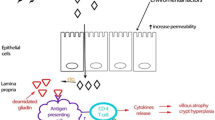
Abstract
Intestinal microbiota plays an important role in maintaining the overall health of an individual. It can be affected by diet but also inflammation of the intestine due to various causes. In the last decade, particular attention has been paid to the study of the interaction between mucosal cells and intestinal microbiota, and to the host immune response to change in community structure. Here, we review the most significant studies on human microbiota in patients with celiac disease, and also the potential biotechnological use of microorganisms for the production of gluten-free products.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arendt EK, Moroni A, Zannini E (2011) Medical nutrition therapy: use of sourdough lactic acid bacteria as a cell factory for delivering functional biomolecules and food ingredients in gluten free bread. Microb Cell Fact 10:S15
Ashorn S, Välineva T, Kaukinen K, Ashorn M, Braun J, Raukola H, Rantala I, Collin P, Mäki M, Luukkaala T, Iltanen S (2009) Serological responses to microbial antigens in celiac disease patients during a gluten-free diet. J Clin Immunol 29:190–195
Bergamo P, Maurano F, Mazzarella G, Iaquinto G, Vocca I, Rivelli AR, De Falco E, Gianfrani C, Rossi M (2011) Immunological evaluation of the alcohol-soluble protein fraction from gluten-free grains in relation to celiac disease. Mol Nutr Food Res 55:1266–1270
Biasucci G, Benenati B, Morelli L, Bessi E, Boehm G (2008) Cesarean delivery may affect the early biodiversity of intestinal bacteria. J Nutr 138:1796S–1800S
Cheng J, Palva AM, de Vos WM, Satokari R (2011) Contribution of the Intestinal Microbiota to Human Health: From Birth to 100 Years of Age. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 358:323–346. doi:10.1007/82_2011_189
Collado MC, Calabuig M, Sanz Y (2007) Differences between the fecal microbiota of coeliac infants and healthy controls. Curr Issues Intest Microbiol 8:9–14
Collado MC, Donat E, Ribes-Koninckx C, Calabuig M, Sanz Y (2008) Imbalances in faecal and duodenal Bifidobacterium species composition in active and non-active coeliac disease. BMC Microbiol 8:232
Collado MC, Donat E, Ribes-Koninckx C, Calabuig M, Sanz Y (2009) Specific duodenal and faecal bacterial groups associated with paediatric coeliac disease. J Clin Pathol 62:264–269
De Palma G, Nadal I, Collado MC, Sanz Y (2009) Effects of a gluten-free diet on gut microbiota and immune function in healthy adult human subjects. Br J Nutr 102:1154–1160
De Palma G, Nadal I, Medina M, Donat E, Ribes-Koninckx C, Calabuig M, Sanz Y (2010) Intestinal dysbiosis and reduced immunoglobulin-coated bacteria associated with coeliac disease in children. BMC Microbiol 10:63
De Palma G, Capilla A, Nova E, Castillejo G, Varea V, Pozo T, Garrote JA, Polanco I, López A, Ribes-Koninckx C, Marcos A, García-Novo MD, Calvo C, Ortigosa L, Peña-Quintana L, Palau F, Sanz Y (2012) Influence of milk-feeding type and genetic risk of developing coeliac disease on intestinal microbiota of infants: the PROFICEL study. PLoS One 7:e30791
Decker E, Hornef M, Stockinger S (2011) Cesarean delivery is associated with celiac disease but not inflammatory bowel disease in children. Gut Microbes 2:91–98
Di Cagno R, De Angelis M, Auricchio S, Greco L, Clarke C, De Vincenzi M, Giovannini C, D’Archivio M, Landolfo F, Parrilli G, Minervini F, Arendt E, Gobbetti M (2004) Sourdough bread made from wheat and nontoxic flours and started with selected lactobacilli is tolerated in celiac sprue patients. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1088–1096
Di Cagno R, Rizzello CG, Gagliardi F, Ricciuti P, Ndagijimana M, Francavilla R, Guerzoni ME, Crecchio C, Gobbetti M, De Angelis M (2009) Different fecal microbiotas and volatile organic compounds in treated and untreated children with celiac disease. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3963–3971
Di Cagno R, De Angelis M, De Pasquale I, Ndagijimana M, Vernocchi P, Ricciuti P, Gagliardi F, Laghi L, Crecchio C, Guerzoni ME, Gobbetti M, Francavilla R (2011) Duodenal and faecal microbiota of celiac children: molecular, phenotype and metabolome characterization. BMC Microbiol 11:219
Friman V, Nowrouzian F, Adlerberth I, Wold AE (2002) Increased frequency of intestinal Escherichia coli carrying genes for S. fimbriae and haemolysin in IgA-deficient individuals. Microb Pathog 32:35–42
Galle S, Schwab C, Dal Bello F, Coffey A, Gänzle MG, Arendt EK (2012) Influence of in-situ synthesized exopolysaccharides on the quality of gluten-free sorghum sourdough bread. Int J Food Microbiol 155:105–112
Gerez CL, Font de Valdez G, Rollán GC (2008) Functionality of lactic acid bacteria peptidase activities in the hydrolysis of gliadin-like fragments. Lett Appl Microbiol 47:427–432
Gerez CL, Dallagnol A, Rollán G, Font de Valdez G (2012) A combination of two lactic acid bacteria improves the hydrolysis of gliadin during wheat dough fermentation. Food Microbiol 32:427–430
Gobbetti M, Rizzello CG, Di Cagno R, De Angelis M (2007) Sourdough lactobacilli and celiac disease. Food Microbiol 24:187–196
Hedberg ME, Moore ER, Svensson-Stadler L, Hörstedt P, Baranov V, Hernell O, Wai SN, Hammarström S, Hammarström ML (2012) Lachnoanaerobaculum gen. nov., a new genus in the Lachnospiraceae: characterization of Lachnoanaerobaculum umeaense gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from the human small intestine, and Lachnoanaerobaculum orale sp. nov., isolated from saliva, and reclassification of Eubacterium saburreum (Prevot 1966) Holdeman and Moore 1970 as Lachnoanaerobaculum saburreum comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2685–2690
Ivanov II, Honda K (2012) Intestinal commensal microbes as immune modulators. Cell Host Microbe 12:496–508
Kamilova AT, Akhmedov NN, Pulatova DB, Nurmatov BA (2001) Intestinal microbiocenosis in children with intestinal enzymopathy. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol 3:97–99
Kopecný J, Mrázek J, Fliegerová K, Kott T (2006) Effect of gluten-free diet on microbes in the colon. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 51:287–290
Kopecný J, Mrázek J, Fliegerová K, Frühauf P, Tucková L (2008) The intestinal microflora of childhood patients with indicated celiac disease. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 53:214–216
M’hir S, Rizzello CG, Di Cagno R, Cassone A, Hamdi M (2009) Use of selected enterococci and Rhizopus oryzae proteases to hydrolyse wheat proteins responsible for celiac disease. J Appl Microbiol 106:421–431
Medina M, De Palma G, Ribes-Koninckx C, Calabuig M, Sanz Y (2008) Bifidobacterium strains suppress in vitro the pro-inflammatory milieu triggered by the large intestinal microbiota of coeliac patients. J Inflamm (Lond) 5:19
Moroni AV, Dal Bello F, Arendt EK (2009) Sourdough in gluten-free bread-making: an ancient technology to solve a novel issue? Food Microbiol 26:676–684
Moroni AV, Arendt EK, Dal BF (2011) Biodiversity of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts in spontaneously-fermented buckwheat and teff sourdoughs. Food Microbiol 28:497–502
Nadal I, Donat E, Ribes-Koninckx C, Calabuig M, Sanz Y (2007) Imbalance in the composition of the duodenal microbiota of children with coeliac disease. J Med Microbiol 56:1669–1674
Nistal E, Caminero A, Herrán AR, Arias L, Vivas S, de Morales JM, Calleja S, de Miera LE, Arroyo P, Casqueiro J (2012) Differences of small intestinal bacteria populations in adults and children with/without celiac disease: effect of age, gluten diet, and disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 18:649–656
Rizzello CG, De Angelis M, Di Cagno R, Camarca A, Silano M, Losito I, De Vincenzi M, De Bari MD, Palmisano F, Maurano F, Gianfrani C, Gobbetti M (2007) Highly efficient gluten degradation by lactobacilli and fungal proteases during food processing: new perspectives for celiac disease. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4499–4507
Rizzello CG, Coda R, De Angelis M, Di Cagno R, Carnevali P, Gobbetti M (2009) Long-term fungal inhibitory activity of water-soluble extract from Amaranthus spp. seeds during storage of gluten-free and wheat flour breads. Int J Food Microbiol 131:189–196
Rollán G, De Angelis M, Gobbetti M, de Valdez GF (2005) Proteolytic activity and reduction of gliadin-like fractions by sourdough lactobacilli. J Appl Microbiol 99:1495–1502
Rühmkorf C, Jungkunz S, Wagner M, Vogel RF (2012) Optimization of homoexopolysaccharide formation by lactobacilli in gluten-free sourdoughs. Food Microbiol 32:286–294
Salvatore S, Hauser B, Devreker T, Arrigo S, Vandenplas Y (2008) Chronic enteropathy and feeding in children: an update. Nutrition 24:1205–1216
Samaşca G, Sur G, Lupan I (2013) Current trends and investigative developments in celiac disease. Immunol Invest 42:273–284
Sánchez E, Nadal I, Donat E, Ribes-Koninckx C, Calabuig M, Sanz Y (2008) Reduced diversity and increased virulence-gene carriage in intestinal enterobacteria of coeliac children. BMC Gastroenterol 8:50
Sánchez E, Donat E, Ribes-Koninckx C, Calabuig M, Sanz Y (2010) Intestinal Bacteroides species associated with coeliac disease. J Clin Pathol 63:1105–1111
Sánchez E, De Palma G, Capilla A, Nova E, Pozo T, Castillejo G, Varea V, Marcos A, Garrote JA, Polanco I, López A, Ribes-Koninckx C, García-Novo MD, Calvo C, Ortigosa L, Palau F, Sanz Y (2011) Influence of environmental and genetic factors linked to celiac disease risk on infant gut colonization by Bacteroides species. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:5316–5323
Sánchez E, Laparra JM, Sanz Y (2012a) Discerning the role of Bacteroides fragilis in celiac disease pathogenesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:6507–6515
Sánchez E, Ribes-Koninckx C, Calabuig M, Sanz Y (2012b) Intestinal Staphylococcus spp. and virulent features associated with coeliac disease. J Clin Pathol 65:830–834
Sanz Y (2010) Effects of a gluten-free diet on gut microbiota and immune function in healthy adult humans. Gut Microbes 1:135–137
Sanz Y, Sánchez E, Marzotto M, Calabuig M, Torriani S, Dellaglio F (2007) Differences in faecal bacterial communities in coeliac and healthy children as detected by PCR and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 51:562–568
Sanz Y, De Pama G, Laparra M (2011) Unraveling the ties between celiac disease and intestinal microbiota. Int Rev Immunol 30:207–218
Schippa S, Iebba V, Barbato M, Di Nardo G, Totino V, Checchi MP, Longhi C, Maiella G, Cucchiara S, Conte MP (2010) A distinctive ‘microbial signature’ in celiac pediatric patients. BMC Microbiol 10:175
Serban DE (2011) The gut microbiota in the metagenomics era: sometimes a friend, sometimes a foe. Roum Arch Microbiol Immunol 70:134–140
Sun-Waterhouse D, Chen J, Chuah C, Wibisono R, Melton LD, Laing W, Ferguson LR, Skinner MA (2009) Kiwifruit-based polyphenols and related antioxidants for functional foods: kiwifruit extract-enhanced gluten-free bread. Int J Food Sci Nutr 60:251–264
Tlaskalová-Hogenová H, Farré-Castany MA, Stĕpánková R, Kozáková H, Tucková L, Funda DP, Barot R, Cukrowska B, Sinkora J, Mandel L, Karská K, Kolínská J (1995) The gut as a lymphoepithelial organ: the role of intestinal epithelial cells in mucosal immunity. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 40:385–391
Zannini E, Jones JM, Renzetti S, Arendt EK (2012a) Functional replacements for gluten. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 3:227–245
Zannini E, Pontonio E, Waters DM, Arendt EK (2012b) Applications of microbial fermentations for production of gluten-free products and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:473–485
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lupan, I., Sur, G., Deleanu, D. et al. Celiac disease microbiota and its applications. Ann Microbiol 64, 899–903 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0780-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-013-0780-0