Abstract
Background
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) has tyrosine kinase activity and is a member of the epidermal growth factor receptor family. This initiates a variety of signal for pathways which leads to cell proliferation and tumourigenesis. In approximately 15–30% of breast cancers and 10–30% of gastric/gastroesophageal cancers, amplification or overexpression of HER2 occurs, and it serves as a prognostic and predictive biomarker. HER-2/neu is one of the most frequently studied molecular biological parameters in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC), but its prognostic impact has not been fully assessed. The objective of the current study was firstly to analyse the presence of HER-2 overexpression in EOC patients and secondly to evaluate association between human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER-2/neu) expression and progression-free survival in patients with EOC.
Method
In this prospective study of 2 years in our department, 186 gynaecological cancers were operated out of which 98 cases were operated for epithelial ovarian cancer and rest for cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, and other subtypes of ovarian cancer. In this study, HER2 gene status was evaluated in EOC by immunohistochemistry analysis, and overall survival of these patients was evaluated.
Results
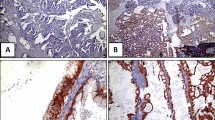
HER-2 overexpression was found in 22 of the 98 investigated cases (22.45%), in which 14 OC (14.29%) were weakly positive and 8 OC (8.16%) were moderately to intensely positive. In the study, increased HER2 expression was associated with decreased progression-free survival (PFS) and hence poor prognosis (P 0.054).
Conclusions
The introduction of HER2-directed therapies has dramatically influenced the outcome of patients with HER2 positive breast and gastric/gastroesophageal cancers. The present study findings provided that HER-2/neu expression in patients with OC has an adverse impact on the PFS. Therefore, our results show that the decision algorithm usually used in breast cancer by HER2 may be appropriate in ovarian cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, et al. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xuv J, et al. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300.
Hunn J, Rodriguez GC. Ovarian cancer: etiology, risk factors, and epidemiology. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2012;55:3–23.
Morgan RJ Jr, Armstrong DK, Alvarez RD, et al. Ovarian cancer, version 1.2016, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2016;14:1134–63.
Cramer DW, Bast RC Jr, Berg CD, et al. Ovarian cancer biomarker performance in prostate, lung, colorectal, and ovarian cancer screening trial specimens. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2011;4:365–74.
Saxena R, Dwivedi A. ErbB family receptor inhibitors as therapeutic agents in breast cancer: current status and future clinical perspective. Med Res Rev. 2012;32:166–215.
Liu N, Wang X, Sheng X. The clinicopathological characteristics of triple-negative epithelial ovarian cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2010;63:240–3.
Lenhard M, Tereza L, Heublein S, et al. Steroid hormone receptor expression in ovarian cancer: progesterone receptor B as prognostic marker for patient’s survival. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:553.
Demir L, Yigit S, Sadullahoglu C, et al. Hormone receptor, HER2/NEU and EGFR expression in ovarian carcinoma–is here a prognostic phenotype? Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15:9739–45.
de Toledo MC, Sarian LO, Sallum LF, et al. Analysis of the contribution of immunologically-detectable HER2, steroid receptors and of the “triple-negative” tumor status to disease-free and overall survival of women with epithelial ovarian cancer. Acta Histochem. 2014;116:440–7.
Yan B, Choo SN, Mulyadi P, et al. Dual-colour HER2/chromosome 17 chromogenic in situ hybridisation enables accurate assessment of HER2 genomic status in ovarian tumours. J Clin Pathol. 2011;64:1097–101.
Zhao D, Zhang F, Zhang W, et al. Prognostic role of hormone receptors in ovarian cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2013;23:25–33.
Ray-Coquard I, Guastalla JP, Allouache D, et al. HER2 Overexpression/amplification and trastuzumab treatment in advanced ovarian cancer: a GINECO phase II study. Clin Ovarian Cancer. 2009;2:17–22.
De Graeff P, Crijns AP, de Jong S, et al. Modest effect of p53, EGFR and HER-2/neu on prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 2009;101:149–59.
Noske A, Schwabe M, Weichert W, et al. An intracellular targeted antibody detects EGFR as an independent prognostic factor in ovarian carcinomas. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:294.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We declare that this manuscript is original; it has not been published anywhere before and is not currently being considered for publication elsewhere. We also confirm that the authors do not have any conflict of interest associated with publication of this work and no significant financial support/funding for this work has been received to influenced the outcome. The manuscript is read, approved, and consent is given by all the authors. We give our permission to reproduce any material of the article.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Dr. Sangeeta Pankaj: Additional Professor, Gynecological Oncology, RCC, IGIMS, Patna. Dr. Jaya Kumari: S.R., IGIMS, Patna. Dr. Vijayanand Choudhary: Additional Professor, Pathology, IGIMS, Patna. Dr. Anita Kumari: Senior Resident, IGIMS, Patna. Dr. Simi Kumari: Senior Resident, IGIMS, Patna. Dr. Anjili Kumari: Senior Resident, IGIMS, Patna. Dr. Syed Nazneen: Senior Resident, IGIMS, Patna. Dr. Richa Madhawi: Assistant Professor, RCC, IGIMS, Patna. Dr. Shishir Kumar: Assistant Professor, Biostatics, Department of Community Medicine, IGIMS, Patna.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pankaj, S., Kumari, J., Choudhary, V. et al. Prognostic Value of HER-2/neu Gene Amplification in Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma. J Obstet Gynecol India 69 (Suppl 2), 177–181 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-018-1186-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-018-1186-5