Abstract
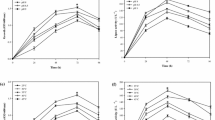
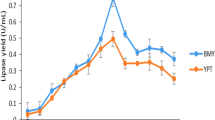
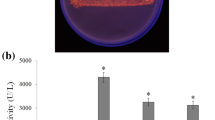
Several medium formulations were screened for the production of a thermostable and organic solvent tolerant lipase by a recombinant Escherichia coli BL21. The highest lipase production (28.9 ± 4.1 IU/mL) was obtained in Luria Bertani medium with the addition of 1% (w/v) glucose. The medium formulation and fermentation conditions were then subjected to sequential optimization. Using a Plackett-Burman design, glucose, NaCl, temperature and induction time were found to be the most significant variables affecting lipase production, and these were then optimized using response surface methodology (RSM). The large value of R 2 (0.979) showed that the quadratic model used for the prediction is highly significant. The optimum levels of these four significant variables (glucose, NaCl, temperature and induction time) as predicted by RSM were 32.4 g/L, 5 g/L, 31.7°C and 2.1 h, respectively. The amount of lipase activity (50.2 ± 4.5 IU/mL) produced under these optimal conditions fitted well to the value (48.9 IU/mL) predicted by RSM. Production of lipase in optimized fermentation was about 2.5-fold higher than in non-optimized fermentation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamczak M, Bornscheuer UT, Bednarski W (2009) The application of biotechnological methods for the synthesis of biodiesel. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 111:808–813
Azaman S, Ramakrishnan NR, Tan J, Rahim R, Abdullah M, Ariff AB (2010) Optimization of an induction strategy for improving interferon-alpha2b production in the periplasm of Escherichia coli using response surface methodology. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 56:141–150
Brozzoli V, Crognale S, Sampedro I, Federici F, Annibale AD, Petruccioli M (2009) Assessment of olive-mill wastewater as a growth medium for lipase production by Candida cylindracea in bench-top reactor. Bioresour Technol 100(13):3395–3402
Dandavate V, Jinjala J, Keharia H, Madamwar D (2009) Production, partial purification and characterization of organic solvent tolerant lipase from Burkholderia multivorans V2 and its application for ester synthesis. Bioresour Technol 100(13):3374–3381
Demain AL, Vaishnav P (2009) Production of recombinant proteins by microbes and higher organisms. Biotechnol Adv 27:297–306
Ebrahimpour A, Rahman RNRA, Ch'ng DHE, Basri M, Salleh AB (2008) A modeling study by response surface methodology and artificial neural network on culture parameters optimization for thermostable lipase production from a newly isolated thermophilic bacterium, Geobacillus stearothermophilus strain ARM. BMC Biotechnol 8:96. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-8-96
Eltaweel MA, Rahman RNZ, Salleh AB, Basri M (2005) An organic solvent stable lipase from Bacillus sp. Strain 42. Ann Microbiol 55(3):187–192
Farliahati MR, Ramanan RN, Rosfarizan M, Puspaningsih NNT, Ariff AB (2010) Enhanced production of xylanase by recombinant Escherichia coli DH5α through optimization of medium composition using response surface methodology. Ann Microbiol 60:279–285
Gao B, Su E, Lin J, Jiang Z, Ma Y, Wei D (2009) Development of recombinant Escherichia coli whole-cell biocatalyst expressing a novel alkaline lipase-coding gene from Proteus sp. for biodiesel production. J Biotechnol 139(2):169–175
Hamid THTA, Eltaweel MA, Rahman RNZRA, Basri M, Salleh AB (2009) Characterization and solvent stable features of Strep-tagged purified recombinant lipase from thermostable and solvent tolerant Bacillus sp. Strain 42. Ann Microbiol 59(1):111–118
Hasan F, Shah AA, Hameed A (2006) Industrial applications of microbial lipases. Enzym Microb Technol 39(2):235–251
Hoffmann F, Weber J, Rinas U (2002) Metabolic adaptation of Escherichia coli during temperature-induced recombinant protein production: 1. Readjustment of metabolic enzyme synthesis. Biotechnol Bioeng 80(3):313–319
Kane JF, Hartley DL (1988) Formation of recombinant protein inclusion bodies in Escherichia coli. Trends Biotechnol 6:95–101
Khare SK, Ruchi D, Anshu G (2008) Lipase from solvent tolerant Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain: Production optimization by response surface methodology and application. Bioresour Technol 99:4796–4802
Kogure T, Wakisaka N, Takaku H, Takagi M (2007) Efficient production of 2-deoxy-scyllo-inosose from d-glucose by metabolically engineered recombinant Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 129:502–509
Kumar SS, Gupta R (2008) An extracellular lipase from Trichosporon asahii MSR 54: Medium optimization and enantioselective deacetylation of phenyl ethyl acetate. Process Biochem 43(10):1054–1060
Kwon DK, Rhee JS (1986) A simple and rapid colorimetric method for determination of free fatty acids for lipase assay. J Am Oil Chem Soc 63:89–92
Liu CH, Lu WB, Chang JS (2006) Optimizing lipase production of Burkholderia sp. by response surface methodology. Process Biochem 41(9):1940–1944
Liu Z, Chi Z, Wang L, Li J (2008) Production, purification and characterization of an extracellular lipase from Aureobasidium pullulans HN2.3 with potential application for the hydrolysis of edible oils. Biochem Eng J 40:445–451
Liu Y, Wang F, Tan T (2009) Cyclic resolution of racemic ibuprofen via coupled efficient lipase and acid-base catalysis. Chirality 21(3):349–353
Low CT, Mohamad R, Tan CP, Long K, Ismail R, Lo SK, Lai OM (2007) Lipase-catalyzed production of medium-chain triacylglycerols from palm kernel oil distillate: Optimization using response surface methodology. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 109(2):107–119
Maldonado LMTP, Herna’ndez VEB, Rivero EM, Rosa APB, Flores JLF, Acevedo LGO, Rodrı’guez ADL (2007) Optimization of culture conditions for a synthetic gene expression in Escherichia coli using response surface methodology: the case of human interferon beta. Biomol Eng 24:217–222
Nikerel IE, Öner ET, Kirdar B, Yildirim R (2006) Optimization of medium composition for biomass production of recombinant Escherichia coli cells using response surface methodology. Biochem Eng J 32(1):1–6
Nthangeni MB, Patterton HG, Tonder A, Vergeer WP, Litthauer D (2001) Over-expression and properties of a purified recombinant Bacillus licheniformis lipase: a comparative report on Bacillus lipases. Enzyme Microb Technol 28(7–8):705–712
Oginoa H, Inouea S, Akagia R, Yasudaa M, Doukyub N, Ishimia K (2008) Refolding of a recombinant organic solvent-stable lipase, which is overexpressed and forms an inclusion body, and activation with lipase-specific foldase. Biochem Eng J 40(3):507–511
Pan H, Xie Z, Bao W, Zhang J (2008) Optimization of culture conditions to enhance cis-epoxysuccinate hydrolase production in Escherichia coli by response surface methodology. Biochem Eng J 42:133–138
Phue JN, Noronha SB, Hattacharyya R, Wolfe AJ, Shiloach J (2005) Glucose metabolism at high density growth of E. coli B and E. coli K: Differences in metabolic pathways are responsible for efficient glucose utilization in E. coli B as determined by microarrays and northern blot analyses. Biotechnol Bioeng 90(7):806–820
Phue JN, Lee SJ, Trinh L, Shiloach J (2008) Modified Escherichia coli B (BL21), a superior producer of plasmid DNA compared with Escherichia coli K (DH5α). Biotechnol Bioeng 101(4):831–836
Rahman RNZRA, Chor LT, Salleh AB, Basri M (2007) Geobacillus zalihaea T1, a novel thermophilic lipolytic bacterium isolated from palm oil mill effluent in Malaysia. BMC Microbiol 7:77. doi:10.1186/1471-2180-7-77
Rajendran A, Palanisamy A, Tiruthagiri V (2008) Evaluation of medium components by Plackett-Burman statistical design for lipase production by Candida rugosa and kinetic modelling. Chin J Biotechnol 24(3):436–444
Seeger A, Schneppe B, McCarthy JEG, Deckwer SD, Rinas U (1995) Comparison of temperature and isopropyl-b-D-thiogalacto-pyranoside-induced synthesis of basic fibroblast growth factor in high-cell-density cultures of recombinant Escherichia coli. Enzym Microb Technol 17:947–953
Sharma SS, Campbel JW, Frisch D, Blattner FR, Harcum SW (2007) Expression of two recombinant chloramphenicol acetyltransferase variants in highly reduced genome Escherichia coli Strains. Biotechnol Bioeng 98(5):1056–1070
Shiloach J, Fass R (2005) Growing E. coli to high cell density—a historical perspective on method development. Biotechnol Adv 23:345–357
Shiloach J, Rinas U (2009) Glucose and acetate metabolism in E. coli—system level analysis and biotechnological applications in protein production processes. In: Lee SY (ed) Systems Biology and Biotechnology of Escherichia coli, vol 18 C. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 377–400. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-9394-4
Shiloach J, Kaufman J, Guillard AS, Fass R (1996) Effect of glucose supply strategy on acetate accumulation, growth, and recombinant protein production by Escherichia coli BL21 (hDE3) and Escherichia coli JM 109. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:421–428
Singh V, Khan M, Khan S, Tripathi CKM (2009) Optimization of actinomycin V production by Streptomyces triostinicus using artificial neural network and genetic algorithm. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:379–385
Vera A, Montalban NG, Arıs A, Villaverde A (2007) The conformational quality of insoluble recombinant proteins is enhanced at low growth temperatures. Biotechnol Bioeng 96(6):1101–1106
Volpato G, Rodrigues RC, Heck JX, Ayub MAZ (2008) Production of organic solvent tolerant lipase by Staphylococcus caseolyticus EX17 using raw glycerol as substrate. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 83(6):821–828
Wang Y, Zhao M, Ou S, Song K, Han X (2009) Preparation of diacylglycerol-enriched palm olein by phospholipase A1-catalyzed partial hydrolysis. Eur J Lipid Sci Technol 111(7):652–662
Wolski E, Menusi E, Mazutti M, Toniazzo G, Rigo E, Cansian RL, Mossi A, Oliveira JV, Luccio MD, Oliveira D, Treichel H (2008) Response surface methodology for optimization of lipase production by an immobilized newly isolated Penicillium sp. Ind Eng Chem Res 47(23):9651–9657
Zhang A, Gao R, Diao N, Xie G, Gao G, Cao S (2009) Cloning, expression and characterization of an organic solvent tolerant lipase from Pseudomonas fluorescens JCM5963. J Mol Catal B Enzym 56:78–84
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelofer, R., Ramanan, R.N., Rahman, R.N.Z.R.A. et al. Sequential optimization of production of a thermostable and organic solvent tolerant lipase by recombinant Escherichia coli . Ann Microbiol 61, 535–544 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0170-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0170-9