Abstract
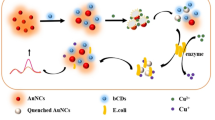
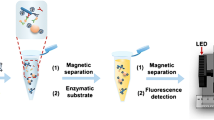
We have demonstrated a simple route for the detection of Escherichia coli using well plates with quantum dot (QD) fluorescent labels. The genetically engineered E. coli strain DH5α, containing green fluorescent protein (GFP), was used as the model system. Two approaches were employed in the detection of E. coli. In the first method, E. coli were specifically adhered onto a streptavidin-coated 96 well plate using biotin-labeled antibodies. In the second approach, E. coli were nonspecifically adsorbed onto the surfaces of 96 well plates without the use of antibodies. Whereas the fluorescence signal from GFP was not correlated with the number of E. coli cells, a linear titer dependence was found from the QD-labeled E. coli. The linear dependence of the antibody-immobilized E. coli persisted up to high (>106 cfu/mL) concentrations of E. coli. However, an exponential increase in the fluorescence intensity was found due to nonspecifically bound E. coli, and the signal intensity was much higher than that of antibody-immobilized E. coli.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). E. coli, http://www.cdc.gov/ecoli/.
Standard Methods for the examination of water and waste water. American public health association, American water works association, water environment federation. http://www.umass.edu/tei/mwwp/acrobat/sm9222DMFT.PDF.
Manafi, M. Fluorogenic and chromogenic enzyme substrates in culture media and identification tests. Int. J. Food Microbiology 31, 45–58 (1996).
So, H.-M. et al. Detection and titer estimation of Escherichia coli using aptamer-functionalized singlew-alled carbon-nanotube field-effect transistors. Small 4, 197–201 (2008).
Zelada-Guillén, G.A., Riu, J., Düzgün, A. & Rius, F.X. Immediate detection of living bacteria at ultralow concentrations using a carbon nanotube based potentiometric aptasensor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 48, 7334–7337 (2009).
El-Boubbou, K., Gruden, C. & Huang, X. Magnetic glycol-nanoparticles: A unique tool for rapid pathogen detection, decontamination, and strain differentiation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129, 13392–13393 (2007).
Cheng, Y. et al. Combining biofunctional magnetic nanoparticles and ATP bioluminescence for rapid detection of Escherichia coli. Talanta 77, 1332–1336 (2009).
Hahn, M.A., Tabb, J.S. & Krauss, T.D. Detection of single bacterial pathogens with semiconductor quantum dots. Anal. Chem. 77, 4861–4869 (2005).
Yang, L. & Li, Y. Simultaneous detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Salmonella typhimurium using quantum dots as fluorescent labels. Analyst 131, 394–401 (2006).
Edgar, R. et al. High-sensitivity bacterial detection using biotin-tagged phage and quantum-dot complexes. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 4841–4845 (2006).
Mukhopadhyay, B., Martins, M.B., Karamanska, R., Russell, D.A. & Field, R.A. Bacterial detection using carbohydrate-functionalized CdS quantum dots: a model study exploiting E. coli recognition of mannosides. Tetrahedron Lett. 50, 886–889 (2009).
Lee, S.J. et al. Sonication treatment of CdTe/CdS semiconductor nanocrystals and their bio-application. Chem. Commun. 5574–5576 (2008).
Bae, P.K. et al. The modification of quantum dot probes used for the targeted imaging of his-tagged fusion proteins. Biomaterials 30, 836–842 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, P.K., So, HM., Kim, K.N. et al. Simple route for the detection of Escherichia coli using quantum dots. BioChip J 4, 129–133 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-010-4207-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-010-4207-8