Abstract
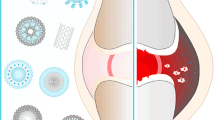
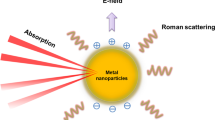
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune systemic inflammatory disease that affects the joints and other vital organs and diminishes the quality of life. The current developments and innovative treatment options have significantly slowed disease progression and improved their quality of life. Medicaments can be delivered to the inflamed synovium via nanoparticle systems, minimizing systemic and undesirable side effects. Numerous nanoparticles such as polymeric, liposomal, and metallic nanoparticles reported are impending as a good carrier with therapeutic properties. Other issues to be considered along are nontoxicity, nanosize, charge, optical property, and ease of high surface functionalization that make them suitable carriers for drug delivery. Metallic nanoparticles (MNPs) (such as silver, gold, zinc, iron, titanium oxide, and selenium) not only act as good carrier with desired optical property, and high surface modification ability but also have their own therapeutical potential such as anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-arthritic properties, making them one of the most promising options for RA treatment. Regardless, cellular uptake of MNPs is one of the most significant criterions for targeting the medication. This paper discusses the numerous interactions of nanoparticles with cells, as well as cellular uptake of NPs. This review provides the mechanistic overview on MNPs involved in RA therapies and regulation anti-arthritis response such as ability to reduce oxidative stress, suppressing the release of proinflammatory cytokines and expression of LPS induced COX-2, and modulation of MAPK and PI3K pathways in Kuppfer cells and hepatic stellate cells. Despite of that MNPs have also ability to regulates enzymes like glutathione peroxidases (GPxs), thioredoxin reductases (TrxRs) and act as an anti-inflammatory agent.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data were used for the research described in the article.
References
Abramson SB, Amin AR, Clancy RM, Attur M (2001) The role of nitric oxide in tissue destruction. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 15:831–845. https://doi.org/10.1053/BERH.2001.0196
Agarwal H, Shanmugam VK (2019) Synthesis and optimization of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Kalanchoe pinnata towards the evaluation of its anti-inflammatory activity. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 54:101291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2019.101291
Agarwal H, Nakara A, Shanmugam VK (2019) Anti-inflammatory mechanism of various metal and metal oxide nanoparticles synthesized using plant extracts: a review. Biomed Pharmacother 109:2561–2572
Ali SS, Morsy R, El-Zawawy NA et al (2017) Synthesized zinc peroxide nanoparticles (ZnO2-NPs): a novel antimicrobial, anti-elastase, anti-keratinase, and anti-inflammatory approach toward polymicrobial burn wounds. Int J Nanomed 12:6059–6073. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S141201
Amin K (2012) The role of mast cells in allergic inflammation. Respir Med 106:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.RMED.2011.09.007
Baldim V, Bedioui F, Mignet N et al (2018) The enzyme-like catalytic activity of cerium oxide nanoparticles and its dependency on Ce3+ surface area concentration. Nanoscale 10:6971–6980. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nr00325d
Benjamin O, Bansal P, Goyal A et al (2019) Disease Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARD) [Updated 2019 Jan 6]. StatPearls Publishing
Bera A, Kumar S (2022) Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in thermal enhanced oil recovery. Fundam Ind Appl Magn Nanoparticles. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-822819-7.00005-3
Bhoi A, Dwivedi SD, Singh D et al (2024) Plant-based approaches for rheumatoid arthritis regulation: mechanistic insights on pathogenesis, molecular pathways, and delivery systems. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 41:39–86. https://doi.org/10.1615/CritRevTherDrugCarrierSyst.2023048324
Bianchi ME, Manfredi AA (2014) How macrophages ring the inflammation alarm. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:2866. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.1324285111
Binnemars-Postma KA, Ten Hoopen HW, Storm G, Prakash J (2016) Differential uptake of nanoparticles by human M1 and M2 polarized macrophages: protein corona as a critical determinant. Nanomedicine (Lond) 11:2889–2902. https://doi.org/10.2217/NNM-2016-0233
Brennan-Olsen SL, Cook S, Leech MT et al (2017) Prevalence of arthritis according to age, sex and socioeconomic status in six low and middle income countries: analysis of data from the world health organization study on global AGEing and adult health (SAGE) Wave 1. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 18:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-017-1624-z
Brenner PT, Krakauer BSP (2005) Regulation of inflammation: a review of recent advances in anti inflammatory strategies. Curr Med Chem—Anti-Inflamm Anti-Allergy Agents 2:274–283. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568014033483752
Britt RD, Locy ML, Tipple TE et al (2012) Lipopolysaccharide-induced Cyclooxygenase-2 expression in mouse transformed clara cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 29:213. https://doi.org/10.1159/000337602
Bullock J, Rizvi SAA, Saleh AM et al (2019) Rheumatoid arthritis: a brief overview of the treatment. Med Princ Pract 27:501–507. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493390
Cele T (2020) Preparation of nanoparticles. In: Avramescu SM, Akhtar K, Fierascu I, Khan SB, Ali F, Asiri AM (eds) Engineered nanomaterials—health and safety. IntechOpen, London, pp 1–14
Chen Z, Bozec A, Ramming A, Schett G (2019) Anti-inflammatory and immune-regulatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 15:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-018-0109-2
Costello RE, Marsden A, Movahedi M et al (2020) The effect of glucocorticoid therapy on mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and concomitant type II diabetes: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Rheumatol 4:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41927-019-0105-4
Devi Dwivedi S, Sahu D, Rathor LS et al (2023) Mineral metabolism and metabolic bone diseases. In: Amponsah SK, Ofori EK, Yashwant PV (eds) Current trends in the diagnosis and management of metabolic disorders. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Dewangan AK, Perumal Y, Pavurala N et al (2017) AC SC. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2017.07.022
Dolati S, Sadreddini S, Rostamzadeh D et al (2016) Utilization of nanoparticle technology in rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Biomed Pharmacother 80:30–41
Dwivedi SD, Yadav K, Bhoi A et al (2024) Targeting pathways and integrated approaches to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 41:87–102. https://doi.org/10.1615/CritRevTherDrugCarrierSyst.2023044719
Fang G, Zhang Q, Pang Y et al (2019) Nanomedicines for improved targetability to inflamed synovium for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: multi-functionalization as an emerging strategy to optimize therapeutic efficacy. J Control Release 303:181–208
Fu H, Guo Y, Fang W et al (2024) Anti-acidification and immune regulation by Nano-ceria-loaded Mg–Al layered double hydroxide for rheumatoid arthritis therapy. Adv Sci 11:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202307094
Fujiwara N, Kobayashi K (2005) Macrophages in inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 4:281–286. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568010054022024
Gokhale JP, Mahajan HS, Surana SS (2019) Quercetin loaded nanoemulsion-based gel for rheumatoid arthritis: in vivo and in vitro studies. Biomed Pharmacother 112:108622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108622
Grumezescu AM (2016) Surface chemistry of nanobiomaterials: applications of nanobiomaterials. Elsvier, Amsterdam
Gul A, Kunwar B, Mazhar M et al (2018) Rutin and rutin-conjugated gold nanoparticles ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis in rats through inhibition of NF-κB and iNOS activation. Int Immunopharmacol 59:310–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.04.017
P. Hemon, Y. Renaudineau, M. Debant, N. Le Goux, S. Mukherjee, W. Brooks OM (2017) Calcium signaling: from normal b cell development to tolerance breakdown and autoimmunity.—archive ouverte HAL. In: Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01528594. Accessed 9 Apr 2022
Holmes C, Cunningham C, Zotova E et al (2009) Systemic inflammation and disease progression in alzheimer disease. Neurology 73:768–774. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181b6bb95
Hwang EY, Lee JH, Lim DW (2020) Compartmentalized bimetal cluster-poly(aniline) hybrid nanostructures for multiplexed detection of autoantibodies in early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Sensors Actuators B Chem 321:128482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128482
Journal AI, Rao K, Aziz S et al (2018) Gum acacia stabilized silver nanoparticles based nano-cargo for enhanced anti-arthritic potentials of hesperidin in adjuvant induced arthritic rats. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1431653
Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I (2019) Nanoparticles: properties, applications and toxicities. Arab J Chem 12:908–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2017.05.011
Kim MH, Seo JH, Kim HM, Jeong HJ (2016) Aluminum-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles attenuate the TSLP levels via suppressing caspase-1 in activated mast cells. J Biomater Appl 30:1407–1416. https://doi.org/10.1177/0885328216629822
Kirdaite G, Leonaviciene L, Bradunaite R et al (2019) Antioxidant effects of gold nanoparticles on early stage of collagen-induced arthritis in rats. Res Vet Sci 124:32–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2019.02.002
Koga A, Thongsiri C, Kudo D et al (2023) Mechanisms underlying the suppression of IL-1β expression by magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles. Biomedicines. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051291
Kronenberg HM (2016) Bone and mineral metabolism: Where are we, where are we going, and how will we get there? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101:795–798. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2015-3607
Li J, Chen L, Xu X et al (2020) Targeted combination of antioxidative and anti-inflammatory therapy of rheumatoid arthritis using multifunctional dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles as a platform. Small 16:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202005661
Liang DY, Li XQ, Li WW et al (2010) Caspase-1 modulates incisional sensitization and inflammation. Anesthesiology 113:945. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0B013E3181EE2F17
Lin N, Simon MC (2016) Hypoxia-inducible factors: Key regulators of myeloid cells during inflammation. J Clin Invest 126:3661–3671
Liu Y, Ma L, Zhou H et al (2018) Polypeptide nano-Se targeting inflammation and theranostic rheumatoid arthritis by anti-angiogenic and NO activating AMPKα signaling pathway. J Mater Chem B 6:3497–3514. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8tb00080h
Liu R, Lv Z, Liu X et al (2021) Improved delivery system for celastrol-loaded magnetic Fe3O4/α-Fe2O3 heterogeneous nanorods: HIF-1α-related apoptotic effects on SMMC-7721 cell. Mater Sci Eng C. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2021.112103
Magna M, Pisetsky DS (2014) The role of HMGB1 in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Mol Med 20:138–146. https://doi.org/10.2119/MOLMED.2013.00164
Mani A, Vasanthi C, Gopal V, Chellathai D (2016) Role of phyto-stabilised silver nanoparticles in suppressing adjuvant induced arthritis in rats. Int Immunopharmacol 41:17–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2016.10.013
Mu Q (2017) Chemical basis of interactions between engineered nanoparticles and biological systems. Physiol Behav 176:139–148. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400295a.Chemical
Pal P, Giri PP, Sinha R (2019) Cyclosporine in resistant systemic arthritis - a cheaper alternative to biologics. Indian J Pediatr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-019-02912-9
Park HS, Nam SH, Kim J et al (2016) Clear-cut observation of clearance of sustainable upconverting nanoparticles from lymphatic system of small living mice. Sci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1038/SREP27407
Presta M, Dell’Era P, Mitola S et al (2005) Fibroblast growth factor/fibroblast growth factor receptor system in angiogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16:159–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CYTOGFR.2005.01.004
Qamar N, John P, Bhatti A (2020) Toxicological and anti-rheumatic potential of trachyspermum ammi derived biogenic selenium nanoparticles in arthritic balb/c mice. Int J Nanomed 15:3497–3509. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S243718
Qamar N, John P, Bhatti A (2021) Emerging role of selenium in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: An insight on its antioxidant properties. J Trace Elem Med Biol 66:126737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2021.126737
Rabiei M, Kashanian S, Samavati SS et al (2021) Nanotechnology application in drug delivery to osteoarthritis (OA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and osteoporosis (OSP). J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 61:102011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2020.102011
Ramaswamy M, Solaimuthu C, Duraikannu S (2019) Antiarthritic activity of synthesized silver nanoparticles from aqueous extract of Moringa concanensis Nimmo leaves against FCA induced rheumatic arthritis in rats. J Drug Deliv Ther. https://doi.org/10.22270/jddt.v9i3.2707
Ramos AP, Cruz MAE, Tovani CB, Ciancaglini P (2017) Biomedical applications of nanotechnology. Biophys Rev 9:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12551-016-0246-2
Ren SX, Zhang B, Lin Y et al (2019) Selenium nanoparticles dispersed in phytochemical exert anti-inflammatory activity by modulating catalase, GPx1, and COX-2 gene expression in a rheumatoid arthritis rat model. Med Sci Monit 25:991–1000. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.912545
Roeleveld DM, Koenders MI (2015) The role of the Th17 cytokines IL-17 and IL-22 in Rheumatoid Arthritis pathogenesis and developments in cytokine immunotherapy. Cytokine 74:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CYTO.2014.10.006
Roome T, Aziz S, Razzak A et al (2019) Opuntioside, opuntiol and its metallic nanoparticles attenuate adjuvant-induced arthritis: novel suppressors of Toll-like receptors -2 and -4. Biomed Pharmacother 112:108624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.108624
Roszkowski L, Ciechomska M (2021) Tuning monocytes and macrophages for personalized therapy and diagnostic challenge in rheumatoid arthritis. Cells 10:1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10081860
Schabbauer G, Tencati M, Pedersen B et al (2004) PI3K-Akt pathway suppresses coagulation and inflammation in endotoxemic mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:1963–1969. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.ATV.0000143096.15099.CE
Shafiey SI, Mohamed WR, Abo-Saif AA (2018) Paroxetine and rivastigmine mitigates adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis in rats: impact on oxidative stress, apoptosis and RANKL/OPG signals. Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.09.046
Simkó M, Fiedeler U, Gazso, (2011) The impact of nanoparticles on cellular functions. Nanotrust Dossiers 007:1–4
Simmonds RE, Foxwell BM (2008) Signalling, inflammation and arthritis: NF-κB and its relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatology 47:584–590. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kem298
Song Y, Ismail M, Shan Q et al (2021) ROS-mediated liposomal dexamethasone: a new FA-targeted nanoformulation to combat rheumatoid arthritis via inhibiting iRhom2/TNF-α/BAFF pathways. Nanoscale 13:20170–20185. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NR05518F
Srivastava S, Patel S, Singh D, Singh MR (2017a) Rationalized insights on causes of rheumatoid arthritis in the elderly and women: special emphasis on treatment strategies. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 34:97–147. https://doi.org/10.1615/CritRevTherDrugCarrierSyst.2017017003
Srivastava S, Singh D, Patel S et al (2017b) Novel carters and targeted approaches: way out for rheumatoid arthritis quandrum. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 40:125–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2017.05.025
Srivastava S, Singh D, Patel S, Singh MR (2017c) Role of enzymatic free radical scavengers in management of oxidative stress in autoimmune disorders. Int J Biol Macromol 101:502–517
Srivastava S, Singh D, Singh MR (2018) Folate-conjugated superoxide dismutase adsorbed over antioxidant mimicking nanomatrix frameworks for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Pharm Sci 107:1530–1539. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xphs.2018.01.026
Sumbayev VV, Yasinska IM, Garcia CP et al (2013) Gold nanoparticles downregulate interleukin-1β-induced pro-inflammatory responses. Small 9:472–477. https://doi.org/10.1002/SMLL.201201528
Suschek C, Schnorr O, Kolb-Bachofen V (2004) The role of iNOS in chronic inflammatory processes in vivo: is it damage-promoting, protective, or active at all? Curr Mol Med 4:763–775. https://doi.org/10.2174/1566524043359908
Tardito S, Martinelli G, Soldano S et al (2019) Macrophage M1/M2 polarization and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Autoimmun Rev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102397
Thota S, Crans DC (2018) Metal Nanoparticles. Met Nanoparticles. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527807093
Tripathi P, Tripathi P, Kashyap L, Singh V (2007) The role of nitric oxide in inflammatory reactions. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 51:443–452. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1574-695X.2007.00329.X
Unterberger S, Davies KA, Rambhatla SB, Sacre S (2021) Contribution of toll-like receptors and the NLRP3 inflammasome in rheumatoid arthritis pathophysiology. ImmunoTargets Ther 10:285–298. https://doi.org/10.2147/itt.s288547
Vaishnavi PR, Gaikwad N, Dhaneria S (2017) Assessment of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use pattern using world health organization indicators: a cross-sectional study in a tertiary care teaching hospital of Chhattisgarh. Indian J Pharmacol 49:445–450. https://doi.org/10.4103/IJP.IJP_189_17
Wallace DF (2016) Regulation of iron homeostasis. Clini Biochem Rev 37(2):51–62
Wynn TA, Vannella KM (2016) Macrophages in tissue repair, regeneration, and fibrosis. Immunity 44:450. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IMMUNI.2016.02.015
Xia T, Zhu Y, Li K et al (2024) Microneedles loaded with cerium-manganese oxide nanoparticles for targeting macrophages in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Nanobiotechnol 22:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12951-024-02374-y
Xu Q, Chen C, Liu B et al (2020) Association of iRhom1 and iRhom2 expression with prognosis in patients with cervical cancer and possible signaling pathways. Oncol Rep 43:41–54. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2019.7389
Yadav K, Chauhan NS, Saraf S et al (2020) Challenges and need of delivery carriers for bioactives and biological agents: an introduction. In: Singh MR, Singh D, Kanwar J, Chauhan NS (eds) Advances and avenues in the development of novel carriers for bioactives and biological agents. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Yadav K, Pradhan M, Singh D, Singh MR (2022) Targeting autoimmune disorders through metal nanoformulation in overcoming the fences of conventional treatment approaches. In: Rezaei N, Yazdanpanah N (eds) Translational autoimmunity. Elsevier Inc, London, pp 361–393
Yan HX, Wu HP, Zhang HL et al (2013) p53 promotes inflammation-associated hepatocarcinogenesis by inducingHMGB1 release. J Hepatol 59:762. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHEP.2013.05.029
Yang T, Yao Q, Cao F et al (2016a) Silver nanoparticles inhibit the function of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 and target genes: insight into the cytotoxicity and antiangiogenesis. Int J Nanomedicine 11:6679. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S109695
Yang X, Liang L, Zong C et al (2016b) Kupffer cells-dependent inflammation in the injured liver increases recruitment of mesenchymal stem cells in aging mice. Oncotarget 7:1084. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6744
Yang Y, Guo L, Wang Z et al (2021) Targeted silver nanoparticles for rheumatoid arthritis therapy via macrophage apoptosis and Re-polarization. Biomaterials 264:120390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120390
Yusuf A, Casey A (2019) Surface modification of silver nanoparticle (AgNP) by liposomal encapsulation mitigates AgNP-induced inflammation. Toxicol Vitr 61:104641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2019.104641
Zhang J, Wang X, Vikash V et al (2016) ROS and ROS-mediated cellular signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/4350965
Zhang C, Huang W, Huang C et al (2022) VHPKQHR peptide modified ultrasmall paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles targeting rheumatoid arthritis for t1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 10:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.821256
Zheng M, Jia H, Wang H et al (2021) Application of nanomaterials in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. RSC Adv 11:7129–7137. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ra00328c
Zhu C, Zhang S, Song C et al (2017) Selenium nanoparticles decorated with Ulva lactuca polysaccharide potentially attenuate colitis by inhibiting NF-κB mediated hyper inflammation. J Nanobiotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1186/S12951-017-0252-Y
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the University Institute of Pharmacy, Pt. Ravishankar Shukla University, Raipur (C.G), for providing tremendous support and the opportunity to complete my review paper.
Funding
No funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Shradha Devi Dwivedi: Methodology, software, writing—original draft, Anita Bhoi.: data curation, writing—original draft preparation. Madhulika Pradhan: validation., writing—reviewing and editing, formal analysis. Keshav Kant Sahu: conceptualization, visualization, writing—reviewing and editing, Deependra Singh: supervision, validation., writing—reviewing and editing, visualization. Manju Rawat Singh: conceptualization, resources, supervision, visualization, investigation, writing—reviewing and editing, funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Informed consent
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Not applicable
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dwivedi, S.D., Bhoi, A., Pradhan, M. et al. Role and uptake of metal-based nanoconstructs as targeted therapeutic carriers for rheumatoid arthritis. 3 Biotech 14, 142 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-024-03990-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-024-03990-z