Abstract
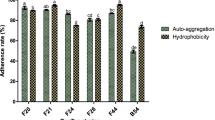
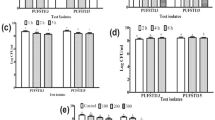
Probiotics have established their efficacy as dietary adjuncts providing benefits to consumers. However, selection of probiotics before incorporation into diet requires close scrutiny in the form of in vitro as well as in vivo tests. Three bacteriocinogenic Bacillus sp., namely, B. licheniformis Me1, B. flexus Hk1, and B. subtilis Bn1 previously isolated from milk, cheese and fermented beans, respectively, were characterized for typical in vitro probiotic criteria. When compared to probiotic Bacillus coagulans, all three cultures were found to possess better acid and bile tolerance. Cultures Me1 and Bn1, except Hk1, showed bile salt hydrolase activity. A marked difference in adhesion to hydrocarbons and auto-aggregation properties from 10–80 and 60–99%, respectively, were observed for the tested cultures. Highest antioxidant activity was measured for culture Hk1 (66.6%), whereas least activity of 53% was observed for culture Bn1. Cultures Me1 and Bn1 were sensitive to all the antibiotics tested, whereas Hk1 and B. coagulans showed resistance to the penicillin group of β-lactum antibiotics. All the tested cultures showed a broad spectrum of activity against food-borne pathogens. In co-cultivation studies, B. licheniformis Me1 completely inhibited the growth of the indicator pathogen Listeria monocytogenes ScottA. Overall, the test cultures exhibiting potential probiotic characteristics, particularly B. licheniformis Me1, can serve as probiotics of commercial interest.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abriouel H, Franz CMAP, Omar NB, Galvez A (2011) Diversity and applications of Bacillus bacteriocins. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35:201–232
Bae HD, Yanke LJ, Cheng KJ, Selinger LB (1999) A novel staining method for detecting phytase activity. J Microbiol Methods 39:17–22
Beaumont M (2002) Flavouring composition prepared by fermentation with Bacillus sp. Int J Food Microbiol 75:189–196
Begley M, Hill C, Gahan CGM (2006) Bile salt hydrolase activity in probiotics. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:1729–1738
Bernhard K, Schrempf H, Goebel W (1978) Bacteriocin and antibiotic resistance plasmids in Bacillus cereus and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 133:897–903
Brashears MM, Galyean ML, Loneragan GH, Killinger-Mann K (2003) Prevalence of Escherichia coli O157, H7 and performance by beef feedlot cattle given Lactobacillus direct-fed microbials. J Food Prot 66:748–754
Caldini G, Trotta F, Cenci G (2002) Inhibition of 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide genotoxicity by Bacillus strains. Res Microbiol 153:165–171
Canzi E, Guglielmetti S, Mora D, Tamagnini I, Parini C (2005) Conditions affecting cell surface properties of human intestinal Bifidobacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 88:207–219
Cartman M, Ragione L, Woodward MJ (2007) Bacterial spore formers as probiotics for poultry. Food Sci Technol Bull 4:21–30
Chateau N, Deschamps AM, Hadj-Sassi A (1994) Heterogeneity of bile salts resistance in the Lactobacillus isolates from a probiotic consortium. Lett Appl Microbiol 18:42–44
Chou L, Weimer B (1999) Isolation and characterization of acid- and bile-tolerant isolates from strains of Lactobacillus acidophilus. J Dairy Sci 82:23–31
Collado MC, Grześkowiak L, Salminen S (2007) Probiotic strains and their combination inhibit in vitro adhesion of pathogens to pig intestinal mucosa. Curr Microbiol 55:260–265
Conway PL, Gorbach SL, Goldin BR (1987) Survival of lactic acid bacteria in the human stomach and adhesion to intestinal cells. J Dairy Sci 70:1–12
Cosson C, Deschamps AM (1994) Behavior of probiotic strains in the presence of bile and bile salts. Nutr Food Microbiol 12:93–98
Cotelle N, Bemier JL, Catteau JP, Pommery J, Wallet JC, Gaydou EM (1996) Antioxidant properties of hydroxyl flavones. Free Radical Biol Med 20:35–43
Cutting SM (2011) Bacillus probiotics. Food Microbiol 28:214–220
De Vecchi E, Drago L (2006) Lactobacillus sporogenes or Bacillus coagulans: misidentification or mislabelling? Int J Probio Prebio 1:3–10
Duan XJ, Zhang WW, Li XM, Wang BG (2006) Evaluation of antioxidant property of extract and fractions obtained from a red alga, Polysiphonia urceolata. Food Chem 95:37–43
Dunne C, O’Mahony L, Murphy L, Thornton G, Morrissey D, O’Halloran S, Feeney M, Flynn S, Fitzgerald G, Daly C, Kiely B, O’Sullivan GC, Shanahan F, Collins JK (2001) In vitro selection criteria for probiotic bacteria of human origin: correlation with in vivo findings. Am J Clin Nutr 73:386S–392S
Durkee DL (2010) Coming out of the dairy case: New developments in shelf stable probiotic foods. http://www.foodmaster.com
EUCAST (2011). Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters. Version 1.3, January 2011. Available at http://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/. Accessed: March 18, 2011
FAO/WHO (2006) Probiotics in food. Health and nutritional properties and guidelines for evaluation. FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 85, ftp://ftp.fao.org/docrep/fao/009/a0512e/a0512e00.pdf
Fuller R (1989) Probiotics in man and animals. J Appl Bacteriol 66:365–378
Ganeshan P, Kumar CS, Bhaker N (2008) Antioxident properties of methanol extract and its solvent fractions obtained from selected Indian red seaweeds. Bioresource Technol 99:2717–2723
Gilbert P, Evans DJ, Evans E, Duguid IG, Brown MRW (1991) Surface characteristics and adhesion of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Appl Bacteriol 71:72–77
Gilliland SE, Staley TE, Bush LJ (1984) Importance in bile tolerance of Lactobacillus acidophilus used as a diatery adjunct. J Dairy Sci 67:3045–3051
Gracheva NM, Gavrilov AF, Soloveva AI, Smirnov VV, Sorokulova IB, Reznik SR, Chudnovskaia NV (1996) The efficacy of the new bacterial preparation biosporin in treating acute intestinal infections. Zh Mikrobiol Epidemiol Immunobiol 1:75–77
Guo XH, Kim JM, Nam HM, Park SY, Kim JM (2010) Screening lactic acid bacteria from swine origins for multistrain probiotics based on in vitro functional properties. Anaerobe 16:321–326
Havenaar R, Huis in’t Veld JHJ (1992) Probiotics: a general view. The lactic acid bacteria. In: Wood BJB (ed) The lactic acid bacteria in health and disease, vol 1. Elsevier, London, pp 151–71
Hong HA, Duc LH, Cutting SM (2005) The use of bacterial spore formers as probiotics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:813–835
Hong HA, Huang JM, Khaneja R, Hiep LV, Urdaci MC, Cutting SM (2008) The safety of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus indicus as food probiotics. J Appl Microbiol 105:510–520
Hosoi T, Kiuchi, K (2004) Production and probiotic effects of natto. In: Ricca E, Henriques AO, Cutting SM (eds) Bacterial spore formers: probiotics and emerging applications. Horizon Bioscience, Norfolk, pp 143–154.
Hyronimus B, Le Marrec C, Hadj Sassi A, Deschamps A (2000) Acid and bile tolerance of spore-forming lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 61:193–197
Inatsu Y, Nakamura N, Yuriko Y, Fushimi T, Watanasiritum L, Kawamoto S (2006) Characterization of Bacillus subtilis strains in Thua nao, a traditional fermented soybean food in northern Thailand. Lett Appl Microbiol 43:237–242
Kim KP, Rhee CH, Park HD (2002) Degradation of cholesterol by Bacillus subtilis SFF34 isolated from Korean traditional fermented flatfish. Lett Appl Microbiol 35:468–472
Lee Y-K, Nomoto K, Salminen S, Gorbach SL (1999) Handbook of Probiotics. Wiley, New York
Maruo T, Sakamoto M, Toda T, Benno Y (2006) Monitoring the cell number of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris FC in human feces by real-time PCR with strain-specific primers designed using the RAPD technique. Int J Food Microbiol 110:69–76
Mazza P (1994) The use of Bacillus subtilis as an antidiarrhoeal microorganism. Boll Chim Farm 133:3–18
Meroni PL, Palmieri R, Barcellini W, De Bartolo G, Zanussi C (1983) Effect of long-term treatment with B. subtilis on the frequency of urinary tract infections in older patients. Chemioterapia 2:142–144
Mora D, Fortina MG, Parini C, Ricci G, Gatti M, Giraffa G, Manachini PL (2002) Genetic diversity and technological properties of Streptococcus thermophilus strains isolated from dairy products. J Appl Microbiol 93:278–287
Nedelcheva P, Denkova Z, Denev P, Slavchev A, Krastanov A (2010) Probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum NBIMCC 2415 with antioxidant activity as a starter culture in the production of dried fermented meat products. Biotech Biotechnological Equip 24:1624–1630
Otero MC, Ocana VS, Nader-Macias EM (2004) Bacterial surface characteristics applied to selection of probiotic microorganisms. Methods Mol Biol 268:435–440
Pereira DIA, mc Cartney AL, Gibson GR (2003) An in vitro study of the probiotic potential of a bile salt hydrolysing Lactobacillus fermentum strain and determination of its cholesterol lowering properties. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4743–4752
Pinchuk IV, Bressollier P, Verneuil B, Fenet B, Sorokulova IB, Megraud F, Urdaci MC (2001) In vitro anti- Helicobacter pylori activity of the probiotic strain Bacillus subtilis is due to secretion of antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:3156–3161
Raghavendra P, Halami PM (2009) Screening, selection and characterization of phytic acid degrading lactic acid bacteria from chicken intestine. Int J Food Microbiol 133:129–134
Rolfe RD (2000) The role of probiotic cultures in the control of gastrointestinal health. J Nutr 130:396S–402S
Rowland I (1999) Probiotics and benefits to human health-the evidence in favour. Environ Microbiol 1:375–382
Salvetti S, Celandroni F, Ghelardi E, Baggiani A, Senesi S (2003) Rapid determination of vitamin B2 secretion by bacteria growing on solid media. J Appl Microbiol 95:1255–1260
Sanders ME, Morelli L, Tompkins TA (2003) Sporeformers as human probiotics: Bacillus, Sporolactobacillus and Brevibacillus. Compre Rev Food Sci Food Safe 2:101–110
Schillinger U, Guigas C, Holzapfel WH (2005) In vitro adherence and other properties of lactobacilli used in probiotic yogurt-like products. Int Dairy J 15:1289–1297
Sorokulova IB (1996) Outlook for using bacteria of the genus Bacillus for the design of new biopreparations. Antibiot Khimioter 41:13–15
Sorokulova IB, Pinchuk IV, Denayrolles M, Osipova IG, Huang JM, Cutting SM, Urdaci MC (2008) The safety of two Bacillus probiotic strains for human use. Dig Dis Sci 53:954–963
Stecchini ML, Torre MD, Munari M (2001) Determination of peroxy radical scavenging of lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 64:183–188
Sumi H, Nakajima N, Yatagai C (1995) A unique strong fibrinolytic enzyme (datsuwokinase) in skipjack “Shiokara”, a Japanese traditional fermented food. Comp Biochem Physiol 112:543–547
Tagg JR, Mac Given AR (1971) Assay system for bacteriocin. J Appl Bacteriol 21:943
Tam NKM, Uyen NQ, Hong HA, Duc LH, Hoa TT, Serra CR, Henriques AO, Cutting SM (2006) The intestinal life cycle of Bacillus subtilis and close relatives. J Bacteriol 188:2692–700
Urdaci MC, Pinchuk I (2004) Antimicrobial activity of Bacillus probiotics In: Ricca E, Henriques AO, Cutting SM (eds) Bacterial spore formers: probiotics and emerging applications. Horizon Bioscience, Norfolk, pp 171–182.
Verschuere L, Rombaut G, Sorgeloos P, Verstraete W (2000) Probiotic bacteria as biological control agents in aquaculture. Mic Mol Biol Rev 64:655–671
Vijayendra SVN, Gupta RC (2011) Assessment of probiotic and sensory properties of dahi and yoghurt prepared using bulk freeze-dried cultures in buffalo milk. Ann Microbiol. doi:10.1007/s13213-011-0331-5
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to acknowledge The Director, CFTRI, Mysore and Head, Food Microbiology Department, CFTRI, for providing the facilities. Work was carried out under MLP83. N.V. acknowledges CSIR for the fellowship. We thank Mrs. Vyshnavi BS for her technical involvement in the initial stage of this work and also Dr. Vijayendra SVN for editing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nithya, V., Halami, P.M. Evaluation of the probiotic characteristics of Bacillus species isolated from different food sources. Ann Microbiol 63, 129–137 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0453-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-012-0453-4