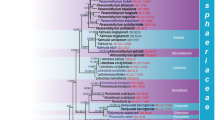
Abstract
Phaeosphaeriaceae is a large and important family in the order Pleosporales which includes economically important plant pathogens. Species may also be endophytes or saprobes on plant hosts, especially on monocotyledons (e.g., Cannaceae, Cyperaceae, Juncaceae, Poaceae); some species have also been reported on dicotyledons. The family previously accommodated 35 sexual and asexual genera and comprised more than 300 species with a range of morphological characters. The morphological characters of taxa in this family are often ambiguous and can be confused with other taxa in Leptosphaeriaceae and Montagnulaceae. Fourteen specimens of the type genera of Phaeosphaeriaceae were loaned from herbaria worldwide and were re-examined and illustrated. Fresh collections were obtained from Italy and Thailand, characterized, examined, isolated into pure culture and used to obtain molecular data. The asexual state was induced where possible on sterile bamboo pieces placed on water agar. Multigene phylogenetic analyses of ITS, LSU, SSU, RPB2 and TEF1 sequence datasets were carried out using maximum likelihood, maximum parsimony and Bayesian analysis. Molecular analyses shows that 21 genera (Amarenomyces, Ampelomyces, Chaetosphaeronema, Dematiopleospora, Entodesmium, Loratospora, Neosetophoma, Neostagonospora, Nodulosphaeria, Ophiobolus, Ophiosphaerella, Paraphoma, Parastagonospora, Phaeosphaeria, Phaeosphaeriopsis, Sclerostagonospora, Setomelanomma, Setophoma, Vrystaatia, Wojnowicia and Xenoseptoria) belong in Phaeosphaeriaceae, while seven genera (Amarenographium, Bricookea, Dothideopsella, Eudarluca, Phaeostagonospora, Scolecosporiella and Tiarospora) are included based on morphological data. Amarenomyces is reinstated and Nodulosphaeria is confirmed in Phaeosphaeriaceae. Eudarluca is distinguished from Sphaerellopsis based on its morphological characters and is typical of Phaeosphaeriaceae. ITS gene phylogenetic analysis indicates that Sphaerellopsis belongs to Leptosphaeriaceae. Ophiobolus species form a clade within Phaeosphaeriaceae while Ophiosphaerella is shown to be polyphyletic. Phaeosphaeria sensu stricto is redefined. Two new species of Phaeosphaeria and one of Phaeosphaeriopsis are introduced while the asexual states of Phaeosphaeria chiangraina and Phaeosphaeriopsis dracaenicola are reported. Scolicosporium minkeviciusii forms a sister clade with Neostagonospora and Parastagonospora in Phaeosphaeriaceae. However, Scolicosporium minkeviciusii is not the type species. Thus, the placement of Scolicosporium sensu stricto in Phaeosphaeriaceae is questionable. Phylogenetic analysis of combined ITS and LSU genes, confirm the placement of Septoriella oudemansii in Phaeosphaeriaceae. However, it is not represented by the generic type, thus the placement of Septoriella is questionable. Setophaeosphaeria is excluded from Phaeosphariaceae as the type species, Sp. hemerocallidis forms a clade at the base of Cucurbitariaceae. Wilmia clusters in Didymosphaeriaceae and is synonymized under Letendraea. Barria, Chaetoplea, Hadrospora, Lautitia, Metameris, Mixtura and Pleoseptum are excluded from Phaeosphaeriaceae based on their morphological characters. The asexual genera Mycopappus and Xenostigmina are excluded from this family based on the phylogenetic evidence; these genera form a clade close to Melanommataceae.

































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas SQ, Iftikhar T, Niaz M, Ali I, Iftikhar N, Abbas A (2012) A new species of Tiarosporella azadarrichta and new fungal records on Azadirachta indica from Pakistan. Pak J Bot 44(6):2093–2102
Abdullah SK, Asensio L, Monfort E, Gomez-Vidal S, Palma-Guerrero J, Salinas J, Lopez-Llorca LV, Jansson HB, Guarro J (2005) Occurrence in Elx, SE Spain of inflorescence rot disease of date palms caused by Mauginiella scaettae. J Phytopathol 153:417–422
Ahn YM, Shearer CA (1998) Re-examination of taxa in Leptosphaeria originally described on host species in Ranunculaceae, Papaveraceae, and Magnoliaceae. Can J Bot 76:258–280
Ainsworth GC, James PW, Hawksworth DL (1971) Ainsworth & Bisby’s dictionary of the fungi, 6th edn. CAB, Kew
Aptroot A (2006) Mycosphaerella and its anamorphs 2. Conspectus of Mycosphaerella. CBS Biodivers Ser 5:1–231
Ariyawansa HA, Kang JC, Alias SA, Chukeatirote E, Hyde KD (2013) Towards a natural classification of Dothideomycetes: the genera Dermatodothella, Dothideopsella, Grandigallia, Hysteropeltella and Gloeodiscus (Dothideomycetes incertae sedis). Phytotaxa 147(2):35–47
Ariyawansa HA, Phookamsak R, Tibpromma S, Kang JC, Hyde KD (2014a) A molecular and morphological reassessment of Diademaceae. Sci World J. doi:10.1155/2014/675348
Ariyawansa HA, Tanaka K, Thambugala KM, Phookamsak R, Tian Q, Camporesi E, Hongsanan S, Monkai J, Wanasinghe DN, Chukeatirote E, Kang JC, Xu JC, McKenzie EHC, Jones EBG, Hyde KD (2014b) A molecular phylogenetic reappraisal of the Didymosphaeriaceae (Montagnulaceae). Fungal Divers. 68. doi:10.1007/s13225-014-0305-6
Ariyawansa HA, Thambugala KM, Maharachchikumbura SSN, Udayanga D, Manamgoda DS, Daranagama A, Shivas RG, Jayawardena R, Phookamsak R, Senanayake IC, Liu JK, Tian Q, Camporesi E, McKenzie EHC, Lücking R, Hawksworth DL, Kang JC, Alias SA, Chukeatirote E, Mortimer PE, Xu JC, Jones EBG, Hyde KD (2014c) Epitypification and neotypification. Fungal Divers (in press)
Arzanlou M, Crous PW (2006) Phaeosphaeriopsis musae. Fungal Planet 9. CBSKNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht
Aveskamp MM, de Gruyter J, Woudenberg JHC, Verkley GJM, Crous PW (2010) Highlights of the Didymellaceae: a polyphasic approach to characterise Phoma and related pleosporalean genera. Stud Mycol 65:1–60
Barr ME (1979) A classification of Loculoascomycetes. Mycologia 71:935–957
Barr (1982) Leptosphaeria sepalorum. Mycotaxon 15:345–348
Barr ME (1987a) New taxa and combinations in the Loculoascomycetes. Mycotaxon 29:501–505
Barr ME (1987b) Prodromus to Class Loculoascomycetes. University of Massachusetts, Massachusetts, Amherst
Barr ME (1990a) Melanommatales (Loculoascomycetes). N Am Flora 13(II):1–129
Barr ME (1990b) Some dictyosporous genera and species of Pleosporales in North America. Mem N Y Bot Gard 62:1–92
Barr ME (1992a) Additions to and notes on the Phaeosphaeriaceae (Pleosporales, Loculoascomycetes). Mycotaxon 43:371–400
Barr ME (1992b) Notes on the Lophiostomataceae (Pleosporales). Mycotaxon 45:191–221
Barr ME (1996) Planistromellaceae, a new family in the Dothideales. Mycotaxon 60:433–442
Barr ME (2002) Teichosporaceae, another family in the Pleosporales. Mycotaxon 82:373–389
Barr ME, Rogerson CT (1999) Some Loculoascomycete species form the Great Basin, USA. Mycotaxon 71:473–480
Bayon C, Yuan Z-W, Ruiz C, Liesebach M, Pei MH (2006) Genetic diversity in the mycoparasite Sphaerellopsis filum inferred from AFLP analysis and ITS–5.8S sequences. Mycol Res 110:1200–1206
Belsare SW, Moniz L, Deo VB (1980) The hyperparasite Ampelomyces quisqualis Ces. from Maharashtra State, India. Biovigyanam 6:173–176
Berlese AN (1892) Leptosphaeria danica. Icones Fungorum 1(2):67–90
Boerema GH (1982) Phoma-soorten van de sectie Plenodomus. Verslagen en Mededelingen Plantenziektenkundige Dienst Wageningen 158(Jaarboek 1981):28–30
Boerema GH (1997) Contributions towards a monograph of Phoma (Coelomycetes) - V. Subdivision of the genus in sections. Mycotaxon 64:321–333
Boerema GH, Dorenbosch MMJ (1979) Mycologisch-taxonomisch onderzoek in Jaarboek 1978. Verslagen en Mededelingen Plantenziektenkundige Dienst 153:17–21
Boerema GH, De Gruyter J, Noordeloos ME, Hamers MEC (2004) Phoma identification manual. Differentiation of specific and infraspecific taxa in culture. CABI Publishing, United Kingdom
Boise JR (1989) On Hadrospora, a new genus in the Phaeosphaeriaceae and Byssothecium alpestris. Mem N Y Bot Gard 49:308–310
Boonmee S, Ko Ko TW, Chukeatirote E, Hyde KD, Chen H, Lei C, McKenzie EHC, Jones EBG, Rampai K, Bahkali AH (2012) Two new Kirschsteiniothelia species with Dendryphiopsis anamorphs cluster in Kirschsteiniotheliaceae fam. nov. Micologia 104(3):698–714
Calatayud V, Etayo J (2001) Five new species of lichenicolous conidial fungi from Spain. Can J Bot 79:223–230
Câmara MPS, O’Neill NR, van Berkum P, Dernoeden PH, Palm ME (2000) Ophiosphaerella agrostis sp. nov. and its relationship to other species of Ophiosphaerella. Mycologia 92:317–325
Câmara MPS, Palm ME, van Berkum P, Stewart EL (2001) Systematics of Paraphaeosphaeria: a molecular and morphological approach. Mycol Res 105:41–56
Câmara MPS, Palm ME, van Berkum P, O’Neill NR (2002) Molecular phylogeny of Leptosphaeria and Phaeosphaeria. Mycologia 94:630–640
Câmara MPS, Ramaley AW, Castlebury LA, Palm ME (2003) Neophaeosphaeria and Phaeosphaeriopsis, segregates of Paraphaeosphaeria. Mycol Res 107:516–522
Cannon PF, Damm U, Johnston PR, Weir BS (2012) Colletotrichum–current status and future directions. Stud Mycol 73:181–213
Carson ML (2005) Yield loss potential of Phaeospharia leaf spot of maize caused by Phaeosphaeria maydis in the United States. Plant Dis 89:986–988
Cesati V (1852) Ampelomyces quisqualis Ces. Botanische Zeitung 10:301–302
Cheng TF, Jia XM, Ma XH, Lin HP, Zhao YH (2004) Phylogenetic study on Shiraia bambusicola by rDNA sequence analyses. J Basic Microbiol 44:339–350
Chomnunti P, Hongsanan S, Aguirre-Hudson B, Tian Q, Peršoh D, Dhami MK, Alias AS, Xu JC, Liu X, Stadler M, Hyde KD (2014) The sooty moulds. Fungal Divers 66:1–36
Clare BG (1964) Ampelomyces quisqualis (Cicinnobolus cesatii) on Queensland Erysiphaceae. University of Queensland Papers 4:147–149
Clements FE, Shear CL (1931) Genera of fungi, 2nd edn. H.W. Wilson Company, New York
Corda ACI (1840) Icones Fungorum hucusque Cognitorum 4: i–iii, 1–63. Prague; apud J.G. Calve [Fridericum Ehrlich]
Crivelli PG (1983) Über die heterogene Ascomycetengattung Pleospora Rabh.: vorschlag für eine Aufteilung. Dissertation ETH Nr. 7318, Zürich, Germany
Crous PW, Palm ME (1999) Systematics of selected foliicolous fungi associated with leaf spots of Proteaceae. Mycol Res 103:1299–1304
Crous PW, Slippers B, Wingfield MJ, Rheeder J, Marasas WFO, Philips AJL, Alves A, Burgess TI, Barber PA, Groenewald JZ (2006) Phylogenetic lineages in the Botryosphaeriaceae. Stud Mycol 55:235–253
Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Lombard L, Wingfield MJ (2008) Homortomyces gen. nov., a new dothidealean pycnidial fungus from the Cradle of Humankind. IMA Fungus 3(2):109–115
Crous PW, Minnis AW, Pereira OL, Alfenas AC, Alfenas RF, Rossman AY, Groenewald JZ (2011) What is Scirrhia? IMA Fungus 2:127–133
Crous PW, Wingfield MJ, Guarro J, Cheewangkoon R et al (2013) Molecular phylogeny and evolution of fungi – Fungal Planet description sheets: 154–213. Persoonia 31:188–296
Crous PW, Shivas RG, Quaedvlieg W, van der Bank M, Zhang Y, Summerell BA, Guarro J, Wingfield MJ, Wood AR, Alfenas AC, Braun U, Cano-Lira JF, García D, Marin-Felix Y, Alvarado P, Andrade JP, Armengol J, Assefa A, den Breeÿen A, Camele I, Cheewangkoon R, De Souza JT, Duong TA, Esteve-Raventós F, Fournier J, Frisullo S, García-Jiménez J, Gardiennet A, Gené J, Hernández-Restrepo M, Hirooka Y, Hospenthal DR, King A, Lechat C, Lombard L, Mang SM, Marbach PAS, Marincowitz S, Marin-Felix Y, Montaño-Mata NJ, Moreno G, Perez CA, Pérez Sierra AM, Robertson JL, Roux J, Rubio E, Schumacher RK, Stchigel AM, Sutton DA, Tan YP, Thompson EH, van der Linde E, Walker AK, Walker DM, Wickes BL, Wong PTW, Groenewald JZ (2014) Fungal Planet Description Sheets: 214–280. Persoonia 32:184–306
Cunfer BM (2000) Stagonospora and Septoria diseases of barley, oat, and rye. Can J Plant Pathol 22:332–348
Cunfer BM, Ueng PP (1999) Taxonomy and identification of Septoria and Stagonospora species on small-grain cereals. Annu Rev Phytopathol 37:267–284
De Bary A (1870) Eurotium, Erysiphe, Cicinnobolus, nebst Bemerkungen über die Geschlechtsorgane der Ascomyceten. In: Beiträge zur Morphologie und Physiologie der Pilze (A. De Bary & M. Woronin, eds). Verlag von C. Winter, Frankfurt, pp 1–95
De Gruyter J, Aveskamp MM, Woudenberg JHC, Verkley GJM, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW (2009) Molecular phylogeny of Phoma and allied anamorph genera: towards a reclassification of the Phoma complex. Mycol Res 113:508–519
De Gruyter J, Woudenberg JH, Aveskamp MM, Verkley GJ, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW (2010) Systematic reappraisal of species in Phoma section Paraphoma, Pyrenochaeta and Pleurophoma. Mycologia 102:1066–1081
De Gruyter J, Woudenberg JHC, Aveskamp AA, Verkley GJM, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW (2012) Redisposition of phoma-like anamorphs in Pleosporales. Stud Mycol 75:1–36
Dennis RWG (1978) British Ascomycetes, 3rd edn. J. Cramer, Vaduz
Dianese JC, Inácio CA, Dornelo-Silva D (2001) Wilmia, a new genus of phaeosphaeriaceous ascomycetes on Memora pedunculata in central Brazil. Mycologia 93:1014–1018
Doilom M, Liu JK, Jaklitsch WM, Ariyawansa H, Wijayawardene NN, Chukeatirote E, Zhang M, McKenzie EHC, Geml J, Voglmayr H, Hyde KD (2013) An outline of the family Cucurbitariaceae. Sydowia 65(1):167–192
Dong JW, Chen WD, Crane JL (1998) Phylogenetic studies of the Leptosphaeriaceae, Pleosporaceae and some other Loculoascomycetes based on nuclear ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycol Res 102:151–156
Eriksson OE (1966) On Eudarluca caricis (Fr.) O. Erikss., comb. nov., a cosmopolitan uredinicolous pyrenomycete. Bot Not 119:33–69
Eriksson OE (1967) On graminicolous pyrenomycetes from Fennoscandia. I, II, III. Ark Bot Ser 26:339–466
Eriksson OE (1981) The families of bitunicate ascomycetes. Opera Bot 60:1–220
Eriksson OE (1982) Notes on ascomycetes and coelomycetes from NW. Europe Mycotaxon 15:189–202
Eriksson OE (2006) Outline of Ascomycota–2006. Myconet 12:1–82
Eriksson OE (2007) Ascomycet-Nytt 1. Svensk Mykologisk Tidskrift 28(2):38–41
Eriksson OE, Hawksworth DL (1990) Outline of the Ascomycetes—1989. Syst Ascomyc Reprint of Volumes 1–4 (1982–1985) 8 (2): 119–318
Eriksson OE, Hawksworth DL (1991) Outline of the Ascomycetes–1990. Syst Ascomyc Reprint of Volumes 1–4 (1982–1985) 9: 39–271
Eriksson OE, Hawksworth DL (1993) Outline of the Ascomycetes – 1993. Syst Ascomyc 12(1–2):51–257
Eriksson OE, Yue J-Z (1990) Notes on bambusicolous pyrenomycetes. Nos. 1–10. Mycotaxon 38:201–220
Farr DF, Bills GF (1995) Wojnowicia colluvium sp. nov. isolated from conifer litter. Mycologia 87(4):518–524
Farr DF, Rossman AY (2014) Fungal databases, systematic mycology and microbiology laboratory, ARS, USDA. Retrieved September 1, 2014, from http://nt.ars-grin.gov/fungaldatabases/
Farr DF, Bills GF, Chamuris GP, Rossman AY (1989) Fungi on plants and plant products in the United States. APS Press, St. Paul
Farr DF, Aime MC, Rossman AY, Palm ME (2006) Species of colletotrichum on agavaceae. Mycol Res 110(12):1395–1408
Fisher PJ, Webster J (1992) A Trematosphaeria endophyte from rice roots and its Zalerion anamorph. Nova Hedw 54:77–81
Gams W (2000) Phialophora and some similar morphologically little-differentiated anamorphs of divergent ascomycetes. Stud Mycol 45:187–200
Griffith D (1899) The common parasite of the powdery mildews. Bull Torrey Bot Club 26:184–188
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. In: Nucleic Acids Symposium Series, pp 95–98
Hawksworth DL (1985) Kirschsteiniothelia a new genus for the Microthelia incrustans–group (Dothideales). Bot J Linn Soc 91:181–202
Hedjaroude A (1969) Études taxonomiques sur les Phaeosphaeria Miyake et leurs formes voisines (ascomycètes). Sydowia 22:57–107
Hodhod MS, Abdel-Wahab MA, Bahkali AHA, Hyde KD (2012) Amarenographium solium sp nov from Yanbu mangroves in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Cryptogam Mycol 33(3):285–294
Holm L (1948) Taxonomical notes onAscomycetes. 1. The Swedish species of the genus Ophiobolus Riess sensu Sacc. Sven Bot Tidskr 42:337–347
Holm L (1957) Etudes taxonomiques sur les pléosporacées. Symb Bot Upsaliens 14:1–188
Hsiang T, Chen F, Goodwin PH (2003) Detection and phylogenetic analysis of mating type genes of Ophiosphaerella korrae. Can J Bot 81(4):307–315
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17(8):754–755
Hyde KD (1992) Fungi from decaying inter-tidal fronds of Nypa fruticans, including three new genera and four new species. J Linn Soc Bot 110:95–110
Hyde KD (1994) Fungi from palms. XII. Three new intertidal ascomycetes from submerged palm fronds. Sydowia 46:257–264
Hyde KD, McKenzie EHC, KoKo TW (2011) Towards incorporating anamorphic fungi in a natural classification – checklist and notes for 2010. Mycosphere 2:1–88
Hyde KD, Jones EBG, Liu JK, Ariyawansa HA, Boehm E, Boonmee S, Braun U, Chomnunti P, Crous PW, Dai DQ, Diederich P, Dissanayake AJ, Doilom M, Doveri F, Hongsanan S, Jayawardena R, Lawrey JD, Li YM, Liu YX, Lücking R, Monkai J, Muggia L, Nelsen MP, Pang KL, Phookamsak R, Senanayake I, Shearer CA, Seutrong S, Tanaka K, Thambugala KM, Wijayawardene NN, Wikee S, Wu HX, Zhang Y, Aguirre-Hudson B, Alias SA, Aptroot A, Bahkali AH, Bezerra JL, Bhat JD, Camporesi E, Chukeatirote E, Gueidan C, Hawksworth DL, Hirayama K, De Hoog S, Kang JC, Knudsen K, Li WJ, Li X, Liu ZY, Mapook A, McKenzie EHC, Miller AN, Mortimer PE, Phillips AJL, Raja HA, Scheuer C, Schumm F, Taylor JE, Tian Q, Tibpromma S, Wanasinghe DN, Wang Y, Xu JC, Yan J, Yacharoen S, Zhang M (2013) Families of Dothideomycetes. Fungal Divers 63:1–313
Hyde KD, Nilsson RH, Alias SA, Ariyawansa HA, Blair JE, Cai L, de Cock AWAM, Dissanayake AJ, Glockling SL, Goonasekara ID, Gorczak M, Hahn M, Jayawardena RS, van Kan JAL, Laurence MH, Lévesque CA, Li X, Liu JK, Maharachchikumbura SSN, Manamgoda DS, Martin FN, McKenzie EHC, McTaggart AR, Mortimer PE, Nair PVR, Pawłowska J, Rintoul TL, Shivas RG, Spies CFJ, Summerell BA, Taylor PWJ, Terhem RB, Udayanga D, Vaghefi N, Walther G, Wilk M, Wrzosek M, Xu JC, Yan JY, Zhou N (2014) One stop shop: backbones trees for important phytopathogenic 5 genera: I (2014). Fungal Divers. doi:10.1007/s13225-014-0298-1
Index Fungorum (2014) http://www.indexfungorum.org/Names/Names.asp
Jones EBG, Sakayaroj J, Suetrong S, Somrithipol S, Pang KL (2009) Classification of marine Ascomycota, anamorphic taxa and Basidiomycota. Fungal Divers 35:1–187
Keener PD (1951) An ascigerous stage of Darluca filum (Biv.) Castagne. Plant Dis Rep 35:86–87
Khashnobish A, Shearer CA (1996) Phylogenetic relationships in some Leptosphaeria and Phaeosphaeria species. Mycol Res 100:1355–1363
Kirk PM, Cannon PF, David JC, Stalpers JA (2001) Dictionary of the Fungi 9th edn. CABI, Wallingford
Kirk PM, Cannon PF, Minter DW, Staplers JA (2008) Dictionary of the Fungi 10th edn. CABI Bioscience, UK
Kiss L (1998) Natural occurrence of Ampelomyces intracellular mycoparasites in mycelia of powdery mildew fungi. New Phytol 140:709–714
Kiss L, Nakasone KK (1998) Ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer sequences do not support the species status of Ampelomyces quisqualis, a hyperparasite of powdery mildew fungi. Curr Genet 33:362–367
Kiss L, Russell J, Szentiványi O, Xu X, Jeffries P (2004) Biology and biocontrol potential of Ampelomyces mycoparasites, natural antagonists of powdery mildew fungi. Biocontrol Sci Tech 14:635–651
Kodsueb R, Dhanasekaran V, Aptroot A, Lumyong S, McKenzie EHC, Hyde KD, Jeewon R (2006) The family Pleosporaceae: intergeneric relationships and phylogenetic perspectives based on sequence analyses of partial 28S rDNA. Mycologia 98:571–583
Kodsueb R, Lumyong S, Ho WH, Hyde KD, McKenzie EHC, Jeewon R (2007) Morphological and molecular characterization of Aquaticheirospora and phylogenetics of Massarinaceae (Pleosporales). Bot J Linn Soc 155:283–296
Kohlmeyer J, Kohlmeyer E (1965) Phaeosphaeria ammophilae. Icones Fungorum Maris 3
Kohlmeyer J, Volkmann-Kohlmeyer B (1993) A trotorquata and Loratospora: new ascomycete genera on Juncus roemerianus. Syst Ascomyc 12:7–22
Kruys A, Eriksson OE, Wedin M (2006) Phylogenetic relationships of coprophilous Pleosporales (Dothideomycetes, Ascomycota), and the classification of some bitunicate taxa of unknown position. Mycol Res 110:527–536
Lawrey JD, Diederich P, Nelsen MP, Freebury C, Broeck DVD, Sikaroodi M, Ertz D (2012) Phylogenetic placement of lichenicolous Phoma species in the Phaeosphaeriaceae (Pleosporales, Dothideomycetes). Fungal Divers 55:195–213
Leuchtmann A (1984) Über Phaeosphaeria Miyake und andere bitunicate Ascomyceten mit mehrfach querseptierten Ascosporen. Sydowia 37:75–194
Liang C, Yang J, Kovács GM, Szentiványi O, Li B, Xu XM, Kiss L (2007) Genetic diversity of Ampelomyces mycoparasites isolated from different powdery mildew species in China inferred from analyses of rDNA ITS sequences. Fungal Divers 24:225–240
Liew ECY, Aptroot A, Hyde KD (2000) Phylogenetic significance of the pseudoparaphyses in Loculoascomycete taxonomy. Mol Phylogenet Evol 16:392–402
Lind J (1913) Danish fungi, as represented in the herbarium of E. Rostrup. 1–650. Denmark, Copenhagen
Liu YJ, Whelen S, Hall BD (1999) Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetes: evidence from an RNA polymerase II subunit. Mol Biol Evol 16:1799–1808
Liu JK, Phookamsak R, Jones EBG, Zhang Y, Ko-Ko TW, Hu HL, Boonmee S, Doilom M, Chukeatirote E, Bahkali AH, Wang Y, Hyde KD (2011) Astrosphaeriella is polyphyletic, with species in Fissuroma gen. nov., and Neoastrosphaeriella gen. nov. Fungal Divers 51:135–154
Liu JK, Phookamsak R, Doilom M, Wiki S, Mei LY, Ariyawansa HA, Boonmee S, Chomnunti P, Dai DQ, Bhat DJ, Romero AI, Xhuang WY, Monkai J, Jones EBG, Chukeatirote E, KoKo TW, Zhoa YC, Wang Y, Hyde KD (2012) Towards a natural classification of Botryosphaeriales. Fungal Divers 57:149–210
Liu YX, Hyde KD, Ariyawansa HA, Li WJ, Zhou DQ, Yang YL, Chen YM, Liu ZY (2013) Shiraiaceae, new family of Pleosporales (Dothideomycetes, Ascomycota). Phytotaxa 103(1):51–60
Lumbsch HT, Huhndorf SM (eds.) (2007) Outline of Ascomycota–2007. Myconet 13:1–58
Lumbsch HT, Huhndorf SM (2010) Outline ofAscomycota–2009. Fieldiana Life Earth Sci 1:1–60
Manamgoda DS, Cai L, McKenzie EHC, Crous PW, Madrid H, Chukeatirote E, Shivas RG, Tan YP, Hyde KD (2012) A phylogenetic and taxonomic re–evaluation of the Bipolaris, Cochliobolus, Curvularia Complex. Fungal Divers 56:131–144
McAlpine D (1902) Fungus diseases of stone-fruit trees in Australia and their treatment, pp 1–165
Minter DW, Rodríguez Hernández M, Mena Portales J (2001) Fungi of the Caribbean: an annotated checklist. PDMS Publishing: 946 pp
Miyake I (1909) Studies on the parasitic fungi of rice in Japan. Bot Mag Tokyo 23:85–97
Miyake I (1910) Studien über die Pilze der Reispflanze in Japan. J Coll Agric Tokyo 2:237–276
Moesz G (1915) Mykologiai közlemények. II. közlemény. Botanikai Kölzlemények 14(5–6):145–158
Monkai J, Liu JK, Boonmee S, Chomnunti P, Chukeatirote E, Jones EBG, Wang Y, Hyde KD (2013) Planistromellaceae (Botryosphaeriales). Cryptogam Mycol 34:45–77
Morales VM, Jasalavich CA, Pelcher LE, Petrie GA, Taylor JL (1995) Phylogenetic relationships among several Leptosphaeria species based on their ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycol Res 99:593–603
Morelet M (1980) Sur quatre Dothideales. Bull Soc Sci Nat Archeol Toulon 227:14–15
Morgan-Jones G, White JF (1983) Studies on the genus Phoma. III. Paraphoma, a new genus to accommodate Phoma radicina. Mycotaxon 18(1):57–65
Müller E (1950) Die schweizerischen Arten der Gattung Leptosphaeria und ihrer Verwandten. Sydowia 4:185–319
Müller E (1952) Die schweizerischen Arten der Gattung Ophiobolus Riess. Ber Schweiz Bot Ges 62:307–339
Müller E, von Arx JA (1962) Die Gattungen der didymosporen Pyrenomyceten. Beitr Krypt Fl Schweiz 11:1–92
Munk A (1957) Danish pyrenomycetes. A preliminary flora. Dansk Bot Ark 17:1–491
Nag Raj TR (1989) Genera coelomycetum. XXVI. Amarenographium, Callistospora, Hyalothyridium, Orphanocoela anam.-gen.nov., Scolecosporiella, and Urohendersoniella. Can J Bot 67(3169–3):186
Nischwitz C, Newcombe G, Anderson LC (2005) Host specialization of the mycoparasite Eudarluca caricis and its evolutionary relationship to Ampelomyces. Mycol Res 109(4):421–428
Nylander JAA (2004) MrModeltest 2.0. Program distributed by the author. Evolutionary Biology Centre, Uppsala University
Oertel B (2011) Pilzgattungen Europas-Liste 6: Notizbuchartige Auswahlliste zur Bestimmungsliteratur für Coelomyceten
Page RDM (1996) TreeView: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Petrak F (1921) Mykologische Notizen. II Ann Mycol 19(1–2):17–128
Petrak F (1944) Über die Gattungen Chaetopyrena Pass., Sclerochaeta v. Höhn., Sclerochaetella v. Höhn., Vermiculariella Oud., Chaetosphaeronema Moesz und Pseudophoma v. Höhn. Ann Mycol 42:58–71
Petrak F, Sydow H (1936) Kritisch-systematische Originaluntersuchungen über Pyrenomyzeten, Sphaeropsideen und Melanconieen. VII. Annal Mycol 34(1–2):11–52
Phookamsak R, Liu JK, Chukeatirote E, McKenzie EHC, Hyde KD (2013) Phylogeny and morphology of Leptosphaerulina saccharicola sp. nov. and Pleosphaerulina oryzae and relationships with Pithomyces. Cryptogam Mycol 34(4):303–319
Phookamsak R, Liu JK, Manamgoda DS, Chukeatirote E, Mortimer PE, McKenzie EHC, Hyde KD (2014) The sexual state of Setophoma. Phytotaxa 176:260–269
Priest MJ (2006) Fungi of Australia: Septoria. CSIRO publishing, Melbourne, Australia, ABRS, Canberra
Quaedvlieg W, Verkley GJM, Shin H-D, Barretto RW, Alfenas AC, Swart WJ, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW (2013) Sizing up Septoria. Stud Mycol 75:307–390
Rabenhorst (1858) Herb myc, ed. 2 no. 725 (in sched)
Raja HA, Ferrer A, Shearer CA (2009) Freshwater ascomycetes: a new genus, Ocala scalariformis gen. et sp. nov, and two new species, Ayria nubispora sp. nov. and Rivulicola cygnea sp. nov. Fungal Divers 34:79–86
Ramaley AW (1995) New fungi from Dasylirion (Agavaceae). Aliso 14:147–153
Ramaley AW (1997) New Paraphaeosphaeria species and their anamorphs. Mycotaxon 61:347–358
Ramaley AW, Barr ME (1995) New dictyosporous species from leaves of Agavaceae. Mycotaxon 54:75–90
Rannala B, Yang Z (1996) Probability distribution of molecular evolutionary trees: a new method of phylogenetic inference. J Mol Evol 43(3):304–311
Reddy PV, Patel R, White JF Jr (1998) Phylogenetic and developmental evidence supporting reclassification of cruciferous pathogens Phoma lingam and Phoma wasabiae in Plenodomus. Can J Bot 76:1916–1922
Rehner S (2001) Primers for elongation factor 1-α (EF1-α). http://ocid.NACSE.ORG/research/deephyphae/EF1primer.pdf
Reiss MLC (1854) Neue Kernpilze. Hedwigia 1:23–28
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19(12):1572–1574
Rossman AY, Farr DF, Castlebury LA, Shoemaker R, Mengistu A (2002) Setomelanomma holmii (Pleosporales, Phaeosphaeriaceae) on living spruce twigs in Europe and North America. Can J Bot 80:1209–1215
Roumeguère C (1880) Revisio Reliquiae Libertianae. – Pars 1(1). Revue Mycologique 2:15–24
Rudakov OL (1979) Fungi of the genus Ampelomyces Ces. Ex Schlecht. Mikol Fitopatol 13:104–110 [In Russian.]
Saccardo PA (1883) Sylloge Fungorum 2, Italy, Pavia, p 815
Saccardo PA (1892) Supplementum Universale, Pars II. Discomyceteae-Hyphomyceteae. Syll Fun 10:1–964
Saccardo PA, Marchal E (1885) Reliquiae mycologicae Westendorpianae. Revue Mycol Toulouse 7:140–149
Saleh AA, Leslie JF (2004) Cephalosporium maydis is a distinct species in the Gaeumannomyces-Harpophora species complex. Mycologia 96(6):1294–1305
Sánchez Márquez S, Bills GF, Zabalgogeazcoa I (2007) The endophytic mycobiota of the grass Dactylis glomerata. Fungal Divers 27:171–195
Sawada K (1959) Descriptive catalogue of Taiwan (Formosan) fungi. Part XI. Spec Publ Coll Agric National Taiwan Univ 8:1–268
Schatz S (1984) The life history, developmental morphology, and taxonomy of Lautitia danica gen. nov., comb. nov. Can J Bot 62:28–32
Schoch CL, Shoemaker RA, Seifert KA, Hambleton S, Spatafora JW, Crous PW (2006) A multigene phylogeny of the Dothideomycetes using four nuclear loci. Mycologia 98:1041–1052
Schoch CL, Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Boehm EWA, Burgess TI, de Gruyter J, de Hoog GS, Dixon LJ, Grube M, Gueidan C, Harada Y, Hatakeyama S, Hirayama K, Hosoya T, Huhndorf SM, Hyde KD, Jones EBG, Kohlmeyer J, Kruys Å, Li YM, Lücking R, Lumbsch HT, Marvanová L, Mbatchou JS, McVay AH, Miller AN, Mugambi GK, Muggia L, Nelsen MP, Nelson P, Owensby CA, Phillips AJL, Phongpaichit S, Pointing SB, Pujade-Renaud V, Raja HA, Rivas Plata E, Robbertse B, Ruibal C, Sakayaroj J, Sano T, Selbmann L, Shearer CA, Shirouzu T, Slippers B, Suetrong S, Tanaka K, Volkmann-Kohlmeyer B, Wingfield MJ, Wood AR, Woudenberg JHC, Yonezawa H, Zhang Y, Spatafora JW (2009) A class–wide phylogenetic assessment of Dothideomycetes. Stud Mycol 64:1–15
Seifert K, Morgan-Jones G, Gams W, Kendrick B (2011) The genera of Hyphomycetes. CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht
Shearer CA (1993) Reexamination of eight taxa originally described in Leptosphaeria on members of the Asteraceae. Mycologia 85:825–834
Shearer CA, Crane JL (1971) Fungi of the Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries. I. Patuxent River. Mycologia 63:237–260
Shearer CA, Crane JL (1999) Freshwater Ascomycetes: Isthmosporella pulchragen. and sp. nov. Mycologia 91:141–144
Shearer CA, Raja HA, Miller AN, Nelson P, Tanaka K, Hirayama K, Marvanová L, Hyde KD, Zhang Y (2009) The molecular phylogeny of freshwater Dothideomycetes. Stud Mycol 64:145–153
Shoemaker RA (1961) Pyrenophora phaeocomes (Reb. ex Fr.) Fr. Can J Bot 39:901–908
Shoemaker RA (1976) Canadian and some extralimital Ophiobolus species. Can J Bot 54:2365–2404
Shoemaker RA (1984) Canadian and some extralimital Nodulosphaeria and Entodesmium species. Can J Bot 62:2730–2753
Shoemaker RA, Babcock CE (1987) Wettsteinina. Can J Bot 65:373–405
Shoemaker RA, Babcock CE (1989a) Bricookea barrae n. sp. compared with Bricookea sepalorum. Stud Mycol 31:165–169
Shoemaker RA, Babcock CE (1989b) Phaeosphaeria. Can J Bot 67:1500–1599
Shoemaker RA, Babcock CE (1992) Applanodictyosporous Pleosporales: Clathrospora, Comoclathris, GraphyIlium, Macrospora, and Platysporoides. Can J Bot 70(8):1617–1658
Silva-Hanlin DMW, Hanlin RT (1999) Small subunit ribosomal RNA gene phylogeny of several loculoascomycetes and its taxonomic implications. Mycol Res 103:153–160
Silvestro D, Michalak I (2011) raxmlGUI: a graphical front-end for RAxML. Org Divers Evol 12:335–337
Sivanesan A (1984) The bitunicate ascomycetes and their anamorph. J. Cramer, Vaduz, 701 pp
Solomon PS, Lowe RGT, Tan KC, Waters ODC, Oliver RP (2006) Stagonospora nodorum: cause of Stagonospora nodorum blotch of wheat. Mol Plant Pathol 7:147–156
Spegazzini C (1908) Fungi aliquot paulistani. Revista del Museo de La Plata 15:7–48
Spegazzini C (1909) Ophiosphaerella. Anales del Museo Nacional de Historia Natural Buenos Aires 19(12):401 [ser. 3, 12]
Spooner BM, Kirk PM (1982) Taxonomic notes on Excipularia and Scolicosporium. Trans Br Mycol Soc 78:247–257
Stafleu FA et al (eds) (1972) International Code of Botanical Nomenclature. International Association for Plant Taxonomy, Utrecht, p 426
Stamatakis A, Hoover P, Rougemont J (2008) A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML Web Servers. Syst Biol 57:758–771
Stukenbrock EH, Banke S, McDonald BA (2006) Global migration patterns in the fungal wheat pathogen Phaeosphaeria nodorum. Mol Ecol 15:2895–2904
Suetrong S, Schoch CL, Spatafora JW, Kohlmeyer J, Volkmann Kohlmeyer B, Sakayaroj J, Phongpaichit S, Tanaka K, Hirayama K, Jones EBG (2009) Molecular systematics of the marine Dothideomycetes. Stud Mycol 64:155–173
Sullivan RF, White JF Jr (2000) Phoma glomerata as a mycoparasite of powdery mildew. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:425–427
Sutton BC (1968) Kellermania and its generic segregates. Can J Bot 46:181–196
Sutton BC (1975) Wojnowicia and Angiopomopsis. Česka Mykologie 29:97–104
Sutton BC (1977) Coelomycetes VI. Nomenclature of generic names proposed for coleomycetes. Mycol Pap 141:1–253
Sutton BC (1980) The Coelomycetes: fungi Imperfecti with pycnidia, acervuli and stromata. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew
Sutton BC, Alcorn JL (1974) Neottiosporina. Aust J Bot 22(3):517–530
Swart HJ, Walker J (1988) Australian leaf-inhabiting fungi. XXVIII. Hendersonia on Eucalyptus. Trans Br Mycol Soc 90(4):633–641
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony, version 4.0 b10. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Szentiványi O, Kiss L, Russell JC, Kovács GM, Varga K, Jankovics T, Lesemann S, Xu XM, Jeffries P (2005) Ampelomyces mycoparasites from apple powdery mildew identified as a distinct group based on single-stranded conformation polymorphism analysis of the rDNA ITS region. Mycol Res 109:429–438
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tanaka E, Harada Y (2003) Hadrospora fallax (Pleosporales) found in Japan. Mycoscience 44:245–248
Tanaka K, Harada Y (2005) Bambusicolous fungi in Japan (6): Katumotoa, a new genus of phaeosphaeriaceous ascomycetes. Mycoscience 46:313–318
Tanaka K, Hirayama K, Yonezawa H, Hatakeyama S, Harada Y, Sano T, Shirouzu T, Hosoya T (2009) Molecular taxonomy of bambusicolous fungi: Tetraplosphaeriaceae, a new pleosporalean family with tetraploa-like anamorphs, and notes on the phylogeny of selected species from bamboo. Stud Mycol 64:175–209
Thambugala KM, Camporesi E, Ariyawansa HA, Phookamsak R, Liu ZY, Hyde KD (2014) Phylogeny and morphology of Phaeosphaeriopsis triseptata sp. nov., and Phaeosphaeriopsis glaucopunctata. Phytotaxa 176:238–250
Theissen F, Sydow H (1915) Die Dothideales. Kritisch-systematisch Originaluntersuchungen. Ann Mycol 13:147–74
Torres MS, Bergen M, Singh S, Bischoff J, Sullivan RF, White JF Jr (2005) Plenodomus morganjonesii sp. nov. and a discussion of the genus Plenodomus. Mycotaxon 93:333–343
Treigiene A, Mel’nik VA (2002) Interesting records of deuteromycetes from Lithuania (in Russian). Mikologiyai Fitopatologiya 36:42–47
Udayanga D, Liu X, Crous PW, McKenzie EHC, Chukeatirote E, Hyde KD (2012) A multi-locus phylogenetic evaluation of Diaporthe (Phomopsis). Fungal Divers 56(1):157–171
Vergnes DM, Zhanarbekova A, Renard M-E, Duveiller E, Maraite H (2006) Mating types of Phaeosphaeria nodorum (anamorph Stagonospora nodorum) from Central Asia. Phytopathology 154:317–319
Verkley GJM, da Silva M, Wicklow DT, Crous PW (2004) Paraconiothyrium, a new genus to accommodate the mycoparasite Coniothyrium minitans, anamorphs of Paraphaeosphaeria, and four new species. Stud Mycol 50:323–335
Verkley GJM, Renfurm R, Göker M, Stielow JB (2014) Novel genera and species of coniothyrium-like fungi in Montagnulaceae (Ascomycota). Persoonia 32:25–51. doi:10.3767/003158514X679191
Vilgalys R, Hester M (1990) Rapid genetic identification and mapping of enzymatically amplified ribosomal DNA from several Cryptococcus species. J Bacteriol 172:4238–4246
von Arx JA, Müller E (1975) A re-evaluation of the bitunicate ascomycetes with keys to families and genera. Stud Mycol 9:1–159
von Höhnel FXR (1915) Fragmente zur Mykologie (XVII. Mitteilung, Nr. 876 bis 943). Sitzungsberichten der Kaiserliche Akademie der Wissenschaften in Wien Mathematische-Naturwissenschaftliche Klasse, Abt. 1 124: 49–159
von Höhnel FXR (1917) Fungi imperfecti. Beiträge zur Kenntnis derselben. Hedwigia 59:236–284
Walker JM (1980) Gaeumannomyces, Linocarpon, Ophiobolus and several other genera of scolecospored ascomycetes and Phialophora conidial states, with a note on hyphopodia. Mycotaxon 11:1–129
Walker JM, Sutton BC, Pascoe IG (1992) Phaeoseptoria eucalypti and similar fungi on Eucalyptus, with description of Kirramyces gen. nov. (Coelomycetes). Mycol Res 96(11):911–924
Wanasinghe DN, Jones EBG, Camporesi E, Boonmee S, Karunarathna SC, Thines M, Mortimer PE, Xu J, Hyde KD (2014) Dematiopleospora mariae gen. sp. nov., from Ononis spinosain Italy. Crypto Mycol 35(2):105–117
Wang Y, Guo L, Hyde KD (2005) Taxonomic placement of sterile morphotypes of endophytic fungi from Pinus tabulaeformis (Pinaceae) in northeast China based on rDNA sequences. Fungal Divers 20:235–260
Webster J (1993) A rice root endophyte identified as Hadrospora fallax. Nova Hedw 57:141–142
Webster J, Lucas MT (1959) Observations on British species of Pleospora. Trans Brit Mycol Soc 42:332–342
Wehmeyer LE (1952) The genera Leptosphaeria, Pleospora and Clathrospora in Mt Rainier National Park. Mycologia 44:621–655
Wehmeyer LE (1961) A world monograph of the genus Pleospora and its segregates. University of Michigan Press, Michigan
Weir BS, Johnston PR, Damm U (2012) The Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex. Stud Mycol 73:115–180
Wetzel HC, Hulbert SH, Tisserat NA (1999) Molecular evidence for the presence of Ophiosphaerella narmarin. comb., a cause of spring dead spot of bermuda grass, in North America. Mycol Res 103:981–989
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic, San Diego, pp 315–322
Wijayawardene NN, McKenzie EHC, Hyde KD (2012) Towards incorporating anamorphic fungi in a natural classification checklist and notes for 2011. Mycosphere 3:157–228
Wijayawardene NN, Camporesi E, Song Y, Dai DQ, Bhat DJ, Mckenzie EHC, Chukeatirote E, Mel’nik VA, Wang Y, Hyde KD (2013a) Multi-gene analyses reveal taxonomic placement of Scolicosporium minkeviciusiiin Phaeosphaeriaceae (Pleosporales). Cryptogam Mycol 34(4):357–366
Wijayawardene NN, Song Y, Bhat DJ, McKenzie EHC, Chukeatirote E, Wang Y, Hyde KD (2013b) Wojnowicia viburni sp. nov. from China and its phylogenetic placement. Sydowia 65(1):113–128
Wijayawardene NN, Bhat DJ, Hyde KD, Camporesi E, Wikee S, Chethana KWT, Tangthirasunun N, Wang Y (2014a) Camarosporium sensu stricto in Pleosporinae, Pleosporales with two new species. Phytotaxa (Accepted)
Wijayawardene NN, Crous PW, Kirk PM, Hawksworth DL et al (2014b) Naming and outline of Dothideomycetes–2014. Fungal Divers 68 (inpress)
Wijayawardene NN, Hyde KD, Bhat DJ, Camporesi E, Schumacher RK, Chethana KWT, Wikee S, Bahkali AH, Wang Y (2014c) Camarosporium-like species are polyphyletic in Pleosporales; introducing Paracamarosporium and Pseudocamarosporium gen. nov. in Montagnulaceae. Cryptogam Mycol 35(2):177–198
Wijayawardene NN, Hyde KD, Bhat DJ, Wanasinghe DN, Song Y, Camporesi E, Schumacher RK, Wang Y (2014d) Additions to coelomycetous taxa in Pleosporinae; introducing Eucamarosporium gen. sp. nov. (in prep)
Wikee S, Udayanga D, Crous PW, Chukeatirote E, Mckenzie EHC, Bahkali AH, Dai DQ, Hyde KD (2011) Phyllosticta—an overview of current status of species recognition. Fungal Divers 51:43–61
Wilson IM, Knoyle JM (1961) Three species of Didymosphaeria on marine algae: D. danica (Berlese) comb. nov., D. pelvetiana Suth. and D. fucicola Suth. Trans Br Mycol Soc 44:55–71
Winter G (1872) Diagnosen neuer Pilze. Hedwigia 11:147–148
Yang Z (1994) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic estimation from DNA sequences with variable rates over sites: approximate methods. J Mol Evol 39:306–314
Yuan ZQ (1994) Barria, a new ascomycetous genus in the Phaeosphaeriaceae. Mycotaxon 51:313–316
Yuan ZQ, Barr ME (1994) Species of Chaetoplea on desert plants in China. Mycotaxon 52:495–499
Yuan ZW, Pei MH, Hunter T, Royle DJ (1998) Eudarluca caricis, the teleomorph of the mycoparasite Sphaerellopsis filum, on blackberry rust Phragmidium violaceum. Mycol Res 102:866–868
Yuan ZL, Lin FC, Zhang CL, Kubicek CP (2010) A new species of Harpophora (Magnaporthaceae) recovered from healthy wild rice (Oryza granulata) roots, representing a novel member of a bene¢cial dark septate endophyte. FEMS Microbiol Lett 307(1):94–101
Zhang Y, Schoch CL, Fournier J, Crous PW, De Gruyter J, Woudenberg JHC, Hirayama K, Tanaka K, Pointing SB, Hyde KD (2009) Multi-locus phylogeny of the Pleosporales: a taxonomic, ecological and evolutionary re-evaluation. Stud Mycol 64:85–102
Zhang Y, Crous PW, Schoch CL, Bahkali AH, Guo LD, Hyde KD (2011) A molecular, morphological and ecological re-appraisal of Venturiales—a new order of Dothideomycetes. Fungal Divers 51:249–277
Zhang Y, Crous PW, Schoch CL, Hyde KD (2012) Pleosporales. Fungal Divers 53:1–221
Zhaxybayeva O, Gogarten JP (2002) Bootstrap, Bayesian probability and maximum likelihood mapping: exploring new tools for comparative genome analyses. BMC Genomics 3(1):4
Acknowledgments
The Royal Golden Jubilee Ph. D. Program (PHD/0090/2551) under Thailand Research Fund, Humidtropics, a CGIAR Research Program that aims to develop new opportunities for improved livelihoods in a sustainable environment and Mae Fah Luang University (grant for study Dothideomycetes No. 56101020032) are gratefully thanked for partially funding this work. KD Hyde acknowledges The Chinese Academy of Sciences, project number 2013T2S0030, for the award of Visiting Professorship for Senior International Scientists at Kunming Institute of Botany. Wen Jing Li and International Fungal Research & Development Centre, Research Institute of Resource Insects, Chinese Academy of Forestry; Ruvishika S. Jayawardena and Institute of Plant and Environment Protection, Beijing Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences; Jun-Bo Yang and Plant Germplasm and Genomics Center in Germplasm Bank of Wild Species, Kunming Institute of Botany are gratefully thanked for the molecular laboratory support. The curators from BPI, BR, NY, S, and UB herbaria are gratefully thanked for loaning specimens and type information. Amy Y. Rossman, Chatsachee Chatpapamon, Dhanushka N. Wanasinghe, Dhanushka Udayanga, E. B. Gareth Jones, Joanne E. Taylor, Saowanee Wikee, Saranyaphat Boonme and Supalak Yacharoen are gratefully thanked for taxonomic literature information, cultures preparation and general assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 34 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phookamsak, R., Liu, JK., McKenzie, E.H.C. et al. Revision of Phaeosphaeriaceae . Fungal Diversity 68, 159–238 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-014-0308-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-014-0308-3