Abstract
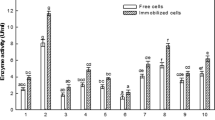
l-asparaginase (ASNase) is a key enzyme widely used as an anti-cancer drug and is also used in the pharmaceutical and food processing industries. This enzyme’s applications are determined by its source and nature. The production of the enzyme through the fermentation process is also crucial for economic feasibility. Searching for a new potent microbial strain is necessary for increased ASNase synthesis. In this work, a potent strain was isolated from the sediment of Chilika Lake and selected for its high ASNase production potential. It was recognized following Bergey’s manual of determinative and phylogenetic analysis was carried out by 16S rDNA sequencing. The isolated organism was Streptomyces sp. HB2AG. Additionally, a genome-wide analysis of HB2AG was performed. The result showed that the HB2AG genome possesses a chromosome with 6,099,956 bp and GC content of 74.0%. The whole genome analysis of the strain HB2AG revealed the presence of ASNase (ansA, ansB) and Asparagine synthase (asnB) in the HB2AG genome. Optimization of media composition is crucial for microbial growth and obtaining the desired end product. The current effort focuses on the Taguchi orthogonal design to determine optimum factor combinations that would allow the strain to produce maximum ASNase enzyme. Results showed that compared to unoptimized media, approximately 1.76-fold higher ASNase production was observed in Sea Water Luria Bertani (SWLB) media, pH-5, 0.5% (w/v) of lactose, 0.5% (w/v) of casein, 2.5% (w/v) NaCl, 1 mM Ca2+ and 0.1% Tween 80.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The data (WGS) is available and the sequence information is given in the manuscript.
References
Alanjary M, Steinke K, Ziemert N (2019) AutoMLST: an automated web server for generating multi-locus species trees highlighting natural product potential. Nucleic Acids Res 47(W1):W276–W282. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz282
Al-Dulimi AG, Al-Saffar AZ, Sulaiman GM, Khalil KA, Khashan KS, Al-Shmgani HS, Ahmed EM (2020) Immobilization of l-asparaginase on gold nanoparticles for novel drug delivery approach as anti-cancer agent against human breast carcinoma cells. J Market Res 9(6):15394–15411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.10.021
Alrumman S, Mostafa Y, Al-Izran KA, Alfaifi M, Taha T, Elbehairi S (2019) Production and anticancer activity of an l-asparaginase from Bacillus licheniformis isolated from the Red Sea, Saudi Arabia. Sci Rep 9(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40512-x
Arima K, Sakamoto T, Araki C, Tamura G (1972) Production of extracellular l-asparaginases by microorganisms. Agric Biol Chem 36(3):356–361. https://doi.org/10.1080/00021369.1972.10860270
Arndt D, Grant JR, Marcu A, Sajed T, Pon A, Liang Y, Wishart DS (2016) PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res 44(W1):W16–W21. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw387
Barka EA, Vatsa P, Sanchez L, Gaveau-Vaillant N, Jacquard C, Klenk H-P, Clément C, Ouhdouch Y, van Wezel GP (2016) Taxonomy, physiology, and natural products of Actinobacteria. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 80(1):1–43. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00019-15
Baskaran R, Vijayakumar R, Mohan P (2011) Enrichment method for the isolation of bioactive actinomycetes from mangrove sediments of Andaman Islands, India. Malays J Microbiol 7(1):26–32
Behera HT, Upadhyay AK, Raina V, Ray L (2019) Optimization of media components for the production of N-acetylchitooligosaccharide from chitin by Streptomyces chilikensis through Taguchi experimental design. J Microbiol Methods 159:194–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2019.03.014
Bertelli C, Laird MR, Williams KP, Group SFURC, Lau BY, Hoad G, Winsor GL, Brinkman FS (2017) IslandViewer 4: expanded prediction of genomic islands for larger-scale datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W30–W35. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx343
Chater KF (1993) Genetics of differentiation in Streptomyces. Annu Rev Microbiol 47:685–714
Costanza R, Kemp WM, Boynton WR (1993) Predictability, scale, and biodiversity in coastal and estuarine ecosystems: implications for management. Ambio 22:88–96
Crichton P, Collee J, Fraser A, Marmion B, Simmons A (1996) Mackie and McCartney, practical medical microbiology. Churchill Livingstone, New York
Darvishi F, Jahanafrooz Z, Mokhtarzadeh A (2022) Microbial l-asparaginase as a promising enzyme for treatment of various cancers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12086-8
de Cassia PJ, Giese EC, de Souza Moretti MM, dos Santos Gomes AC, Perrone OM, Boscolo M, da Silva R, Gomes E, Martins DAB (2017) Effect of metal ions, chemical agents and organic compounds on lignocellulolytic enzymes activities. Enzyme Inhib Activators 29:139–164
De la Fuente M, Lombardero L, Gómez-González A, Solari C, Angulo-Barturen I, Acera A, Vecino E, Astigarraga E, Barreda-Gómez G (2021) Enzyme therapy: current challenges and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 22(17):9181
Deshpande N, Choubey P, Agashe M (2014) Studies on optimization of growth parameters for l-asparaginase production by Streptomyces ginsengisoli. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/895167
Dominguez DC (2004) Calcium signalling in bacteria. Mol Microbiol 54(2):291–297. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2004.04276.x
El-Hadi AA, Ahmed HM, Hamzawy RA (2019) Optimization and characterization of L-asparaginase production by a novel isolated Streptomyces spp. strain. Egypt Pharm J 18(2):111. https://doi.org/10.4103/epj.epj_23_18
El-Naggar NE-A (2015) Extracellular production of the oncolytic enzyme, l-asparaginase, by newly isolated Streptomyces sp. strain NEAE-95 as potential microbial cell factories: optimization of culture conditions using response surface methodology. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 16(2):162–178
Gupta S, Wang C, Raetz EA, Schore R, Salzer WL, Larsen EC, Maloney KW, Mattano LA Jr, Carroll WL, Winick NJ (2020) Impact of asparaginase discontinuation on outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 38(17):1897. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.19.03024
Hadapsar P (2010) Isolation, optimization and production of l-asparaginase from coliform bacteria. Asian J Biotechnol 2(3):169–177
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PH, Staley JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergey’s Manual of determinate bacteriology.
Hsu S, Lockwood J (1975) Powdered chitin agar as a selective medium for enumeration of actinomycetes in water and soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 29(3):422–426. https://doi.org/10.1128/am.29.3.422-426.1975
Illanes A, Guerrero C, Vera C, Wilson L, Conejeros R, Scott F (2016) Lactose-derived prebiotics: a process perspective. Academic Press
Izadpanah Qeshmi F, Homaei A, Khajeh K, Kamrani E, Fernandes P (2022) Production of a novel marine Pseudomonas aeruginosa recombinant l-Asparaginase: insight on the structure and biochemical characterization. Mar Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10126-022-10129-9
Javadi M, Bouzari S, Oloomi M (2017) Horizontal gene transfer and the diversity of Escherichia coli. Escherichia coli-Recent Advances on Physiology, Pathogenesis and Biotechnological Applications
Jia R, Wan X, Geng X, Xue D, Xie Z, Chen C (2021) Microbial l-asparaginase for application in acrylamide mitigation from food: current research status and future perspectives. Microorganisms 9(8):1659. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9081659
Kim O-S, Cho Y-J, Lee K, Yoon S-H, Kim M, Na H, Park S-C, Jeon YS, Lee J-H, Yi H (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 62(Pt_3):716–721. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.038075-0
Kumar S, Dasu VV, Pakshirajan K (2010) Localization and production of novel l-asparaginase from Pectobacterium carotovorum MTCC 1428. Process Biochem 45(2):223–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2009.09.011
Lee I, Chalita M, Ha S-M, Na S-I, Yoon S-H, Chun J (2017) ContEst16S: an algorithm that identifies contaminated prokaryotic genomes using 16S RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67(6):2053–2057. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.001872
Mahajan RV, Saran S, Kameswaran K, Kumar V, Saxena R (2012) Efficient production of l-asparaginase from Bacillus licheniformis with low-glutaminase activity: optimization, scale up and acrylamide degradation studies. Biores Technol 125:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.08.086
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Carbasse JS, Peinado-Olarte RL, Göker M (2022) TYGS and LPSN: a database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 50(D1):D801–D807. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab902
Mukherjee R, Bera D (2022) Statistical optimization of asparaginase production by a novel isolated bacterium Brevibacillus borstelensis ML12 using Plackett-Burman design and response surface methodology. J Appl Biol Biotechnol 10(3):1–1. https://doi.org/10.7324/JABB.2022.100303
Munhoz Costa I, Custódio Moura D, Meira Lima G, Pessoa A, Oresco dos Santos C, de Oliveira MA, Monteiro G (2022) Engineered asparaginase from Erwinia chrysanthemi enhances asparagine hydrolase activity and diminishes enzyme immunoreactivity-a new promise to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 97(1):228–239. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.6933
Narayana K, Kumar K, Vijayalakshmi M (2008) l-asparaginase production by Streptomyces albidoflavus. Indian J Microbiol 48(3):331–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-008-0018-1
Nielsen CK, Kjems J, Mygind T, Snabe T, Meyer RL (2016) Effects of Tween 80 on growth and biofilm formation in laboratory media. Front Microbiol 7:1878. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.01878
Organization WH (2019) World Health Organization model list of essential medicines for children: 7th list 2019. World Health Organization
Ozer EA (2018) ClustAGE: a tool for clustering and distribution analysis of bacterial accessory genomic elements. BMC Bioinform 19(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-018-2154-x
Palaniappan S, Shanmugam S, Packiyaraj V, Kannan S, Shanmugam V, Thangavel B, Packium M (2013) Efficient production of l-asparaginase by marine Streptomyces sp. isolated from Bay of Bengal, India. Afr J Microbiol Res 7(31):4015–4021. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJMR12.2184
Paul V, Tiwary BN (2020) An investigation on the acrylamide mitigation potential of L-asparaginase from Aspergillus terreus BV-C strain. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 27:101677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2020.101677
Prakasham R, Rao CS, Rao RS, Lakshmi GS, Sarma P (2007) l-asparaginase production by isolated Staphylococcus sp.–6A: design of experiment considering interaction effect for process parameter optimization. J Appl Microbiol 102(5):1382–1391. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2006.03173.x
Prihanto A, Wakayama M (2016) Marine microorganism: an underexplored source of l-asparaginase. Adv Food Nutr Res 79:1–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.afnr.2016.07.005
Priyangini F, Walde SG, Chidambaram R (2018) Extraction optimization of pectin from cocoa pod husks (Theobroma cacao L.) with ascorbic acid using response surface methodology. Carbohyd Polym 202:497–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.103
Radha R, Gummadi SN (2021) Optimisation of physical parameters pH and temperature for maximised activity and stability of Vibrio cholerae l-asparaginase by statistical experimental design. Indian Chem Eng 63(4):425–434. https://doi.org/10.1080/00194506.2020.1758224
Rao RT, Sharma S, Sivakumar N, Jayakumar K (2020) Genomic islands and the evolution of livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus genomes. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20202287
Ray L, Suar M, Pattnaik AK, Raina V (2013) Streptomyceschilikensis sp. Nov., a halophilic streptomycete isolated from brackish water sediment. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 63(8):2757–2764. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.046284-0
Saleena SK, Johnson JI, Joseph JK, Padinchati KK, Abdulla MH (2022) Production and optimization of l-asparaginase by Streptomyces koyangensis SK4 isolated from Arctic sediment. J Basic Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.202200116
Shakambari G, Ashokkumar B, Varalakshmi P (2019) l-asparaginase–A promising biocatalyst for industrial and clinical applications. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 17:213–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2018.11.018
Shivlata L, Satyanarayana T (2015) Thermophilic and alkaliphilic Actinobacteria: biology and potential applications. Front Microbiol 6:1014. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2015.01014
Sushma C, Anand AP, Veeranki VD (2017) Enhanced production of glutaminase free l-asparaginase II by Bacillus subtilis WB800N through media optimization. Korean J Chem Eng 34(11):2901–2915. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-017-0211-1
Tanaya Behera H, Mojumdar A, Kumari K, Kumar Gouda S, Das S, Ray L (2022) Exploration of genomic and functional features of chitinolytic bacterium Streptomyces chilikensis RC1830, isolated from Chilika Lake, India. 3 Biotech 12(5):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03184-5
Tennalli GB, Garawadmath S, Sequeira L, Murudi S, Patil V, Divate MN, Hungund BS (2022) Media optimization for the production of alkaline protease by Bacillus cereus PW3A using response surface methodology. J Appl Biol Biotechnol 10(4):1–6. https://doi.org/10.7324/JABB.2022.100403
Tripathy SS, Dash S, Gupta N (2011) Screening and selection of some fungi for production of extracellular amylase. Indian J Fundam Appl Life Sci 1:131–136
Van Dijk EL, Auger H, Jaszczyszyn Y, Thermes C (2014) Ten years of next-generation sequencing technology. Trends Genet 30(9):418–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2014.07.001
Wakil SM, Adelegan AA (2015) Screening, production and optimization of l-asparaginase from soil bacteria isolated in Ibadan, South-western Nigeria. J Basic Appl Sci 11:39–51. https://doi.org/10.6000/1927-5129.2015.11.06
Wang Y, Xu W, Wu H, Zhang W, Guang C, Mu W (2021) Microbial production, molecular modification, and practical application of l-asparaginase: a review. Int J Biol Macromol 186:975–983. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.107
Zuo S, Xue D, Zhang T, Jiang B, Mu W (2014) Biochemical characterization of an extremely thermostable l-asparaginase from Thermococcus gammatolerans EJ3. J Mol Catal B Enzym 109:122–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2014.08.02
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the kind cooperation of Dr. Sujay Singh, Director, Imgenex India Private Limited for the completion of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rath, G., Nivedita, S., Behera, S.S. et al. l-Asparaginase producing novel Streptomyces sp. HB2AG: optimization of process parameters and whole genome sequence analysis. 3 Biotech 13, 201 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03620-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03620-0