Abstract
Exposure to toxins through contaminated food is a serious concern. For the detection of toxins in complex matrices, there are many analytical instrumentation-based methods; however, these approaches are generally expensive, laborious to perform, and require skilled technicians. Thus, they can only be utilized in centralized laboratories. To efficiently prevent the contamination by toxins and improve food safety, the use of on-site toxin detection methods enabling simple, rapid, sensitive, specific, reliable, and affordable identification of toxins is required. A colorimetric toxin detection strategy providing a naked-eye readout platform suits these requirements. Notably, the implementation of nanomaterials in the colorimetric strategy has proven to rapidly generate a higher capacity for detectable color responses owing to their unique physicochemical and catalytic properties. In this review, recent research on colorimetric toxin detection utilizing diverse nanostructures including noble metal nanoparticles and enzyme-like catalytic nanomaterials (nanozymes) is reviewed and discussed. Current challenges and future prospects for the utilization of nanomaterials in colorimetric toxin detection are also discussed.

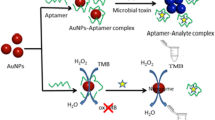
Reproduced with permission from Elsevier

Reproduced with permission from Elsevier

Reproduced with permission from Elsevier

Reproduced with permission from Elsevier
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization. Natural toxins in food. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/natural-toxins-in-food. Accessed 29 Apr 2020
Goud, K.Y., Kailasa, S.K., Kumar, V., Tsang, Y.F., Lee, S.E., Gobi, K.V., Kim, K.-H.: Progress on nanostructured electrochemical sensors and their recognition elements for detection of mycotoxins: a review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 121, 205–222 (2018)
Cinar, A., Onbaşi, E.: Mycotoxins: the hidden danger in foods. In: Sabunocuoglu, S. (ed.) Mycotoxins and Food Safety, pp. 1–21. IntechOpen, Boston (2019)
Rocha, M.E.B., Freire, F.D.C.O., Maia, F.E.F., Guedes, M.I.F., Rondina, D.: Mycotoxins and their effects on human and animal health. Food Control 36, 159–165 (2014)
Bano, K., Khan, W.S., Cao, C., Khan, R.F., Webster, T.J.: Biosensors for detection of marine toxins. In: Wu, A., Khan, W.S. (eds.) Nanobiosensors: From Design to Application, pp. 329–356. Wiley-VCH, Germany (2020)
Lan, L., Yao, Y., Ping, J., Ying, Y.: Recent progress in nanomaterial-based optical aptamer assay for the detection of food chemical contaminants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 9, 23287–23301 (2017)
Holzinger, M., Le Goff, A., Cosnier, S.: Nanomaterials for biosensing applications: a review. Front. Chem. 2, 1–10 (2014)
Malhotra, B.D., Srivastava, S., Ali, M.A., Singh, C.: Nanomaterial-based biosensors for food toxin detection. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 174, 880–896 (2014)
Sharma, R., Ragavan, K.V., Thakur, M.S., Raghavarao, K.S.M.S.: Recent advances in nanoparticle based aptasensors for food contaminants. Biosens. Bioelectron. 74, 612–627 (2015)
Xue, Z., Zhang, Y., Yu, W., Zhang, J., Wang, J., Wan, F., Kim, Y., Liu, Y., Kou, X.: Recent advances in aflatoxin B1 detection based on nanotechnology and nanomaterials—a review. Anal. Chim. Acta 1069, 1–27 (2019)
Ahn, G., Sekhon, S.S., Jeon, Y.-E., Kim, M.-S., Won, K., Kim, Y.-H., Ahn, J.-Y.: Detection of endotoxins using nanomaterials. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Sci. 9, 259–268 (2017)
Shin, H.Y., Park, T.J., Kim, M.I.: Recent research trends and future prospects in nanozymes. J. Nanomater. 756278, 1–11 (2015)
Wang, F., Liu, S., Lin, M., Chen, X., Lin, S., Du, X., Li, H., Ye, H., Qiu, B., Lin, Z., Guo, L., Chen, G.: Colorimetric detection of microcystin-LR based on disassembly of orient-aggregated gold nanoparticle dimers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 68, 475–480 (2015)
Csáki, A., Stranik, O., Fritzsche, W.: Localized surface plasmon resonance based biosensing. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 18, 279–296 (2018)
Cordeiro, M., Carlos, F.F., Pedrosa, P., Lopez, A., Baptista, P.V.: Gold nanoparticles for diagnostics: advances towards points of care. Diagnostics 6, 1–20 (2016)
Lismont, M., Dreesen, L.: Comparative study of Ag and Au nanoparticles biosensors based on surface plasmon resonance phenomenon. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 32, 1437–1442 (2012)
Huang, Y., Ren, J., Qu, X.: Nanozymes: classification, catalytic mechanisms, activity regulation, and applications. Chem. Rev. 119, 4357–4412 (2019)
Huang, L., Chen, K., Zhang, W., Zhu, W., Liu, X., Wang, J., Wang, R., Hu, N., Suo, Y., Wang, J.: ssDNA-tailorable oxidase-mimicking activity of spinel MnCo2O4 for sensitive biomolecular detection in food sample. Sens. Actuators, B 269, 79–87 (2018)
Batule, B.S., Park, K.S., Gautam, S., Cheon, H.J., Kim, M.I., Park, H.G.: Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of sonochemically synthesized protein copper nanoflowers and its application for the sensitive detection of glucose. Sens. Actuators, B 283, 749–754 (2019)
Kim, M.S., Cho, S., Joo, S.H., Lee, J., Kwak, S.K., Kim, M.I., Lee, J.: N- and B-codoped graphene: a strong candidate to replace natural peroxidase in sensitive and selective bioassays. ACS Nano 13, 4312–4321 (2019)
Gao, L., Zhuang, J., Nie, L., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y., Gu, N., Wang, T., Feng, J., Yang, D., Perrett, S., Yan, X.: Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2, 577–583 (2007)
Lai, W., Wei, Q., Xu, M., Zhuang, J., Tang, D.: Enzyme-controlled dissolution of MnO2 nanoflakes with enzyme cascade amplification for colorimetric immunoassay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 89, 645–651 (2017)
Liu, W., Gan, C., Chang, W., Qileng, A., Lei, H., Liu, Y.: Double-integrated mimic enzymes for the visual screening of microcystin-LR: copper hydroxide nanozyme and G-quadruplex/hemin DNAzyme. Anal. Chim. Acta 1054, 128–136 (2019)
Sun, S., Zhao, R., Feng, S., Xie, Y.: Colorimetric zearalenone assay based on the use of an aptamer and of gold nanoparticles with peroxidase-like activity. Microchim. Acta 185, 1–7 (2018)
Tan, F., Xie, X., Xu, A., Deng, K., Zeng, Y., Yang, X., Huang, H.: Fabricating and regulating peroxidase-like activity of eggshell membrane-templated gold nanoclusters for colorimetric detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Talanta 194, 634–642 (2019)
Wang, C., Qian, J., Wang, K., Yang, X., Liu, Q., Hao, N., Wang, C., Dong, X., Huang, X.: Colorimetric aptasensing of ochratoxin A using Au@Fe3O4 nanoparticles as signal indicator and magnetic separator. Biosens. Bioelectron. 77, 1183–1191 (2016)
Bazin, I., Tria, S.A., Hayat, A., Marty, J.-L.: New biorecognition molecules in biosensors for the detection of toxins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 87, 285–298 (2017)
Gu, H., Duan, N., Wu, S., Hao, L., Xia, Y., Ma, X., Wang, Z.: Graphene oxide-assisted non-immobilized SELEX of okdaic acid aptamer and the analytical application of aptasensor. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–9 (2016)
Ha, S.-J., Park, J.-H., Lee, B., Kim, M.-G.: Label-free direct detection of saxitoxin based on a localized surface plasmon resonance aptasensor. Toxins 11, 500–517 (2019)
Kant, K., Shahbazi, M.-A., Dave, V.K., Ngo, T.A., Chidambara, V.A., Than, L.Q., Bang, D.D., Wolff, A.: Microfluidic devices for sample preparation and rapid detection of foodborne pathogens. Biotechnol. Adv. 36, 1003–1024 (2018)
Luan, Y., Chen, Z., Xie, G., Chen, J., Lu, A., Li, C., Fu, H., Ma, Z., Wang, J.: Rapid visual detection of aflatoxin B1 by label-free aptasensor using unmodified gold nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 15, 1357–1361 (2015)
Wang, X., Niessner, R., Knopp, D.: Controlled growth of immunogold for amplified optical detection of aflatoxin B1. Analyst 140, 1453–1458 (2015)
Ji, Y., Ren, M., Li, Y., Huang, Z., Shu, M., Yang, H., Xiong, Y., Xu, Y.: Detection of aflatoxin B1 with immunochromatographic test strips: enhanced signal sensitivity using gold nanoflowers. Talanta 142, 206–212 (2015)
Wu, K., Ma, C., Zhao, H., Chen, M., Deng, Z.: Sensitive aptamer-based fluorescene assay for ochratoxin A based on RNase H signal amplification. Food Chem. 277, 273–278 (2019)
Tian, F., Zhou, J., Jiao, B., He, Y.: A nanozyme-based cascade colorimetric aptasensor for amplified detection of ochratoxin A. Nanoscale 11, 9547–9555 (2019)
He, Y., Tian, F., Zhou, J., Zhao, Q., Fu, R., Jiao, B.: Colorimetric aptasensor for ochratoxin A detection based on enzyme-induced gold nanoparticle aggregation. J. Hazard. Mater. 388, 121758 (2019)
Tian, F., Zhou, J., Fu, R., Cui, Y., Zhao, Q., Jiao, B., He, Y.: Multicolor colorimetric detection of ochratoxin A via structure-switching aptamer and enzyme-induced metallization of gold nanorods. Food Chem. 320, 126607 (2020)
Sun, Y., Xing, G., Yang, J., Wang, F., Deng, R., Zhang, G., Hu, X., Zhang, Y.: Development of an immunochromatographic test strip for simultaneous qualitative and quantitative detection of ochratoxin A and zearalenone in cereal. J. Sci. Food Agric. 96, 3673–3678 (2016)
Morabito, S., Silvestro, S., Faggio, C.: How the marine biotoxins affect human health. Nat. Prod. Res. 32, 621–631 (2018)
Wei, J., Chang, W., Qileng, A., Liu, W., Zhang, Y., Rong, S., Lei, H., Liu, Y.: Dual-modal split-type immunosensor for sensitive detection of microcystin-LR: Enzyme-induced photoelectrochemistry and colorimetry. Anal. Chem. 90, 9606–9613 (2018)
Fu, L.-L., Zhao, X.-Y., Ji, L.-D., Xu, J.: Okadaic acid (OA): Toxicity, detection and detoxification. Toxicon 160, 1–7 (2019)
Lago, J., Rodríguez, L.P., Blanco, L., Vieites, J.M., Cabado, A.G.: Tetrodotoxin, an extremely potent marine neurotoxin: distribution, toxicity, origin and therapeutical uses. Mar. Drugs 13, 6384–6406 (2015)
Ling, S., Li, X., Zhang, D., Wang, K., Zhao, W., Zhao, Q., Wang, R., Yuan, J., Xin, S., Wang, S.: Detection of okadaic acid (OA) and tetrodotoxin (TTX) simultaneously in seafood samples using colloidal gold immunoassay. Toxicon 165, 103–109 (2019)
Jin, X., Chen, J., Zeng, X., Xu, L., Wu, Y., Fu, F.: A signal-on magnetic electrochemical immunosensor for ultra-sensitive detection of saxitoxin using palladium-doped graphitic carbon nitride-based non-competitive strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 128, 45–51 (2019)
Mondal, B., Ramlal, S., Lavu, P.S., Bhavanashri, N., Kingston, J.: Highly sensitive colorimetric biosensor for staphylococcal enterotoxin B by a label-free aptamer and gold nanoparticles. Front. Microbiol. 9, 1–8 (2018)
Zhou, D., Xie, G., Cao, X., Chen, X., Zhang, X., Chen, H.: Colorimetric determination of staphylococcal enterotoxin B via DNAzyme-guided growth of gold nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 183, 2753–2760 (2016)
Aguila, J.L., Varshney, A.K., Wang, X., Stanford, L., Scharff, M., Fries, B.C.: Detection and measurement of staphylococcal enterotoxin-like K (SEl-K) secretion by Staphylococcus aureus clinical isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 52, 2536–2543 (2014)
Alexis, L., Zhang, L., Hu, D., Salmain, M., Mazouzi, Y., Flack, R., Liedberg, B., Boujday, S.: Core–shell gold/silver nanoparticles for localized surface plasmon resonance-based naked-eye toxin biosensing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 46462–46471 (2019)
Selvaprakash, K., Chen, Y.-C.: Glycosylated protein-functionalized gold nanoparticle-based detection of heat-labile enterotoxin from complex samples. Sens. Actuators, B 322, 128640 (2018)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government [Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2019R1A2C1087459)] and by the Gachon University research fund of 2019 (GCU-2019-0812). This work was also supported under the framework of international cooperation program managed by NRF (NRF-2019K2A9A2A06020985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, Q.H., Kim, M.I. Using Nanomaterials in Colorimetric Toxin Detection. BioChip J 15, 123–134 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00013-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00013-4