011)
S.R. Chen, Y. Dai, J. Zhao, L. Lin, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, A mechanistic overview of triptolide and celastrol, natural products from tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. Front Pharmacol. 104, 1–13 (2018)
V. Mishra, P. Nayak, N. Yadav, M. Singh, M.M. Tambuwala, A.A.A. Aljabali, Orally administered self-emulsifying drug delivery system in disease management: advancement and patents. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 18(2), 315–332 (2021)
K. Arun, N. Arun, Nano cocrystals: crystal engineering from a nanotechnological perspective. Curr Pharm Des. 27, 2445–2453 (2021)
V.R. Patel, Y.K. Agrawal, Nanosuspension: an approach to enhance solubility of drugs. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2(2), 81–87 (2011)
J.K. Patra, G. Das, L.F. Fraceto, E.V.R. Campos, M.D.P. Rodriguez-Torres, L.S. Acosta-Torres, L.A. Diaz-Torres, R. Grillo, M.K. Swamy, S. Sharma, S. Habtemariam, H.S. Shin, Nano based drug delivery systems: recent developments and future prospects. J Nanobiotechnology. 16(1), 1–33 (2018)
Y. Zhu, J. Ye, Q. Zhang, Self-emulsifying drug delivery system improve oral bioavailability: role of excipients and physico-chemical characterization. Pharm Nanotechnol. 08(4), 290–301 (2020)
J. Hu, Y. Sheng, J. Shi, B. Yu, Z. Yu, G. Liao, Long circulating polymeric nanoparticles for gene/drug delivery. Curr Drug Metab. 19(9), 723–738 (2018)
S.Q. Zhang, Q. Fu, Y.J. Zhang, J.X. Pan, L. Zhang, Z.R. Zhang, Z.M. Liu, Surface loading of nanoparticles on engineered or natural erythrocytes for prolonged circulation time: strategies and applications. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 42, 1040–1054 (2021)
J. Whited, C.K. Rama, X.L. Sun, Synthesis and evaluation of protein-phenylboronic acid conjugates as lectin mimetics. ACS Omega 3, 13467–13473 (2018)
L. Liu, T. Rambarran, H. Sheardown, Phenylboronic acid modified hydrogel materials and their potential for use in contact lens-based drug delivery. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 20, 1–15 (2022)
C. Li, Z. Huang, Z. Liu, L. Ci, Z. Liu, Y. Liu, X. Yan, W. Lu, Sulfonate-modified phenylboronic acid-rich nanoparticles as a novel mucoadhesive drug delivery system for vaginal administration of protein therapeutics: improved stability, mucin-dependent release and effective intravaginal placement. Int J Nanomed. 11, 5917–5930 (2016)
G. Prosperi-Porta, S. Kedzior, B. Muirhead, H. Sheardown, Phenylboronic-acid-based polymeric micelles for mucoadhesive anterior segment ocular drug delivery. Biomacromol 17, 1449–1457 (2016)
X. Zhang, Y. Wang, C. Zheng, C. Li, Phenylboronic acid-functionalized glycopolymeric nanoparticles for biomacromolecules delivery across nasal respiratory. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 82, 76–84 (2012)
P.R. Wagh, P. Desai, S. Prabhu, J. Wang, Nanotechnology-based celastrol formulations and their therapeutic applications. Front Pharmacol. 12, 1–9 (2021)
J. Zhao, D. Luo, Z. Zhang, N. Fan, Y. Wang, H. Nie, J. Rong, Celastrol-loaded PEG-PCL nanomicelles ameliorate inflammation, lipid accumulation, insulin resistance and gastrointestinal injury in diet-induced obese mice. J Control Release. 28, 188–197 (2019)
R. Li, Y. Li, J. Zhang, Q. Liu, T. Wu, J. Zhou, H. Huang, Q. Tang, C. Huang, Y. Huang, Z. Zhang, G. Zhang, Y. Zhao, L. Ma, Y. Feng, L. Mo, M. Han, J. He, Targeted delivery of celastrol to renal interstitial myofibroblasts using fibronectin-binding liposomes attenuates renal fibrosis and reduces systemic toxicity. J Control Release. 320, 32–44 (2020)
P.H. Tran, T.T. Tran, B.J. Lee, Enhanced solubility and modified release of poorly water-soluble drugs via self-assembled gelatin-oleic acid nanoparticles. Int J Pharm. 455, 235–240 (2013)
W.M. Li, D.M. Liu, S.Y. Chen, Amphiphilically-modified gelatin nanoparticles: self-assembly behavior, controlled biodegradability, and rapid cellular uptake for intracellular drug delivery. J Mater Chem. 21, 12381–12388 (2011)
L. van der Fits, S. Mourits, J.S. Voerman, M. Kant, L. Boon, J.D. Laman, F. Cornelissen, A.M. Mus, E. Florencia, E.P. Prens, E. Lubberts, Imiquimod-induced psoriasislike skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J Immunol. 182, 5836–5845 (2009)
V. Dubey, D. Mishra, T. Dutta, M. Nahar, D.K. Saraf, N.K. Jain, Dermal and transdermal delivery of an anti-psoriatic agent via ethanolic liposomes. J Control Release. 123, 148–154 (2007)
K. Nakajima, S. Sano, Mouse models of psoriasis and their relevance. J Dermatol. 45, 252–263 (2018)
D. Ihtatho, M.H. Fadzil, A.M. Affandi, S.H. Hussein, Area assessment of psoriasis lesions for PASI scoring. J Med Eng Technol. 33, 426–436 (2009)
R.G. Langley, C.N. Ellis, Evaluating psoriasis with psoriasis area and severity index, psoriasis global assessment, and lattice system physician’s global assessment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 51, 563–569 (2004)
D. Šmejkalová, T. Muthný, K. Nešporová, M. Hermannová, E. Achbergerová, G. Huerta-Angeles, M. Svoboda, M. Čepa, V. Machalová, D. Luptáková, V. Velebný, Hyaluronan polymeric micelles for topical drug delivery. Carbohydr Polym. 156, 86–96 (2017)
M. Zhang, J. Cheng, J. Hu, J. Luo, Y. Zhang, F. Lu, H. Kong, H. Qu, Y. Zhao, Green Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex-based carbon dots for ameliorating imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like infammation in mice. J Nanobiotechnology. 19, 105 (2021)
K.M. Sachin, S.A. Karpe, M. Singh, A. Bhattarai, Study on surface properties of sodiumdodecyl sulfate and dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide mixed surfactants and their interaction with dyes. Heliyon. 5, 01510 (2019)
M.S. Freag, W.M. Saleh, O.Y. Abdallah, Self-assembled phospholipid-based phytosomal nanocarriers as promising platforms for improving oral bioavailability of the anticancer celastrol. Int J Pharm. 15, 18–26 (2018)
E. Atef, N. Altuwaijri, Using Raman spectroscopy in studying the effect of propylene glycol, oleic acid, and their combination on the rat skin. AAPS PharmSciTech 19, 114–122 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Collaborative Grant-in-Aid of the HBUT National “111” Center for Cellular Regulation and Molecular Pharmaceutics (XBTK-2021009). This research was also supported by a grant from “Hubei Youth Science and technology plan” in 2018 and Scientific Research Program of Hubei Provincial Department of Education of China (B2017047) and Research Funds from Hubei University of Technology (GCRC20200013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Su, J., Lin, N., You, X. et al. Phenylboronic acid-functionalized gelatin–oleic acid nanoparticles for high loading and efficient transdermal delivery of Celastrol towards the treatment of psoriasis. Macromol. Res. 31, 1029–1042 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-023-00194-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-023-00194-x