Abstract
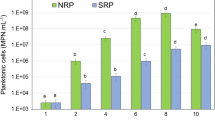
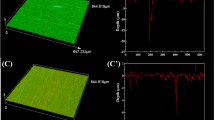
In this work, we study the microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) of AISI 316L (1–2% Mn) and AISI 202 (8–12% Mn) in the presence of manganese-oxidizing biofilms. Microbiological and 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing analysis on biofilms formed on the surfaces of both the SS materials after exposure to seawater for two months showed the presence of predominant Mn-oxidizing bacteria (MnOB) groups. The Mn contents in the biofilms formed on AISI 202 and 316L were 0.577 and 0.193 ppm, respectively. Mixed biofilms of 11 pure axenic cultures of MnOB isolated and identified from both the SS biofilms were used for MIC studies on SS. Electrochemical studies showed four orders of magnitude high icorr values (1.271 × 10–4 A.cm−2) and the onset of crevice corrosion potentials (502 mV) confirming the localized corrosion of AISI 202 and 316L, respectively, under MnOB biofilms. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic (XPS) analysis on biotic surfaces showed a reduced Mn content from 10.1 to 7.9 atom.% confirming the Mn oxidation in AISI 202. This study confirms that MnOB biofilms on the SS surfaces can lead to MIC due to biogenic Mn oxidation, depletion of Fe and Mn content, and enrichment of Cr content.











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this manuscript [and its supplementary information files].
References
Acuña N, Ortega-Morales BO, Valadez-González A (2006) Biofilm colonization dynamics and its influence on the corrosion resistance of austenitic UNS S31603 stainless steel exposed to Gulf of Mexico seawater. Mar Biotechnol 8(1):62–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-10005-15145-10127
Anandkumar B, George R, Tamilvani S, Padhy N, Mudali UK (2011) Studies on microbiologically influenced corrosion of SS304 by a novel manganese oxidizer, Bacillus flexus. Biofouling 27(6):675–683. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.08922011.08597001
Anandkumar B, Krishna NG, George R, Parvathavarthini N, Kamachi Mudali U (2013) Studies on Breakdown of passivity of titanium covered with in vitro biofilms. J Corrosion Sci Eng 16:1–32
Anandkumar B, George RP, Rao CJ, Philip J (2019) In situ application of alternate potentials with chlorination synergistically enhanced biofouling control of titanium condenser materials. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2019.104746
Anantharaman K, Brown CT, Hug LA, Sharon I, Castelle CJ, Probst AJ, Thomas BC, Singh A, Wilkins MJ, Karaoz U (2016) Thousands of microbial genomes shed light on interconnected biogeochemical processes in an aquifer system. Nat Commun 7(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13219
APHA (1989) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water. 17th Edition edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association, and Water Environment Federation, Washington
Baddoo N (2013) Steel Design Guide: Structural Stainless Steel. In. American Institute of Steel Construction, Chicago, IL, USA, p 159
Balakrishnan A, Jena G, Pongachira George R, Philip J (2021) Polydimethylsiloxane–graphene oxide nanocomposite coatings with improved anti-corrosion and anti-biofouling properties. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(6):7404–7422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11068-5
Balamurugan P, Joshi MH, Rao TS (2011) Microbial fouling community analysis of the cooling water system of a nuclear test reactor with emphasis on sulphate reducing bacteria. Biofouling 27(9):967–978. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2011.618636
Bender ML, Klinkhammer GP, Spencer DW (1977) Manganese in seawater and the marine manganese balance. Deep-Sea Res 24(9):799–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/0146-6291(77)90473-8
Bernardini S, Bellatreccia F, Della Ventura G, Sodo A (2020) A reliable method for determining the oxidation state of manganese at the microscale in mn oxides via raman spectroscopy. Geostandards Geoanalytical Res 45(1):223–244. https://doi.org/10.1111/ggr.12361
Chen M-Y, Lee D-J, Tay J-H, Show K-Y (2007) Staining of extracellular polymeric substances and cells in bioaggregates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75(2):467–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-00006-00816-00255
de Messano LV, Sathler L, Reznik LY, Coutinho R (2009) The effect of biofouling on localized corrosion of the stainless steels N08904 and UNS S32760. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 63(5):607–614
Dec W, Mosiałek M, Socha RP, Jaworska-Kik M, Simka W, Michalska J (2017) Characterization of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans biofilm on high-alloyed stainless steel: XPS and electrochemical studies. Mater Chem Phys 195:28–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.1004.1011
DePalma SR (1993) Manganese oxidation by Pseudomonas putida. Harvard University Cambridge, Massachusetts, ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, 9412329
Dexter S, Xu K, Luther GI (2003) Mn cycling in marine biofilms: effect on the rate of localized corrosion. Biofouling 19:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1080/0892701021000044093
Dharmarajan S, Chandrasekaran K, Sundaram M, Narayanan P (2021) Electro-analysis of freshwater biofilm on stainless steel surface at different temperatures. Vacuum 194:110546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110546
Dick GJ, Lee YE, Tebo BM (2006) Manganese(II)-oxidizing Bacillus Spores in guaymas basin hydrothermal sediments and plumes. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(5):3184–3190. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.72.5.3184-3190.2006
Dickinson WH, Lewandowski Z (1996) Manganese biofouling and the corrosion behavior of stainless steel. Biofouling 10(1–3):79–93. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927019609386272
Dickinson WH, Wiatr C (2013) Manganese-related corrosion and fouling in water systems. Analyst 20:20–35
Dickinson WH, Caccavo F Jr, Lewandowski Z (1996) The ennoblement of stainless steel by manganic oxide biofouling. Corrosion Sci 38(8):1407–1422. https://doi.org/10.1016/0010-1938X(1496)00031-00035
George RP, Mudali UK, Raj B (2016) Characterizing biofilms for biofouling and microbial corrosion control in cooling water systems. Anti-Corrosion Methods Mater 63(6):477–489. https://doi.org/10.1108/acmm-07-2014-1401
George RP KMU, Anandkumar B (2017) Metal-Microbe Synergy Mechanisms in Localized Corrosion of Stainless Steels. Paper presented at the CORCON2017, Mumbai India
Gopal J, Muraleedharan P, Sarvamangala H, George R, Dayal R, Tata B, Khatak H, Natarajan K (2008) Biomineralisation of manganese on titanium surfaces exposed to seawater. Biofouling 24(4):275–282. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927010802056467
Hamilton W (2003) Microbially influenced corrosion as a model system for the study of metal microbe interactions: a unifying electron transfer hypothesis. Biofouling 19(1):65–76. https://doi.org/10.1080/0892701021000041078
Hedberg YS, Odnevall Wallinder I (2016) Metal release from stainless steel in biological environments: a review. Biointerphases 11(1):018901
Ilton ES, Post JE, Heaney PJ, Ling FT, Kerisit SN (2016) XPS determination of Mn oxidation states in Mn (hydr) oxides. Appl Surface Sci 366:475–485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.1012.1159
Ivarsson M, Broman C, Gustafsson H, Holm NG (2015) Biogenic Mn-oxides in subseafloor basalts. PLoS ONE 10(6):e0128863. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0128863
Jones PR, Cottrell MT, Kirchman DL, Dexter SC (2007) Bacterial community structure of biofilms on artificial surfaces in an estuary. Microb Ecol 53(1):153–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-006-9154-5
Julien C, Massot M, Baddour-Hadjean R, Franger S, Bach S, Pereira-Ramos J (2003) Raman spectra of birnessite manganese dioxides. Solid State Ionics 159(3–4):345–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2738(1003)00035-00033
Julien C, Massot M, Poinsignon C (2004) Lattice vibrations of manganese oxides: part I. Periodic structures. Spectrochimica Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 60(3):689–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1386-1425(1003)00279-00278
Katsikogianni M, Missirlis Y (2004) Concise review of mechanisms of bacterial adhesion to biomaterials and of techniques used in estimating bacteria-material interactions. Eur Cell Mater 8(3):37–57. https://doi.org/10.22203/eCM.v22008a22205
Kip N, van Veen JA (2015) The dual role of microbes in corrosion. ISME J 9(3):542–551. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.169
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874
Lakshman Kumar A, Eashwar M, Sreedhar G, Vengatesan S, Prabu V, Shanmugam V (2019) Portraying manganese biofilms via a merger of EPR spectroscopy and cathodic polarization. Biofouling 35(7):768–784. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.08922019.01658747
Lamim VB, Procópio L (2021) Influence of acidification and warming of seawater on biofouling by bacteria grown over API 5L steel. Indian J Microbiol 61(2):151–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-021-00925-7
Lee JS, Little BJ (2018) A mechanistic approach to understanding microbiologically influenced corrosion by metal-depositing bacteria. Corrosion 75(1):6–11. https://doi.org/10.5006/2899
Lewandowski Z, Dickinson W, Lee W (1997) Electrochemical interactions of biofilms with metal surfaces. Water Sci Technol 36(1):295–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0273-1223(1097)00336-00333
Liang J, Bai Y, Men Y, Qu J (2017) Microbe–microbe interactions trigger Mn(II)-oxidizing gene expression. ISME J 11(1):67–77. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2016.106
Liao J, Fukui H, Urakami T, Morisaki H (2010) Effect of biofilm on ennoblement and localized corrosion of stainless steel in fresh dam-water. Corrosion Sci 52(4):1393–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2010.1301.1012
Linhardt P (2010) Twenty years of experience with corrosion failures caused by manganese oxidizing microorganisms. Mater Corrosion 61(12):1034–1039. https://doi.org/10.1002/maco.201005769
Little BJ, Hinks J, Blackwood DJ (2020) Microbially influenced corrosion: towards an interdisciplinary perspective on mechanisms. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 154:105062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2020.105062
Liu H, Sharma M, Wang J, Cheng YF, Liu H (2018) Microbiologically influenced corrosion of 316L stainless steel in the presence of Chlorella vulgaris. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 129(209–216):2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2018.1003.1001
Mayhew LE, Swanner ED, Martin AP, Templeton AS (2008) Phylogenetic relationships and functional genes: distribution of a gene mnxG encoding a putative manganese-oxidizing enzyme in Bacillus species. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(23):7265–7271. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00540-08
Meng H, Hu X, Neville A (2007) A systematic erosion–corrosion study of two stainless steels in marine conditions via experimental design. Wear 263(1–6):355–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2006.1012.1007
Menzel P, Ng KL, Krogh A (2016) Fast and sensitive taxonomic classification for metagenomics with Kaiju. Nat Commun 7(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11257
Moradi M, Duan J, Ashassi-Sorkhabi H, Luan X (2011) De-alloying of 316 stainless steel in the presence of a mixture of metal-oxidizing bacteria. Corrosion Sci 53(12):4282–4290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2011.4208.4043
Morgan JJ (2005) Kinetics of reaction between O2 and Mn (II) species in aqueous solutions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69(1):35–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2004.1006.1013
Mudali UK, George R, Anandkumar B (2016) Metal-Microbe Synergy in Pitting Corrosion of Stainless Steels. In: CORROSION 2016, 2016. OnePetro
Nagarajan S, Rajendran N (2009) Crevice corrosion behaviour of superaustenitic stainless steels: dynamic electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy studies. Corros Sci 51(2):217–224
Narenkumar J, Sathishkumar K, Selvi A, Gobinath R, Murugan K, Rajasekar A (2017) Role of calcium-depositing bacteria Agrobacterium tumefaciens and its influence on corrosion of different engineering metals used in cooling water system. 3 Biotech 7(6):374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-017-1007-z
Nejad Ababaf A, Jafari E (2023) Study of microbiologically influenced corrosion of the welded stainless steel 316L. J Mater Eng Perform. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-022-07718-z
Neville A, Hodgkiess T (2000) Corrosion of stainless steels in marine conditions containing sulphate reducing bacteria. Br Corros J 35(1):60–69. https://doi.org/10.1179/000705900101501092
Ogawa A, Kanematsu H, Sano K, Sakai Y, Ishida K, Beech IB, Suzuki O, Tanaka T (2016) Effect of silver or copper nanoparticles-dispersed silane coatings on biofilm formation in cooling water systems. Materials. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080632
Olesen BH, Avci R, Lewandowski Z (1998) Ennoblement of stainless steel studied by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. In: CORROSION 98, NACE International
Olsson C-O, Landolt D (2003) Passive films on stainless steels—chemistry, structure and growth. Electrochim Acta 48(9):1093–1104. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(1002)00841-00841
Park JH, Kim B-S, Chon C-M (2018) Characterization of iron and manganese minerals and their associated microbiota in different mine sites to reveal the potential interactions of microbiota with mineral formation. Chemosphere 191:245–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.1010.1050
Post JE, McKeown DA, Heaney PJ (2020) Raman spectroscopy study of manganese oxides: tunnel structures. Am Mineral 105(8):1175–1190. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2020-7390
San NO, Nazır H, Dönmez G (2014) Microbially influenced corrosion and inhibition of nickel–zinc and nickel–copper coatings by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Corrosion Sci 79:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2013.1011.1004
Seyama H, Tani Y, Miyata N, Soma M, Iwahori K (2008) Characterization of pebble surfaces coated with biogenic manganese oxides by SIMS, XPS and SEM. Appl Surface Sci 255(4):1509–1511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.1511.1004
Sheng X, Pehkonen SO, Ting YP (2012) Biocorrosion of stainless steel 316 in seawater: inhibition using an azole type derivative. Corros Eng Sci Technol 47(5):388–393. https://doi.org/10.1179/1743278212Y.0000000014
Shi X, Avci R, Lewandowski Z (2002) Microbially deposited manganese and iron oxides on passive metals—their chemistry and consequences for material performance. Corrosion 58(9):728–738
Singhal D, Boase S, Field J, Jardeleza C, Foreman A, Wormald PJ (2012) Quantitative analysis of in vivo mucosal bacterial biofilms. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 1:57–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.20082
Swaraj S, Kumar R, Harinath YV, Rao TS (2013) Biocidal efficacy of ozone and chlorine on planktonic and biofilm cells of two marine bacteria species. Ozone-Sci Eng 35(2):90–100. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919512.2013.759841
Szeinbaum N, Burns JL, DiChristina TJ (2014) Electron transport and protein secretion pathways involved in Mn (III) reduction by Shewanella oneidensis. Environ Microbiol Rep 6(5):490–500. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.12173
Szeinbaum N, Nunn BL, Cavazos AR, Crowe SA, Stewart FJ, DiChristina TJ, Reinhard CT, Glass JB (2020) Novel insights into the taxonomic diversity and molecular mechanisms of bacterial Mn (III) reduction. Environ Microbiol Rep 12(5):583–593. https://doi.org/10.1111/1758-2229.1286
Szklarska-Smialowska Z (1986) Pitting corrosion of metals
Tebo BM, Johnson HA, McCarthy JK, Templeton AS (2005) Geomicrobiology of manganese (II) oxidation. Trends Microbiol 13(9):421–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tim.2005.1007.1009
Teske A, Hinrichs KU, Edgcomb V, Gomez AV, Kysela D, Sylva SP, Sogin ML, Jannasch HW (2002) Microbial diversity of hydrothermal sediments in the Guaymas Basin: evidence for anaerobic methanotrophic communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1994–2007
Tian W, Du N, Li S, Chen S, Wu Q (2014) Metastable pitting corrosion of 304 stainless steel in 3.5% NaCl solution. Corros Sci 85:372–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2014.04.033
Tran TTT, Kannoorpatti K, Padovan A, Thennadil S, Nguyen Dang N (2019) Effect of nickel on the adhesion and corrosion ability of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on stainless steel. J Mater Eng Perform 28(9):5797–5805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-019-04283-w
Tran TTT, Kannoorpatti K, Padovan A, Thennadil S (2021) A study of bacteria adhesion and microbial corrosion on different stainless steels in environment containing Desulfovibrio vulgaris. Royal Soc Open Sci 8(1):201577. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.201577
Venkatnarayanan S, Murthy PS, Kirubagaran R, Venugopalan VP (2016) Effect of chlorination on barnacle larval stages: implications for biofouling control and environmental impact. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation 109:141–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.01.011
Wang Y, Qian P-Y (2009) Conservative fragments in bacterial 16S rRNA genes and primer design for 16S ribosomal DNA amplicons in metagenomic studies. PLoS ONE 4(10):e7401
Watts G, Youens-Clark K, Slepian M, Wolk D, Oshiro M, Metzger G, Dhingra D, Cranmer L, Hurwitz B (2017) 16S rRNA gene sequencing on a benchtop sequencer: accuracy for identification of clinically important bacteria. J Appl Microbiol 123(6):1584–1596
Yang W, Zhang Z, Zhang Z, Chen H, Liu J, Ali M, Liu F, Li L (2013) Population structure of manganese-oxidizing bacteria in stratified soils and properties of manganese oxide aggregates under manganese–complex medium enrichment. PLoS ONE 8(9):e73778. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073778
Yuan S, Pehkonen S (2007) Microbiologically influenced corrosion of 304 stainless steel by aerobic Pseudomonas NCIMB 2021 bacteria: AFM and XPS study. Colloids Surf, B 59(1):87–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2007.1004.1020
Zhang T, Liu M, Sun J, Shi Y, Zeng J, Lou K (2012) Bacterial diversity in rock varnish of extreme arid region of Turpan Basin. Acta Ecol Sin 32(5):265–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chnaes.2012.07.006
Zhang P, Xu D, Li Y, Yang K, Gu T (2015) Electron mediators accelerate the microbiologically influenced corrosion of 304 stainless steel by the Desulfovibrio vulgaris biofilm. Bioelectrochemistry 101:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2014.1006.1010
Zhao X, Wang X, Liu B, Xie G, Xing D (2018) Characterization of manganese oxidation by Brevibacillus at different ecological conditions. Chemosphere 205:553–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.1004.1130
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Shri. R. Selvam, and Dr. Geetisubhra Jena, CSTD, MMG, IGCAR, Kalpakkam for their helps in specimen preparation and EIS analysis, respectively. The authors also wish to thank Dr. R. Divakar, Director MMG and Dr. B. Venkatraman, Director IGCAR, Kalpakkam and for providing constant support and encouragements.
Funding
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. All authors certify that they have no affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript. The authors have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: AB. Methodology: AB, NGKD. Formal analysis and investigation: AB. Writing—original draft preparation: AB. Writing—review and editing: JP, NGKD. Resources: JP. Supervision: JP.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical standards
The research presented in the manuscript involved NO human participants and any animals. Hence, NO informed consent is applicable.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Balakrishnan, A., Dhaipule, N.G.K. & Philip, J. Microbiologically influenced corrosion of AISI 202 and 316L stainless steels under manganese-oxidizing biofilms. 3 Biotech 14, 12 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03845-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03845-z