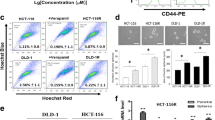
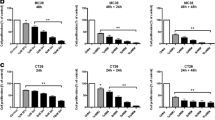
Abstract
Bevacizumab is the standard treatment for colorectal cancer (CRC) in the advanced stage. However, poor diagnosis identified due to the bevacizumab resistance in many CRC patients. Previous studies have found that CRC stem cells (CCSCs) and interleukin 22 (IL-22) are involved in the resistance of bevacizumab, however, the mechanism of remains unclear. In this study, we established the bevacizumab drug-resistant cell line HCT-116-R by concentration gradient method, and the cell viability was detected by CCK-8 assay. The resistance of bevacizumab in CRC cell lines HCT-116-R was identified by characterizing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Additionally, HCT-116-R cell lines were isolated from CCSCs and their tumorigenicity was validated in nude mice. We observed that that compared with the matched group, the expression of IL-22, IL-22R, STAT3, and GP130 in drug-resistant cells increased distinctly, with blocked IL-22 cells were successfully constructed by lentiviral interference. The level of proteins in stem cell landmarks (EpCAM, CD133), and stem cell landmarks (Oct4, Sox2) was identified by western blotting. Furthermore, the IL-22 role was evaluated by xenograft model. We found that short hairpin RNA (shRNA) suppression of IL-22 expression can restore the sensitivity of drug-resistant CCSCs to bevacizumab, Moreover, xenograft tumor models show that suppression of IL-22 can increase the anti-tumor influence of bevacizumab. In summary, we demonstrated that CCSCs play a major part in bevacizumab-resistant CRC. Inhibiting the signaling pathway of IL-22/STAT3 can improve the anti-tumor influence on bevacizumab in vitro and in vivo. Thus, IL-22 may represent a new anti-bevacizumab target in CRC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Available upon request.
References
Benlahfid M, Traboulsi W, Sergent F et al (2018) Endocrine gland-derived vascular endothelial growth factor (EG-VEGF) and its receptor PROKR2 are associated to human colorectal cancer progression and peritoneal carcinomatosis. Cancer Biomark 21:345–354. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-170499
Bruno S, Herrera Sanchez MB, Chiabotto G et al (2021) Human liver stem cells: a liver-derived mesenchymal stromal cell-like population with pro-regenerative properties. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:644088
Chou HH, Chen WC, Yang LY et al (2021) Postoperative adjuvant dose-dense chemotherapy with bevacizumab and maintenance bevacizumab after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for advanced ovarian cancer: a phase II AGOG/TGOG trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 262:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2021.04.017
Cui C, Chen X, Liu Y et al (2018) Galactosyltransferase v activates notch1 signaling in glioma stem-like cells and promotes their transdifferentiation into endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 293:2219–2230. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA117.000682
Fang C, Lin J, Zhang T et al (2021) Metastatic colorectal cancer patient with microsatellite stability and BRAFV600E mutation showed a complete metabolic response to PD-1 blockade and bevacizumab: a case report. Front Oncol 11:652394. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.652394
Hamdollah Zadeh MA, Amin EM, Hoareau-Aveilla C et al (2015) Alternative splicing of TIA-1 in human colon cancer regulates VEGF isoform expression, angiogenesis, tumour growth and bevacizumab resistance. Mol Oncol 9:167–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2014.07.017
Ishima Y, Inoue A, Fang J et al (2015) Poly-S-nitrosated human albumin enhances the antitumor and antimetastasis effect of bevacizumab, partly by inhibiting autophagy through the generation of nitric oxide. Cancer Sci 106:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12577
Koltsova EK, Grivennikov SI (2014) IL-22 gets to the stem of colorectal cancer. Immunity 40:639–641
Kryczek I, Lin Y, Nagarsheth N et al (2014) IL-22+CD4+ T cells promote colorectal cancer stemness via STAT3 transcription factor activation and induction of the methyltransferase DOT1L. Immunity 40:772–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2014.03.010
Liang J, Piao Y, Henry V et al (2015) Interferon-regulatory factor-1 (IRF1) regulates bevacizumab induced autophagy. Oncotarget 6:31479–31492. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.5491
Mendonça L, Trindade A, Carvalho C et al (2019) Metastasis is impaired by endothelial-specific Dll4 loss-of-function through inhibition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and reduction of cancer stem cells and circulating tumor cells. Clin Exp Metastasis 36:365–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10585-019-09973-2
Mossner S, Kuchner M, Modares NF et al (2020) Synthetic interleukin 22 (IL-22) signaling reveals biological activity of homodimeric IL-10 receptor 2 and functional cross-talk with the IL-6 receptor gp130. J Biol Chem 295:12378–12397. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.ra120.013927
Ottaiano A, Scala S, Santorsola M et al (2021) Aflibercept or bevacizumab in combination with FOLFIRI as second-line treatment of mRAS metastatic colorectal cancer patients: the ARBITRATION study protocol. Ther Adv Med Oncol 13:1758835921989223. https://doi.org/10.1177/1758835921989223
Rocha R, Torres Á, Ojeda K et al (2018) The adenosine A3 receptor regulates differentiation of glioblastoma stem-like cells to endothelial cells under hypoxia. Int J Mol Sci 19:1228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041228
Rosenberg JE, Ballman KA, Halabi S et al (2021) Randomized Phase III Trial of gemcitabine and cisplatin with bevacizumab or placebo in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma: results of CALGB 90601 (Alliance). J Clin Oncol 39:2486–2496. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.21.00286
Shah AA (2022) Tumor Angiogenesis and VEGFR-2: mechanism, pathways and current biological therapeutic interventions. Curr Drug Metab 22:50–59. https://doi.org/10.2174/18755453mtewxnzq0x
Wang R, Bhattacharya R, Ye X et al (2017) Endothelial cells activate the cancer stem cell-associated NANOGP8 pathway in colorectal cancer cells in a paracrine fashion. Mol Oncol 11:1023–1034. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12071
Wang JX, Wu HL, Zhu M, Zhou R (2020) Role of anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy compared with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: an update meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Pathol Oncol Res 26:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-017-0365-5
Wei Y, Shi D, Liang Z et al (2019) IL-17A secreted from lymphatic endothelial cells promotes tumorigenesis by upregulation of PD-L1 in hepatoma stem cells. J Hepatol 71:1206–1215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2019.08.034
Yan J, Yu J, Yuan S et al (2021) Musculin is highly enriched in Th17 and IL-22-producing ILC3s and restrains pro-inflammatory cytokines in murine colitis. Eur J Immunol 51:995–998
Yanagisawa H, Sugimoto M, Miyashita T (2021) Mathematical simulation of tumour angiogenesis: angiopoietin balance is a key factor in vessel growth and regression. Sci Rep 11:419. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-79824-8
Yoo C, Kim JH, Ryu MH et al (2021) Clinical outcomes with multikinase inhibitors after progression on first-line atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a multinational multicenter retrospective study. Liver Cancer 10:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1159/000512781
Zamani ARN, Avci ÇB, Ahmadi M et al (2020) Estradiol modulated colorectal cancer stem cells bioactivity and interaction with endothelial cells. Life Sci 257:118078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118078
Zhang Y, Liu J, Zou T et al (2021) DPSCs treated by TGF-β1 regulate angiogenic sprouting of three-dimensionally co-cultured HUVECs and DPSCs through VEGF-Ang-Tie2 signaling. Stem Cell Res Ther 12:281. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02349-y
Funding
This project was supported by the Research project plan of Medical Science in Hebei Province. No. 20210875.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XQ: conceptualization; investigation; methodology; writing a original draft. HR: data curation; analysis; review and editing. LY: analysis; review and editing. LL: visualization; supervision; resources review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This study was approved by the animal ethics committee of the second hospital of Hebei Medical University.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the animal ethics committee of the second hospital of Hebei Medical University.
Consent for publication
All authors agree for publication.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qin, X., Ruan, H., Yuan, L. et al. Colorectal cancer tumor stem cells mediate bevacizumab resistance through the signal IL-22-STAT3 signaling pathway. 3 Biotech 13, 327 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03742-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03742-5