Abstract
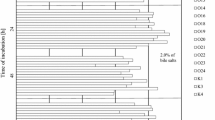
One hundred and two strains of Lactobacillus plantarum, all isolated from traditional dairy products of minority nationalities, were evaluated for in vitro probiotic properties, including acid and bile tolerance, aggregation activity, and antibacterial activity. Of these, 12 strains with a high tolerance to simulated gastric juice (pH 2.5, 3 h of incubation) were selected, of which eight of these also showed a good tolerance to bile salt. All selected 12 strains showed a high autoaggregation percentage after being incubated at room temperature for 20 h, and nine of these significantly inhibited growth of the five indicator intestinal pathogens. Six L. plantarum strains (IMAU10120, IMAU10156, IMAU40126, IMAU70004, IMAU60042, and IMAU60171) were selected for further evaluation of their fermentation characteristics, sensory quality, and viable counts, both during the fermentation process of soymilk and following a 28-day storage of the soymilk. The six strains had an acid-producing ability at the refrigerated temperature. All of the fermented soymilk samples had a viable count above log 8.45 CFU/ml, and viability in the samples was maintained during storage. Based on both the probiotic properties and fermented characteristics, L. plantarum IMAU10120 was the best potential probiotic strain of those tested for the production of fermented functional soymilk.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai S, Suzuky H, Fujimake M, Sakurai Y (1996) Studies on flavour components in soybean. Part 2. Phenolic acids in defatted soybean flour. Agric Biol Chem 30:364–369
Buono MA, Setser C, Erickson LE, Fung DYC (1990) Soymilk yoghurt: sensory evaluation and chemical measurement. J Food Sci 55:528–531
Chateau N, Deschamps AM, Sassi AH (1994) Heterogeneity of bile salts resistance in the Lactobacillus isolates of a probiotic consortium. Lett Appl Microbiol 18:2–4
Chun J, Kwon DY, Kim JS, Kim JH (2008) Sensory properties of soy yoghurts prepared from yellow and black soymilk using Streptococcus infantarius 12 and Weisellia sp. 4. J Sci Food Agric 88:1845–1849
Collado MC, Meriluoto J, Salminen S (2007) Measurement of aggregation properties between probiotics and pathogens: In vitro evaluation of different methods. J Microbiol Methods 71:71–74
Collado MC, Meriluoto J, Salminen S (2008) Adhesion and aggregation properties of probiotic and pathogen strains. Eur Food Res Technol 226:1065–1073
Conway PL, Gorbach SL, Goldin BR (1987) Survival of lactic acid bacteria in the human stomach and adhesion to intestinal cells. J Dairy Sci 70:1–12
Holzapfel WH, Haberer P, Geisen R, Björkroth J, Schillinger U (2001) Taxonomy and important features of probiotic microorganisms in food and nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr 73:365–373
Hsieh ML, Chou CC (2006) Mutagenicity and antimutagenic effect of soymilk fermented with lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 111:43–47
Jen-Wan H, Roch-Chui Y, Cheng-Chun C (2000) Changes in some components of soymilk during fermentation with bifidobacteria. Food Res Int 33:393–397
Jin L, Hyun SY, Kyu WC, Sejong O, Sae HK, Taehoon C, Bongjoon K, Kwang YW (2011) Evaluation of probiotic characteristics of newly isolated Lactobacillus spp.: Immune modulation and longevity. Int J Food Microbiol 148:80–86
Kailasapathy K, Chin J (2000) Survival and therapeutic potential of probiotic organisms with reference to Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium spp. Immunol. Cell Biol 78:80–88
Kailasapathy K, Rybka S (1997) Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium spp. – their therapeutic potential and survival in yogurt. Aust J Dairy Tech 52:28–35
Kazuhiro H, Joseph R (2000) The role of probiotic bacteria in cancer prevention. Microbes Infection 2:681–686
Kitawaki R, Nishimura Y, Takagi N, Iwasaki M, Tsuzuki K, Fukuda M (2009) Effects of Lactobacillus fermented soymilk and soy yogurt on hepatic lipid accumulation in rats fed a cholesterol-free diet. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:1484–1488
Lee YK, Salminen S (1995) The coming of age of probiotics. Trends Food Sci Technol 6:241–245
Macedo RF, Freitas RJ, Pandey A, Soccol CR (1999) Production and shelf-life studies of low cost beverage with soymilk, buffalo cheese whey and cow milk fermented by mixed cultures of Lactobacillus casei ssp. shirota and Bifidobacteriumadolescentis. J Basic Microbiol 39:243–251
Osaana ND, Henriksson A, Vasiljevic T, Shah NP (2007) α-Galactosidase and proteolytic activities of selected probiotic and dairy cultures in fermented soymilk. Food Chem 104:10–20
Parvez S, Malik KA, Kang SA, Kim HY (2006) Probiotics and their fermented food products are beneficial for health. J Appl Microbiol 100:1171–1185
Reid G, Sanders ME, Gaskins HR, Gibson GR, Mercenier A, Rastall RA, Roberfroid MB, Rowland I, Cherbut C, Klaenhammer TR (2003) New scientific paradigms for probiotics and prebiotics. J Clin Gastroenterol 37:105–118
Rekha CR, Vijayalakshmi G (2011) Isoflavone phytoestrogens in soymilk fermented with β-glucosidase producing probiotic lactic acid bacteria. Int J Food Sci Nutr 62:111–120
Salvador A, Fiszman SM (2004) Textural and sensory characteristics of whole and skimmed flavored set-type yogurt during long storage. J Dairy Sci 87:4033–4041
Sanders ME, Klaenhammer TR (2001) Invited Review: The scientific basis of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM functionality as a probiotic. J Dairy Sci 84:319–331
Scalabrini P, Rossi M, Spettoli P, Matteuzzi D (1998) Characterization of Bifidobacterium strains for use in soymilk fermentation. Int J Food Microbiol 39:213–219
Shimakawa Y, Matsubara S, Yuki N, Ikeda M, Ishikawa F (2003) Evaluation of Bifidobacterium breve strain Yakult-fermented soymilk as a probiotic food. Int J Food Microbiol 81:131–136
Tharmaraj N, Shah NP (2003) Selective enumeration of Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus, Streptococcus thermophilus, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacteria, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, and Propionibacteria. J Dairy Sci 86:2288–2296
Tsangalis D, Shah NP (2004) Metabolism of oligosaccharides and aldehydes and production of organic acids in soymilk by probiotic bifidobacteria. Int J Food Sci Technol 39:1–14
Vinderola G, Capellini B, Villarreal F, Suárez V, Quiberoni A, Reinheimer J (2008) Usefulness of a set of simple in vitro tests for the screening and identification of probiotic candidate strains for dairy use. LWT–Food Sci Technol 41:1678–1688
Walker DK, Gilliland SE (1993) Relationship among bile tolerance, bile salt deconjugation, and assimilation of cholesterol by Lactobacillus acidophilus. J Dairy Sci 76:956–961
Wang YC, Yu RC, Chou CC (2002) Growth and survival of bifidobacteria and lactic acid bacteria during the fermentation and storage of cultured soymilk drink. Food Microbiol 19:501–508
Wang YC, Yu RC, Chou CC (2006) Antioxidative activities of soymilk fermented with lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. Food Microbiol 23:128–135
Williams NT (2010) Probiotics. Am J Health Syst Pharm 67:449–458
Yan B, Yanchao Z, Yong Z, Yong L, Shuiquan W, Ximei D, Yanyan W, Heping Z (2010) Screening of potential probiotic properties of Lactobacillus fermentum isolated from traditional dairy products. Food Control 21:695–701
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (863 Planning) (Grant 2007AA10Z353), Earmarked Fund for Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System of China and National Key Technology R and D Program (No.2009BADC1B01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bao, Y., Zhang, Y., Li, H. et al. In vitro screen of Lactobacillus plantarum as probiotic bacteria and their fermented characteristics in soymilk. Ann Microbiol 62, 1311–1320 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0377-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0377-4