Abstract
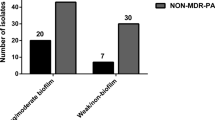
The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence of type III effector proteins (ExoS, ExoU, ExoT and ExoY)-encoding genes among clonally unrelated nosocomial Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains and to analyze their distribution in respect to the infection site and antimicrobial resistance. Polymerase chain reaction-based detection of the genes was performed on 176 non-duplicate P. aeruginosa isolates from three University hospitals in Sofia, previously genotyped by random amplified polymorphic DNA technique. The prevalence of the studied genes was as follows: exoS–61.9%, exoU–32.4%, exoT–100%, and exoY–85.8%. The part of P. aeruginosa strains harboring either the exoS (54.0%) or the exoU (23.8%) gene was higher (P < 0.001) than that of isolates containing both genes (8.5%). The gene dissemination varied according to the infection localization. The exoU gene manifested a higher spread (P < 0.001) among multidrug-resistant (MDR) than in non-MDR strains (42.6 vs 18.7%). In conclusion, the P. aeruginosa type III secretion system is present in nearly all studied isolates but the individual isolates from distinct infection sites differ in their effector genotypes. The ubiquity of type III effector proteins-encoding genes among clinical isolates is consistent with an important role for this system in P. aeruginosa pathogenesis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allewelt M, Coleman FT, Grout M, Priebe GP, Pier GB (2000) Acquisition of expression of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExoU cytotoxin leads to increased bacterial virulence in a murine model of acute pneumonia and systemic spread. Infect Immun 68:3998–4004
Berthelot P, Attree I, Plésiat P, Chabert J, de Bentzmann S, Pozzetto B, Grattard F, the Groupe d’Etudes des Septicémies à Pseudomonas aeruginosa (2003) Genotypic and phenotypic analysis of type III secretion system in a cohort of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia isolates: evidence for a possible association between O serotypes and exo genes. J Infect Dis 188:512–518
Blanc DS, Petignat C, Janin B, Bille J, Francioli P (1998) Frequency and molecular diversity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa upon admission and during hospitalization: a prospective epidemiologic study. Clin Microbiol Infect 4:242–247
CLSI (2007) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, 17th informational supplement, M100-S17. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne
Di Martino P, Gagniere H, Berry H, Bret L (2002) Antibiotic resistance and virulence properties of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from mechanically ventilated patients with pneumonia in intensive care units: comparison with imipenem-resistant extra-respiratory tract isolates from uninfected patients. Microbes Infect 4:613–620
Engel J, Balachandran P (2009) Role of Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III effectors in disease. Curr Opin Microbiol 12:61–66
Feltman H, Schulert G, Khan S, Jain M, Peterson L, Hauser AR (2001) Prevalence of type III secretion genes in clinical and environmental isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 147:2659–2669
Finck-Barbancon V, Goranson J, Zhu L, Sawa T, Wiener-Kronish JP, Fleiszig SM, Wu C, Mende-Mueller L, Frank DW (1997) ExoU expression by Pseudomonas aeruginosa correlates with acute cytotoxicity and epithelial injury. Mol Microbiol 25:547–557
Finnan S, Morrissey JP, O’Gara F, Boyd EF (2004) Genome diversity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis patients and the hospital environment. J Clin Microbiol 42:5783–5792
Garey KW, Vo QP, Larocco MT, Gentry LO, Tam VH (2008) Prevalence of type III secretion protein exoenzymes and antimicrobial susceptibility patterns from bloodstream isolates of patients with Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia. J Chemother 20:714–720
Goehring UM, Schmidt G, Pedersen KJ, Aktories K, Barbieri JT (1999) The N-terminal domain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S is a GTPase-activating protein for Rho GTPases. J Biol Chem 274:36369–36372
Hauser A (2009) The type III secretion system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: infection by injection. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:654–665
Hauser AR, Cobb E, Bodi M, Mariscal D, Valles J, Engel JN, Rello J (2002) Type III protein secretion is associated with poor clinical outcomes in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Crit Care Med 30:521–528
Kirikae T, Mizuguchi Y, Arakawa Y (2008) Investigation of isolation rates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa with and without multidrug resistance in medical facilities and clinical laboratories in Japan. J Antimicrob Chemother 61:612–615
Krall R, Schmidt G, Aktories K, Barbieri JT (2000) Pseudomonas aeruginosa ExoT is a Rho GTPase-activating protein. Infect Immun 68:6066–6068
Kurahashi K, Kajikawa O, Sawa T, Ohara M, Gropper MA, Frank DW, Martin TR, Wiener-Kronish JP (1999) Pathogenesis of septic shock in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. J Clin Invest 104:743–750
Lanotte P, Watt S, Mereghetti L, Dartiguelongue N, Rastegar-Lari A, Goudeau A, Quentin R (2004) Genetic feature of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from cystic fibrosis patients compared with those of isolates from other origins. J Med Microbiol 53:73–81
Lomholt JA, Poulsen K, Kilian M (2001) Epidemic population structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: evidence for a clone that is pathogenic to the eye and that has a distinct combination of virulence factors. Infect Immun 69:6284–6295
Nicas TI, Bradley J, Lochner JE, Iglewski BH (1985a) The role of exoenzyme S in infections with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis 152:716–721
Nicas TI, Frank DW, Stenzel P, Lile JD, Iglewski BH (1985b) Role of exoenzyme S in chronic Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol 4:175–179
Pagani L, Colinon C, Migliavacca R, Labonia M, Docquier JD, Nucleo E, Spalla M, Li Bergoli M, Rossolini GM (2005) Nosocomial outbreak caused by multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa producing IMP-13 metallo-β-lactamase. J Clin Microbiol 43:3824–3828
Phillips RM, Six DA, Dennis EA, Ghosh P (2003) In vivo phospholipase activity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytotoxin ExoU and protection of mammalian cells with phospholipase A2 inhibitors. J Biol Chem 278:41326–41332
Pinheiro MRS, Lacerda HR, Melo RGL, Maciel MA (2008) Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: factors relating to mortality with emphasis on resistance pattern and antimicrobial treatment. Braz J Infect Dis 12:509–515
Pirnay J-P, Bilocq F, Pot B, Cornelis P, Zizi M, Van Eldere J, Deschaght P, Vaneechoutte M, Jennes S, Pitt T, De Voss D (2009) Pseudomonas aeruginosa population structure revisited. PLoS ONE 4:e7740. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0007740
Rajan S, Saiman L (2002) Pulmonary infections in patients with cystic fibrosis. Semin Respir Infect 17:47–56
Schulert GS, Feltman H, Rabin SD, Martin CG, Battle SE, Rello J, Hauser AR (2003) Secretion of the toxin ExoU is a marker for highly virulent Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates obtained from patients with hospital-acquired pneumonia. J Infect Dis 188:1695–1706
Sekiguchi J, Asagi T, Miyoshi-Akiyama T, Kasai A, Mizuguchi Y, Araake M, Fujino T, Kikuchi H, Sasaki S, Watari H, Kojima T, Miki H, Kanemitsu K, Kunishima H, Kikuchi Y, Kaku M, Yoshikura H, Kuratsuji T, Kirikae T (2007) Outbreaks of multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in community hospitals in Japan. J Clin Microbiol 45:979–989
Stover CK, Pham XQ, Erwin AL et al (2000) Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature 406:959–964
Strateva T (2008) Microbiological and molecular-genetic investigations on resistance mechanisms and virulence factors in clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PhD dissertation, Medical University of Sofia, Bulgaria
Tamura M, Ajayi T, Allmond LR, Moriyama K, Wiener-Kronish JP, Sawa T (2004) Lysophospholipase A activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III secretory toxin ExoU. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 316:323–331
Vallis AJ, Fink-Barbacon V, Yahr TL, Frank DW (1999) Biological effects of Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III-secreted proteins on CHO cells. Infect Immun 67:2040–2044
Van Delden C, Iglewski BH (1998) Cell-to-cell signaling and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Emerg Infect Dis 4:551–560
Wang CY, Jerng JS, Cheng KY, Lee LN, Yu CJ, Hsueh PR, Yang PC (2006) Pandrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa among hospitalised patients: clinical features, risk-factors and outcomes. Clin Microbiol Infect 12:63–68
Winstanley C, Kaye SB, Neal TJ, Chilton HJ, Miksch S, Hart CA, Microbiology Ophthalmic Group (2005) Genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates associated with ulcerative keratitis. J Med Microbiol 54:519–526
Yahr TL, Vallis AJ, Hancock MK, Barbieri JT, Frank DW (1998) ExoY, an adenylate cyclase secreted by the Pseudomonas aeruginosa type III system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13899–13904
Zaborina O, Kohler JE, Wang Y, Bethel C, Shevchenko O, Wu L, Turner JR, Alverdy JC (2006) Identification of multi-drug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates that are highly disruptive to the intestinal epithelial barrier. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob 5:14
Zhu H, Conibear TCR, Bandara R, Aliwarga Y, Stapleton F, Willcox MDP (2006) Type III secretion system-associated toxins, proteases, serotypes, and antibiotic resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates associated with keratitis. Curr Eye Res 31:297–306
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by a grant from the Medical University of Sofia (Council of Medical Science, project no. 4/2009, grant no. 20/2009).
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strateva, T., Markova, B., Ivanova, D. et al. Distribution of the type III effector proteins-encoding genes among nosocomial Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from Bulgaria. Ann Microbiol 60, 503–509 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0079-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-010-0079-3