Abstract
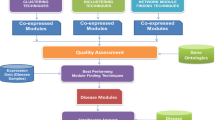
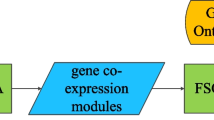
In recent microarray studies, the gene-set analysis is one of the most popular computational approaches to find significant gene-sets that show significantly differential expression between case and control groups of samples. For this purpose, it employs a variety of biological resources such as pathway databases, gene ontology, literatures, and etc., to generate candidate functional gene-sets at the first step. Out of these candidates, then, the most significant ones are identified by taking such gene-sets that have sufficiently high statistical significance in expression difference between case and control groups. Here the significance of each gene-set is usually evaluated based on its representative score obtained from the expression profiles of its constituent genes. In practice, however, the representative score for a gene-set may not be easily able to capture overall characteristics of the expression patterns of its constituent genes. For example, it can occur that some genes in a specific functional gene-set show very different expression pattern from a majority of genes in the same gene-set. In such a case, those genes cause the problem that the representative score for a gene-set gets weakened, eventually leading to the hindrance in estimating the statistical significance of the gene-set. To handle this problem, thus, we propose an approach to employ gene modules, a group of genes which do not only share a specific function in common but are also strongly correlated to each other, as the candidate functional gene-sets for the gene-set analysis. Specifically, from each gene-set of the same functionality, we attempt to filter out the “bad” genes, of which expression patterns in a functional gene-set are not strongly correlated to those of a majority of genes in the same gene-set, by generating co-expressed functional gene modules from each gene-set. Also, for the significance evaluation of these gene modules, a nonparametric Wilcoxon ranksum test is employed. From our experiments, it is observed that our proposed approach to co-expressed functional modules generation for gene-set analysis can greatly improve the performance on the identification of significant gene-sets differentially expressed in a specific disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, A. Advanced analysis of gene expression microarray data. World Scientific (2006).
McLachlan, G.J., Do, K.A. & Ambrose, C. Analyzing microarray gene expression data. WILEY-INTERSCIENCE John Wiley & Sons (2004).
Subramanian, A. et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genomewide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 15545–15550 (2005).
Taskesen, E. Sub-typing of model organisms based on gene expression data. Bioinformatics Technical University of Delft Research Assignment (2006).
Kim, S.Y. & Volsky D.J. PAGE: parametric analysis of gene set enrichment. BMC Bioinformatics 8, 144 (2005).
KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes, http://www.genome.ad.jp/kegg/.
Kanehisa, M., Goto, S., Kawashima S. & Nakaya, A. The KEGG databases at GenomeNet. Nucleic Acids Res. 30, 42–46 (2002).
Gene Ontology, http://www.geneontology.org/.
Hogg, R.V., Craig, A.T. & Mckean, J. Introduction to Mathematical Statistics, 6th Edition. Pearson Education (2005).
Bhattacharjee, A. et al. Classification of human lung carcinomas by mRNA expression profiling reveals distinct adenocarcinoma subclasses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 20;98, 13790–13795 (2001).
Armstrong, S.A. et al. MLL translocations specify a distinct gene expression profile that distinguishes a unique leukemia. Nature Genetics 30, 41–47 (2001).
MSigDB: Molecular Signatures Database, http://www.broadinstitute.org/gsea/index.jsp.
David, W.M. Bioinformatics: sequence and genome analysis, 2/E. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press (2004).
Weinberg, R.A. The biology of CANCER. Carland Science (2007).
Tan, P.N., Steinbach, M. & Kumar, V. Introduction to data mining. Pearson Education, Inc. (2006).
Zuber, V. & Strimmer, K. Gene ranking and biomarker discovery under correlation. Bioinformatics 15;25, 2700–2707 (2009).
Marc M. Triola, M.D. & Mario, F.T. Biostatistics for the Biological and Health Sciences. Pearson Education, Inc. (2006).
Lee, E., Chuang, H.Y., Kim, J.W., Ideker, T. & Lee, D. Inferring pathway activity toward precise disease classification. PLoS Computational Biology 4, e1000217 (2008).
Dudoit, S. & van der Laan, M.J. Multiple Testing Procedures and Applications to Genomics. Springer (2007).
Gentleman, R., Carey, V., Huber, W., Irizarry, R. & Dudoit, S. Bioinformatics and Computational Biology Solutions Using R and Bioconductor. Springer (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, J., Shin, M. Identification of significant gene-sets differentially expressed in a specific disease by co-expressed functional gene modules generation. BioChip J 4, 204–209 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-010-4307-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-010-4307-5