Abstract
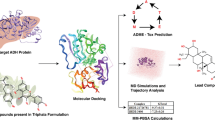
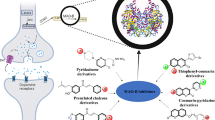
In our continuous effort to develop novel antiepileptic drug, a new series of nipecotic acid derivatives having1,3,4-thiadiazole nucleus were designed and synthesized. This study aims to improve the lipophilicity of nipecotic acid by attaching some lipophilic anchors like thiadiazole and substituted aryl acid derivatives. In our previous study, we noticed that the N-substituted oxadiazole derivative of nipecotic acid exhibited significant antiepileptic activity in the rodent model. The synthesized compounds were characterized by FT-IR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, Mass, and elemental analysis. The anticonvulsant activity was evaluated by using the maximal electroshock-induced seizure model in rats (MES) and the subcutaneous pentylenetetrazol (scPTZ) test in mice. None of the compounds were found to be active in the MES model whereas compounds (TN2, TN9, TN12, TN13, and TN15) produced significant protection against the scPTZ-induced seizures model. The compounds showing antiepileptic activity were additionally evaluated for antidepressant activity by using the forced swim test, 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP)-induced head twitch test, and learned helplessness test. All the molecules that showed anticonvulsant activity (TN2, TN9, TN12, TN13, and TN15), also exerted significant antidepressant effects in the animal models. The selected compounds were subjected to different toxicity studies. Compounds were found to have no neurotoxicity in the rota-rod test and devoid of hepatic and renal toxicity in 30 days repeated oral toxicity test. Further, a homology model was developed to perform the in-silico molecular docking and dynamics studies which revealed the similar binding of compound TN9 within the active binding pocket and were found to be the most potent anti-epileptic agent. The market expectation for newly developed antiepileptic thiadiazole-based nipecotic acid derivatives is significant, driven by their potential to offer improved therapeutic outcomes and reduced side effects, addressing a critical need in epilepsy treatment. These innovative compounds hold promise for meeting the demand for more effective and safer antiepileptic medications.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data supporting this study are included within the article and supporting materials.
References
Adkins JC, Noble SJD (1998) Tiagabine 55(3):437–460
Aggarwal M, Kondeti B, McKenna RJEootp, (2013) Anticonvulsant/antiepileptic carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat 23(6):717–724
Ahmed SN, Siddiqi ZAJS (2006) Antiepileptic drugs and liver disease. Seizure 15(3):156–164
Anisman H, Merali Z (2001) Rodent models of depression: learned helplessness induced in mice. Curr Protoc Neurosci 14(1):8.10 C (11-18.10 C. 15)
Can NÖ, Can ÖD, Osmaniye D, Demir Özkay ÜJM (2018) Synthesis of some novel thiadiazole derivative compounds and screening their antidepressant-like activities. Molecules 23(4):716
Castagné V, Hernier AM, Porsolt R (2014) CNS safety pharmacology. Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences, Elseiver
Chen Z, Brodie MJ, Liew D, Kwan P (2018) Treatment outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy treated with established and new antiepileptic drugs: a 30-year longitudinal cohort study. JAMA Neurol 75(3):279–286
Daina A, Michielin O, Zoete V (2017) SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci Rep 7(1):1–13
Dalby NOJN (2000) GABA-level increasing and anticonvulsant effects of three different GABA uptake inhibitors. Neuropharmacology 39(12):2399–2407
Elger CE, Johnston SA, Hoppe CJS (2017) Diagnosing and treating depression in epilepsy. Seizure 44:184–193
El-Habr EA, Dubois LG, Burel-Vandenbos F, Bogeas A, Lipecka J, Turchi L, Lejeune F-X, Coehlo PLC, Yamaki T, Wittmann BM (2017) A driver role for GABA metabolism in controlling stem and proliferative cell state through GHB production in glioma. Acta Neuropathol 133(4):645–660
Ertem DH, Dirican AC, Aydın A, Baybas S, Sözmen V, Ozturk M, Altunkaynak YJP, neurosciences c, (2017) Exploring psychiatric comorbidities and their effects on quality of life in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 71(4):280–288
Estrin D, Govindan R, Heidemann J, Kumar S (1999) Next century challenges: Scalable coordination in sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the 5th Annual ACM/IEEE International Conference on Mobile computing and networking, 1999. ACM, pp 263–270
Ganeshpurkar A, Singh R, Gore PG, Kumar D, Gutti G, Kumar A, Singh SK (2020a) Structure-based screening and molecular dynamics simulation studies for the identification of potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Mol Simul 46(3):169–185
Ganeshpurkar A, Singh R, Kumar D, Divya SS, Kumar A, Singh SK (2020b) Computational binding study with α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor of Anvylic-3288: an allosteric modulator. Mol Simul 46(13):975–986
Ganeshpurkar A, Singh R, Kumar D, Gore P, Shivhare S, Sardana D, Rayala S, Kumar A, Singh SK (2022a) Identification of sulfonamide based butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors through scaffold hopping approach. Int J Biol Macromol 203:195–211
Ganeshpurkar A, Singh R, Kumar D, Gutti G, Gore P, Sahu B, Kumar A, Singh SK (2022b) Identification of sulfonamide-based butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors using machine learning. Future Med Chem 14(14):1049–1070
Ganeshpurkar A, Singh R, Kumar D, Gutti G, Sardana D, Shivhare S, Singh RB, Kumar A, Singh SK (2022c) Development of homology model, docking protocol and Machine-Learning based scoring functions for identification of Equus caballus’s butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors. J Biomol Struct Dyn 40(24):13693–13710
Ganeshpurkar A, Singh R, Shivhare S, Divya, Kumar D, Gutti G, Singh R, Kumar A, Singh SK (2022d) Improved machine learning scoring functions for identification of Electrophorus electricus’s acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Mol Divers 26(3):1455–1479
Ganeshpurkar A, Singh R, Singh RB, Kumar D, Kumar A, Singh SK (2022e) Identification of potential AChE inhibitors through combined machine-learning and structure-based design approaches. Indian J Biochem Biophy 59(6):619–631
Ghadimi S, Latif Mousavi S, Javani Z (2008) Synthesis, lipophilicity study and in vitro evaluation of some rodenticides as acetylcholinesterase reversible inhibitors. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem 23(2):213–217
Hansen SL, Sperling BB, Sánchez C (2004) Anticonvulsant and antiepileptogenic effects of GABAA receptor ligands in pentylenetetrazole-kindled mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28(1):105–113
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy. Accessed 15 Jan 2023
Johannessen SI, Johannessen Landmark C (2010) Antiepileptic drug interactions-principles and clinical implications. Curr Neuropharmacol 8(3):254–267
Jurik A, Zdrazil B, Holy M, Stockner T, Sitte HH, Ecker GF (2015) A binding mode hypothesis of tiagabine confirms liothyronine effect on γ-aminobutyric acid transporter 1 (GAT1). J Med Chem 58(5):2149–2158
Kanner AM (2003) Depression in epilepsy: prevalence, clinical semiology, pathogenic mechanisms, and treatment. Biol Psychiat 54(3):388–398
Kanner AM (2006) Depression and epilepsy: a new perspective on two closely related disorders. Epilepsy Currents 6(5):141–146
Kanner AM (2008) Mood disorder and epilepsy: a neurobiologic perspective of their relationship. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 10(1):39
Kanner AM (2016) Management of psychiatric and neurological comorbidities in epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol 12(2):106
Kontoyianni M, McClellan LM, Sokol GS (2004) Evaluation of docking performance: comparative data on docking algorithms. J Med Chem 47(3):558–565
Kunimatsu T, Yamada T, Miyata K, Yabushita S, Seki T, Okuno Y, Matsuo MJT (2004) Evaluation for reliability and feasibility of the draft protocol for the enhanced rat 28-day subacute study (OECD Guideline 407) using androgen antagonist flutamide. Toxicology 200(1):77–89
Lambert MV, Robertson MMJE (1999) Depression in epilepsy: etiology, phenomenology, and treatment. Epilepsia 40:s21–s47
Lattmann E, Lattmann P, Boonprakob Y, Airarat W, Singh H, Offel M, Sattayasai J (2009) In vivo evaluation of substituted 3-amino-1, 4-benzodiazepines as anti-depressant, anxiolytic and anti-nociceptive agents. Arzneimittelforschung 59(02):61–71
Löscher WJS (2011) Critical review of current animal models of seizures and epilepsy used in the discovery and development of new antiepileptic drugs. Seizure 20(5):359–368
Luna-Munguia H, Orozco-Suarez S, Rocha LJN (2011) Effects of high frequency electrical stimulation and R-verapamil on seizure susceptibility and glutamate and GABA release in a model of phenytoin-resistant seizures. Neuropharmacology 61(4):807–814
Madsen KK, White HS, Schousboe A (2010) Neuronal and non-neuronal GABA transporters as targets for antiepileptic drugs. Pharmacol Therap 125(3):394–401
Madsen KK, Ebert B, Clausen RP, Krogsgaard-Larsen P, Schousboe A, White SH (2011) Selective GABA transporter inhibitors tiagabine and EF1502 exhibit mechanistic differences in their ability to modulate the ataxia and anticonvulsant action of the extrasynaptic GABAA receptor agonist gaboxadol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 338(1):214–219
Ochoa JG, Kilgo WA (2016) The role of benzodiazepines in the treatment of epilepsy. Curr Treat Options Neurol 18(4):18
Pearlman DA, Feyfant E, Sherman W (2023) Advances in biologics modeling with bioluminate Schrödinger newsletter
Penmatsa A, Wang KH, Gouaux E (2015a) X-ray structures of Drosophila dopamine transporter in complex with nisoxetine and reboxetine. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22(6):506–508
Penmatsa A, Wang KH, Gouaux E (2015b) X-ray structures of Drosophila dopamine transporter in complex with nisoxetine and reboxetine. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22(6):506
Petrera M, Wein T, Allmendinger L, Sindelar M, Pabel J, Höfner G, Wanner KTJC (2016) Development of highly potent GAT1 inhibitors: synthesis of nipecotic acid derivatives by Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reactions. ChemMedChem 11(5):519–538
Porsolt RD, Le Pichon M, Jalfre M (1977) Depression: a new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 266(5604):730–732
Reddy DS, Kulkarni SK (1998) Possible role of nitric oxide in the nootropic and antiamnesic effects of neurosteroids on aging-and dizocilpine-induced learning impairment. Brain Res 799(2):215–229
Riquelme-Alcazar J, González-Vargas R, Moya PR (2020) ABC transporters and drug resistance in epilepsy: biological plausibility, pharmacogenetics and precision medicine. Rev Neurol 70(1):23–32
Rocha L, Alonso-Vanegas M, Martínez-Juárez IE, Orozco-Suárez S, Escalante-Santiago D, Feria-Romero IA, Zavala-Tecuapetla C, Cisneros-Franco JM, Buentello-García RM, Cienfuegos J (2015) GABAergic alterations in neocortex of patients with pharmacoresistant temporal lobe epilepsy can explain the comorbidity of anxiety and depression: the potential impact of clinical factors. Front Cell Neurosci 8:442
Rudzik A, Hester J, Tang A, Straw R, Friis W (1973) Triazolobenzodiazepines, a new class of central nervous system-depressant compounds. The Benzodiazepines. Raven Press, New York, pp 285–297
Sałat K, Podkowa A, Mogilski S, Zaręba P, Kulig K, Sałat R, Malikowska N, Filipek BJPR (2015) The effect of GABA transporter 1 (GAT1) inhibitor, tiagabine, on scopolamine-induced memory impairments in mice. Pharmacol Rep 67(6):1155–1162
Salpekar JJF (2016) Mood disorders in epilepsy. Focus 14(4):465–472
Schachter SC (2001) Pharmacology and clinical experience with tiagabine. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2(1):179–187
Scimemi A (2014) Structure, function, and plasticity of GABA transporters. Front Cell Neurosci 8:161
Sharma B, Verma A, Sharma UK, Prajapati S (2014) Efficient synthesis, anticonvulsant and muscle relaxant activities of new 2-((5-amino-1, 3, 4-thiadiazol-2-yl) methyl)-6-phenyl-4, 5-dihydropyridazin-3 (2H)-one derivatives. Med Chem Res 23:146–157
Siddiqui N, Ahsan W (2011) Synthesis, anticonvulsant and toxicity screening of thiazolyl–thiadiazole derivatives. Med Chem Res 20(2):261–268
Singh GK, Kumar V (2011) Acute and sub-chronic toxicity study of standardized extract of Fumaria indica in rodents. J Ethnopharmacol 134(3):992–995
Singh R, Bhattacharya S, Acharya S (2000) Studies on extracts of Elaeocarpus sphaericus fruits on in vitro rat mast cells. Phytomedicine 7(3):205–207
Singh GK, Garabadu D, Muruganandam A, Joshi VK, Krishnamurthy SJPB (2009) Antidepressant activity of Asparagus racemosus in rodent models. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91(3):283–290
Singh RB, Singh GK, Chaturvedi K, Kumar D, Singh SK, Zaman MKJMCR (2018) Design, synthesis, characterization, and molecular modeling studies of novel oxadiazole derivatives of nipecotic acid as potential anticonvulsant and antidepressant agents. Med Chem Res 27(1):137–152
Singh RB, Das N, Singh GK, Singh SK, Zaman K (2020) Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of 3-[5-(aryl-[1, 3, 4] oxadiazole-2-yl]-piperidine derivatives as anticonvulsant and antidepressant agents. Arab J Chem 13(5):5299–5311
Swinyard EA, Brown WC, Goodman LS (1952) Comparative assays of antiepileptic drugs in mice and rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 106(3):319–330
Thomas P (2004) Treatment protocol for long-term anti-epilepsy drugs in adults with refractory partial epilepsy. Revue Neurologique. 160:5S252-264
Treiman DMJE (2001) GABAergic mechanisms in epilepsy. Epilepsia 42:8–12
Veber DF, Johnson SR, Cheng H-Y, Smith BR, Ward KW, Kopple KD (2002) Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates. J Med Chem 45(12):2615–2623
Witt J-A, Helmstaedter C (2017) How can we overcome neuropsychological adverse effects of antiepileptic drugs? Expert Opin Pharmacother 18(6):551–554
Yogeeswari P, Sriram D, Saraswat V, Ragavendran JV, Kumar MM, Murugesan S, Thirumurugan R, Stables J (2003) Synthesis and anticonvulsant and neurotoxicity evaluation of N 4-phthalimido phenyl (thio) semicarbazides. Eur J Pharm Sci 20(3):341–346
Yusuf M, Khan RA, Ahmed B (2008) Syntheses and anti-depressant activity of 5-amino-1, 3, 4-thiadiazole-2-thiol imines and thiobenzyl derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem 16(17):8029–8034
Zaccara G, Cincotta M, Borgheresi A, Balestrieri FJED (2004) Adverse motor effects induced by antiepileptic drugs. Epileptic Disord 6(3):153–168
Zafar S, Jabeen I (2018) Structure, function, and modulation of γ-aminobutyric acid transporter 1 (GAT1) in neurological disorders: a pharmacoinformatic prospective. Front Chem 6:397
Acknowledgements
We thank to all our authors for their valuable suggestions and support. Authors are also thankful to CIF, IIT-BHU, Varanasi, India for providing NMR.
Funding
Authors did not receive any specific financial support from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RBS, KZ and GKS designed the research study; RBS has synthesized compounds and performed the spectral analysis; RBS and GKS performed pharmacological activity; ND performed the in-silico study. RBS, ND and GKS wrote the paper. PP critically revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Consent for publication
All authors have given their consent to publish this article.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, G.K., Kumari, B., Das, N. et al. Design, synthesis, molecular docking and pharmacological evaluation of some thiadiazole based nipecotic acid derivatives as a potential anticonvulsant and antidepressant agents. 3 Biotech 14, 71 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03897-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03897-1