Abstract
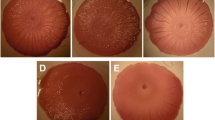
In this study, we investigated the survival, adhesion and the morphology of Shigella after its incubation in various concentrations of salts. Our results showed that, after 48 h of incubation, the rate of cell survival is inversely proportional to the increase of salinity of the medium. In addition to that, the results prove the evidence that the concentration of salt can significantly influence the capacity of Shigella to produce biofilm on Congo red agar and on polystyrene microplate wells. Adherence and invasion assays of Shigella were performed with KB cells line. Indeed, an increase of the salts concentration enhances the ability of Shigella species to attach and to invade the tissue culture cells. The percentage of adherence was increased to 15% and the invasion to 90% at 6% of salt. The atomic force micrographs showed a reduction of the cells’ size after stress.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abee T, Wouters JA (1999) Microbial stress response in minimal processing. Int J Food Microbiol 50:65–91
Adam B, Baillie GS, Douglas LJ (2002) Mixed species biofilms of Candida albicans and Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Med Microbiol 51:344–349
Ahmed F, Ansaruzzaman M, Haque E, Rao MR, Clemens JD (2001) Epidemiology of postshigellosis persistent diarrhea in young children. Pediatr Infect Dis J 20:525–530
Bernardini ML, Fontaine A, Sansonetti PJ (1990) The two-component regulatory system OmpR-EnvZ controls the virulence of Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol 172:6274–6281
Berry A, DeVault JD, Chakrabarty AM (1989) High osmolarity is a signal for enhanced algD biofilm detachment. Appl Environ Microbiol l70:7418–7425
Braga PC, Ricci D (1998) Atomic force microscopy: application to investigation of Escherichia coli morphology before and after exposure to cefodizime. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42:18–22
Briandet R, Meylheuc T, Maher C, Bellon-Fontaine MN (1999) Listeria monocytogenes Scott A: cell surface charge, hydrophobicity, and electron donor and acceptor characteristics under different environmental growth conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5328–5333
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2005) Preliminary FoodNet data on the incidence of infection with pathogens transmitted commonly through food — 10 sites, United States, 2004. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 54:352–356.
Chaieb K, Chehab O, Zmantar T, Rouabhia M, Mahdouani K, Bakhrouf A (2007) In vitro effect of pH and ethanol on biofilm formation by clinical ica positive Staphylococcus epidermidis strains. Ann Microbiol 57:431–437
Christensen GD, Simpson WA, Younger JJ, Baddour LM, Barrett FF, Melton DM, Beachey EH (1985) Adherence of coagulase-negative staphylococci to plastic tissue culture plates: a quantitative model for the adherence of staphylococci to medical devices. J Clin Microbiol 22:996–1006
Donlan RM, Costerton JW (2002) Biofilms: survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin Microbiol Rev 15:167–193
Ellafi A, Denden I, Ben Abdallah F, Souissi I, Bakhrouf A (2009) Survival and adhesion ability of Shigella spp. Strains after their incubation in seawater microcosms. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:1161–1168
Freeman DJ, Falkiner FR, Keane CT (1989) New method for detecting slime production by coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Pathol 42:872–874
Galin JE, Curtiss R (1991) Distribution of the invA, -B, -C, and -D genes of Salmonella typhimurinum among other Salmonella serovars: invA mutants of Salmonella typhi are deficient for entry into mammalian cells. Infect Immun 59:2901–2908
Givskov M, Eberl L, Moller S, Poulsen LK, Molin S (1994) Responses to nutrient starvation in Pseudomonas putida KT2442: analysis of general cross-protection, cell shape, and macromolecular content. J Bacteriol 176:7–14
Hamadi F, Latrache H, Elghmari A, Mabrrouki M, Ellouali M, Kuider N (2004) Effect of pH and ionic strength on hydrophobicity and electron donor and acceptor characteristics of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Ann Microbiol 54:213–225
Hoben HJ, Somasegaran P (1982) Comparison of the pour, spread, and drop plate methods for enumeration of Rhizobium spp. In inoculants made from presterilized peat. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:1246–1247
Huisman GW, Siegele DA, Zambrano MM, Kolter R et al (1996) Morphological and physiological changes during stationary phase in Escherichia coli and Salmonella. In: Neidhardt FC, Curtiss R, Gross CA, Ingraham JL, Lin EEC (eds) Cellular and molecular biology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 1672–1682
Hunt SM, Werner EM, Huang B, Hamilton MA, Stewart PS (2004) Hypothesis for the role of nutrient starvation in biofilm detachment. Appl Environ Microbiol l70:7418–7425
Jana TK, Srivastava AK, Csery K, Arora DK (2000) Influence of growth and environmental conditions transcription in mucoid and nonmucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains. J Bacteriol 171:2312–2317
Jiang X, Chai TJ (1996) Survival of Vibrio parahaemolyticus at low temperatures under starvation conditions and subsequent resuscitation of viable nonculturable cells. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1300–1305
Kalchayanand N, Dunne P, Sikes A, Ray B (2004) Viability loss and morphological change of foodborne pathogens following exposure to hydrostatic pressures in the presence and absence of bacteriocins. Int J Food Microbiol 91:91–98
Kjelleberg S, Humphrey BA, Marschall K (1983) Initial phases of starvation and activity of bacteria st surface. Appl Environ Microbiol 46:978–984
Leodocia MP, Kelynne ER, Shelley MP (1995) Increased protein secretion and adherence to HeLa cells by Shigella spp. following growth in the presence of Bile salts. Infect Immun 63:3642–3648
Lewis K (2001) Riddle of biofilm resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:999–1007
Mack D, Bartscht K, Fischer C et al (2001) Genetic and biochemical analysis of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm accumulation. Method Enzymol 336:215–239
Maurelli AT, Blackmon B, Curtiss RIII (1984) Temperature-dependent expression of on cell surface hydrophobicity of Pseudomonas fluorescens in non-specific adhesion. Can J Microbiol 46:28–37
Morita RY (1993) Bioavailability of energy and the starvation state. In: Kjelleberg S (ed) Starvation in bacteria. Plenum, New York, pp 1–23
Rachid S, Ohlsen K, Wallner U, Hacker J, Michael HM, Ziebuhr W (2000) Alternative transcription factor sigma (B) is involved in regulation of biofilm expression in a Staphylococcus aureus mucosal isolate. J Bacteriol 182:6824–6826
Subashkumar R, Thayumanavan T, Vivekanandhan G, Lakshmanaperumalsamy P (2006) Occurrence of Aeromonas hydrophila in acute gasteroenteritis among children. Indian J Med Res 123:61–66
Tartera C., Metcalf S.E. 1993. Osmolarity and growth phase overlap in regulation of Salmonella typhi. Adherence to and invasion of human intestinal cells. Inf Imm., 3084-3089.
Touati A, Achour W, Abbassi MS, Benhassen A (2007) Detection of ica genes and slime production in a collection of Staphylococcus epidermidis strains from catheter-related infections in neutropenic patients. Pathol Biol 55:277–282
Vesterlund S, Paltta J, Karp M, Ouwehand AC (2005) Adhesion of bacteria to resected human colonic tissue: quantitative analysis of bacterial adhesion and viability. Res Microbiol 156:238–244
Zaika LL, Phillips JG (2005) Model of the combined effects of temperature, pH and sodium chloride concentration on survival of Shigella flexneri strain 5348. Int J Food Microbiol 101:179–187
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr. Rafik Harreth for providing culture cells (Laboratory of Transmissible Diseases and Biologically Active Substances, Faculty of Pharmacy, Monastir, Tunisia).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellafi, A., Abdallah, F.B., Lagha, R. et al. Biofilm production, adherence and morphological alterations of Shigella spp. under salt conditions. Ann Microbiol 61, 741–747 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0190-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0190-5