Abstract
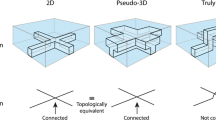
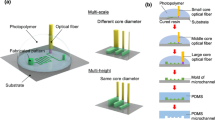
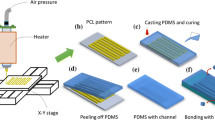
We report on a simple way to produce three-dimensional (3D) microstructures embedded in microchannel which is used as a micromixer in a microfluidic device. The micromilling machine has great capability of easily transferring the microstructured matter design onto the device substrate. According to the determined microstructure design, the different channel depths, widths, and complicated designs of microstructure are easily realized by the micromilling machine and thermoplastic substrate. These results provide a cost-effective way to produce master molds or their replica for the generation of complicated 3D micromixer embedded microfluidic devices. Furthermore, the complicated microstructure is suitable to use as micromixer which is important in microfluidicbased applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Squires, T.M. & Quake, S.R. Microfluidics: fluidic physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77, 977–1026 (2005).
Wang, K.W. et al. Organoclay-assisted interfacial polymerization for microfluidic production of monodisperse PEG-microdroplets and in situ encapsulation of E. coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 109, 289–294 (2012).
Lee, K.G. et al. Synthesis and utilization of E. coliencapsulated PEG-based microdroplet using a microfluidic chip for biological application. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 107, 747–751 (2010).
Song, H., Chen, D.L. & Ismagilov, R.F. Reactions in droplets in microfluidic channels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 45, 7336–7356 (2006).
Song, Y., Hormes, J. & Kumar, C.S.S.R. Microfluidic synthesis of nanomaterials. Small 4, 698–711 (2008).
Hou, H.W. et al. Deformability based cell marginationA simple microfluidic design for malaria-infected erythrocyte separation. Lab. Chip 10, 2605–2613 (2010).
Dittrich, P.S. & Manz, A. Lab-on-a-chip: microfluidics in drug discovery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 5, 210–218 (2006).
Ghanim, M.H. & Abuullah, M.Z. Design of disposable DNA biosensor microchip with amperometirc detection featuring PCB substrate. BioChip J. 7, 51–56 (2013).
Khandurina, J. et al. Integrated system for rapid PCRbased DNA analysis in microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 72, 2995–3000 (2010).
Liao, Y. et al. Rapid prototyping of three-dimensional microfluidic mixers in glass by femtosecond laser direct writing. Lab. Chip 12, 746–749 (2012).
Nguyen, N.-T. & Wu, Z. Micromixers-a review. J. Micromech. Microeng. 15, R1–R16 (2005).
Lee, C.Y., Chang, C.L., Wang, T.N. & Fu, L.M. Microfluidic mixing: a review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12, 3263–3287 (2011).
Chen, J. & Yang, R. Electroosmotic flow mixing in zigzag microchannels. Electrophoresis 28, 975–983 (2007).
Mengeaud, V., Josserand, J. & Girault, H.G. Mixing processes in a zigzag microchannel: Finite element simulations and optical study. Anal. Chem. 74, 4279–4286 (2002).
Leong, T.G., Zarafshar, A.M. & Gracias, D.H. Threedimensional fabrication at small size scales. Small 6, 792–806 (2010).
Whitesides, G.M., Ostuni, E., Takayama, S., Jiang, X. & Ingber, D.E. Soft lithography in biology and biochemicstry. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 3, 335–373 (2001).
Xia, Y. & Whitesides G.M. Soft lithography. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 28, 153–184 (1998).
Pemg, B., Wu, C., Shen, Y. & Lin, Y. Microfluidic chip fabrication using hot embossing and thermal bonding of COP. Polym. Adv. Technol. 21, 457–466 (2010).
Cameron, N.S., Roberge, H., Vers, T., Jakeway, S.C. & Crabtree, H.J. High fidelity, high yield production of microfluidic devices by hot embossing lithography: rheology and stiction. Lab. Chip 6, 936–941 (2006).
Qu, S. et al. Microfluidic devices fabricated in poly (methyl methacrylate) using hot-embossing with integrated sampling capillary and fiber optics for fluorescence detection. Lab. Chip 2, 88–95 (2002).
Truckenmuller, R. et al. Thermoforming of film-based biomedical microdevices. Adv. Mater. 23, 1311–1325 (2011).
Therriault, D., White, S.R. & Lewis, J.A. Chaotic mixing in three-dimensional microvascular networks fabricated by direct-write assembly. Nat. Mater. 2, 265–271 (2003).
McDonald, J.C. et al. Prototyping of microfluidic devices in poly(dimethylsiloxane) using solid-object printing. Anal. Chem. 74, 1537–1545 (2002).
Grimes, A. et al. Shrinky-Dink microfluidics: rapid generation of deep and rounded patterns. Lab. Chip 8, 170–172 (2008).
Chao, S.H., Carlson, R. & Meldrum, D.R. Rapid fabrication of microchannels using microscale plasma activated templating (μPLAT) generated water molds. Lab. Chip 7, 641–643 (2007).
Nunes, P.S., Ohlsson, P.D., Ordeig, O. & Kutter, J.P. Cyclic olefin polymers: emerging materials for labon-a-chip application. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 9, 145–161 (2010).
Wilson, M.E. et al. Fabrication of circular microfluidic channels by combining mechanical micromilling and soft lithography. Lab. Chip 11, 1550–1555 (2011).
Stroock, A.D. Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 295, 647–651 (2002).
Rezk, A.R., Qi, A., Friend, J.R., Li, W.H. & Yeo, L.Y. Uniform mixing in paper-based microfluidic systems using surface acoustic waves. Lab. Chip 12, 773–779 (2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, B.S., Lee, K.G., Choi, H.W. et al. Facile fabrication of plastic template for three-dimensional micromixer-embedded microfluidic device. BioChip J 7, 104–111 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-013-7204-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-013-7204-x