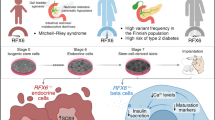
Abstract
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is associated with many health complications and is potentially a morbid condition. As prevalence increases at an alarming rate around the world, research into new antidiabetic compounds with different mechanisms is the top priority. Therefore, the preclinical experimental induction of DM is imperative for advancing knowledge, understanding pathogenesis, and developing new drugs. Efforts have been made to examine recent literature on the various induction methods of Type I and Type II DM. The review summarizes the different in vivo models of DM induced by chemical, surgical, and genetic (immunological) manipulations and the use of pathogens such as viruses. For good preclinical assessment, the animal model must exhibit face, predictive, and construct validity. Among all reported models, chemically induced DM with streptozotocin was found to be the most preferred model. However, the purpose of the research and the outcomes to be achieved should be taken into account. This review was aimed at bringing together models, benefits, limitations, species, and strains. It will help the researcher to understand the pathophysiology of DM and to choose appropriate animal models.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
It is a review article; hence, no laboratory data was generated.
References
Alkandahri MY, Sujana D, Hasyim DM, Shafirany MZ, Sulastri L et al (2021) Antidiabetic activity of extract and fractions of castanopsis costata leaves on alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Pharmacogn J 13(6):1589–1593. https://doi.org/10.5530/pj.2021.13.204
Amare YE (2021) Methanolic Extract of Myrsine africana leaf ameliorates hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia in alloxan-induced diabetic albino mice. eCAM 398:765263. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3987656
Arulmozhi DK, Veeranjaneyulu A, Bodhankar SL (2004) Neonatal streptozotocin-induced rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a glance. Indian J Pharmacol 36(4):217–221
Arya A, Jamil Al-Obaidi MM, Karim RB, Taha H, Khan AK et al (2015) Extract of Woodfordia fruticosa flowers ameliorates hyperglycemia, oxidative stress and improves β-cell function in streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. J Ethnopharmacol 175:229–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.08.057
Aswar U, Patil R, Bodhankar S (2019) Short review on the induction of obesity in laboratory animals. Diabesity 5(4):25–31. https://doi.org/10.15562/diabesity.2019.58
Aurora S, Shreesh KO, Divya V (2009) Characterization of Streptozotocin Induced Diabetes Mellitus in Swiss Albino Mice. Glob J Pharmacol 3(2):81–84
Azushima K, Gurley SB, Coffman TM (2017) Modelling diabetic nephropathy in mice. Nat Rev Nephrol 14(1):48–56. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2017.142
Badole S, Patel N, Bodhankar S, Jain B, Bhardwaj S (2006) Antihyperglycemic activity of aqueous extract of leaves of Cocculus hirsutus (L.) Diels in alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Indian J Pharmacol 38(1):49–53. https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7613.19853
Baek HS, Yoon JW (1990) Role of macrophages in the pathogenesis of encephalomyocarditis virus-induced diabetes in mice. J Virol 64(12):5708–5715. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.64.12.5708-5715.1990
Barragán-Iglesias P, Oidor-Chan VH, Loeza-Alcocer E, Pineda-Farias JB, Velazquez-Lagunas I et al (2018) Evaluation of the neonatal streptozotocin model of diabetes in rats: evidence for a model of neuropathic pain. Pharmacol Rep 70(2):294–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharep.2017.09.002
Bonner-Weir S, Trent DF, Honey RN, Weir GC (1981) Responses of neonatal rat islets to streptozotocin. Limited B cell regeneration and hyperglycemia. Diabetes 30(1):64–69. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.30.1.64
Campbell J, Chaikof L, Davidson IW (1954) Metahypophyseal diabetes produced by growth hormone. Endocrinology 54(1):48–58. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo-54-1-48
Cho YR, Kim HJ, Park SY, Ko HJ, Hong EG et al (2007) Hyperglycemia, maturity-onset obesity, and insulin resistance in NONcNZO10/LtJ males, a new mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293(1):E327–E336. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00376.2006
Christen U, Bender C, Von Herrath MG (2012) Infection as a cause of type 1 diabetes? Curr Opin Rheumatol 24(4):417–423. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0b013e3283533719
Cooksey RC, Jouihan HA, Ajioka RS, Hazel MW, Jones DL et al (2004) Oxidative stress, β-cell apoptosis, and decreased insulin secretory capacity in mouse models of hemochromatosis. Endocrinology 145(11):5305–5312. https://doi.org/10.2119/2007-00114.Jouihan
Craighead JE, McLane MF (1968) Diabetes mellitus: Induction in mice by encephalomyocarditis virus. Science 162(3856):913–914. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.162.3856.913
Cummings BP, Digitale EK, Stanhope KL, Graham JL, Baskin DG et al (2008) Development and characterization of a novel rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus: the UC Davis type 2 diabetes mellitus UCD-T2DM rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 295(6):R1782–R1793. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.90635.2008
Dandona P, Hussain MAM, Varghese Z, Politis D, Flynn DM, Hoffbrand AV (1983) Insulin Resistance and Iron Overload. Ann Clin Biochem 20(2):77–79. https://doi.org/10.1177/000456328302000203
Domingues A, Sartori A, Golim M, Valente L, Rosa L, Ishikawa L, Siani A, Viero R (2011) Prevention of experimental diabetes by Uncaria tomentosa extract: Th2 polarization, regulatory T cell preservation or both? J Ethnopharmacol 137(1):635–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.06.021
Dowarah J, Singh VP (2020) Anti-diabetic drugs recent approaches and advancements. Bioorg Med Chem 28(5):115263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2019.115263
Drel VR, Pacher P, Stavniichuk R, Xu W, Zhang J et al (2011) Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase inhibition counteracts renal hypertrophy and multiple manifestations of peripheral neuropathy in diabetic Akita mice. Int J Mol Med 28(4):629–635. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2011.709
Dubuc PU (1976) The development of obesity, hyperinsulinemia, and hyperglycemia in ob/ob mice. Metabolism 25(12):1567–1574. https://doi.org/10.1016/0026-0495(76)90109-8
Ellerman KE, Richards CA, Guberski DL, Shek WR, Like AA (1996) Kilham rat triggers T cell-dependent autoimmune diabetes in multiple strains of rat. Diabetes 45(5):557–562. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.45.5.557
Etgen GJ, Oldham BA (2000) Profiling of Zucker diabetic fatty rats in their progression to the overt diabetic state. Metab 49(5):684–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0026-0495(00)80049-9
Farooqi S, O’Rahilly S (2009) Leptin: a pivotal regulator of human energy homeostasis. Am J Clin Nutr 89(3):980–984. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2008.26788C
Feder JN, Gnirke A, Thomas W, Tsuchihashi Z, Ruddy DA et al (1996) A novel MHC class I-like gene is mutated in patients with hereditary haemochromatosis. Nat Genet 13(4):399–408. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0896-399
Federiuk IF, Casey HM, Quinn MJ, Wood MD, Ward WK (2004) Induction of type-1 diabetes mellitus in laboratory rats by use of alloxan: route of administration, pitfalls, and insulin treatment. Comp Med 54(3):252–257
Furman BL (2015) Streptozotocin-induced diabetic models in mice and rats. Curr Protoc Pharmacol 70(1):5–47. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471141755.ph0547s70
Gao T, Jiao Y, Liu Y, Li T, Wang Z, Wang D (2019) Protective effects of konjac and inulin extracts on type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Res 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/3872182
Ghasemi A, Khalifi S, Jedi S (2014) Streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced rat model of type 2 diabetes. Acta Physiol Hung 101(4):408–420. https://doi.org/10.1556/APhysiol.101.2014.4.2
Gorus FK, Malaisse WJ, Pipeleers DG (1982) Selective uptake of alloxan by pancreatic B cells. Biochem J 208(2):513–515. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj2080513
Goto Y, Kakizaki M, Masaki N (1976) Production of spontaneous diabetic rats by repetition of selective breeding. Tohoku J Exp Med 119(1):85–90. https://doi.org/10.1620/tjem.119.85
Gregori S, Giarratana N, Smiroldo S, Adorini L (2003) Dynamics of pathogenic and suppressor T cells in autoimmune diabetes development. J Immunol 171(8):4040–4047. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.171.8.4040
Hales CN, Desai M, Ozanne SE, Crowther NJ (1996) Fishing in the stream of diabetes: From measuring insulin to the control of fetal organogenesis. Biochem Soc Trans 24(2):341–350. https://doi.org/10.1042/bst0240341
Hammeso WW, Emiru YK, Getahun KA, Kahaliw W (2019) Antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic activities of the leaf latex extract of aloe megalacantha baker (Aloaceae) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic model. eCAM 2019. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/8263786
Hanchang W, Khamchan A, Wongmanee N, Seedadee C (2019) Hesperidin ameliorates pancreatic β-cell dysfunction and apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model. Life Sci 235:116858. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116858
Hayashi Y, Utsuyama M, Kurashima C, Hirokawa K (1989) Spontaneous development of organ-specific autoimmune lesions in aged C57BL/6 mice. Clin Exp Immunol 78(1):120–126
Himpe E, Cunha DA, Song I, Bugliani M, Marchetti P (2016) Phenylpropenoic acid glucoside from rooibos protects pancreatic beta cells against cell death induced by acute injury. PLoS ONE 11(6):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0157604
Hirasawa K, Jun HS, Maeda K, Kawaguchi Y, Itagaki S et al (1997) Possible role of macrophage-derived soluble mediators in the pathogenesis of encephalomyocarditis virus-induced diabetes in mice. J Virol 71(5):4024–4031. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.71.5.4024-4031.1997
Holmberg R, Refai E, Höög A, Crooke RM, Graham M et al (2011) Lowering apolipoprotein CIII delays onset of type 1 diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(26):10685–10689. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1019553108
Hotamisligil GS (2006) Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 444(7121):860–867. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05485
Hu TG, Wen P, Shen WZ, Liu F, Li Q et al (2019) Effect of 1-Deoxynojirimycin isolated from mulberry leaves on glucose metabolism and gut microbiota in a streptozotocin-induced diabetic mouse. Model J Nat Prod 82(8):2189–2200. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.9b00205
Huang J, Simcox J, Mitchell TC, Jones D, Cox J et al (2013) Iron regulates glucose homeostasis in liver and muscle via AMP-activated protein kinase in mice. FASEB J 27(7):2845–2854. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.12-216929
Ingalls AM, Dickie MM, Snell GD (1950) Obese, a new mutation in the house mouse. J Hered 41(12):315–317. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a106073
Iwase M, Nunoi K, Wakisaka M, Kikuchi M, Maki Y et al (1991) Spontaneous recovery from non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus induced by neonatal streptozotocin treatment in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Metabolism 40(1):10–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/0026-0495(91)90184-X
Jörns A, Günther A, Hedrich HJ, Wedekind D, Tiedge M, Lenzen S (2005) Immune cell infiltration, cytokine expression, and β-cell apoptosis during the development of type 1 diabetes in the spontaneously diabetic LEW.1AR1/Ztm-iddm rat. Diabetes 54(7):2041–2052. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.54.7.2041
Jouihan HA, Cobine PA, Cooksey RC, Hoagland EA, Boudina S et al (2008) Iron-mediated inhibition of mitochondrial manganese uptake mediates mitochondrial dysfunction in a mouse model of hemochromatosis. Mol Med 14(3–4):98–108. https://doi.org/10.2119/2007-00114
Jun HS, Yoon JW (2001) The role of viruses in Type I diabetes: two distinct cellular and molecular pathogenic mechanisms of virus-induced diabetes in animals. Diabetologia 44(3):271–285. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001250051614
Jwad M, Yousif Al-Fatlawi H, Student PD (2022) Types of diabetes and their effect on the immune system. J Adv Pharm Pract 4(1):21–30
Karasawa H, Takaishi K, Kumagae Y (2011) Obesity-induced diabetes in mouse strains treated with gold thioglucose: a novel animal model for studying β-cell dysfunction. Obesity 19(3):514–521. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2010.171
Kava R, Peterson RG, West DB, Greenwood MRC (1990a) Wistar diabetic fatty rat. ILAR J 32(3):9–13. https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.32.3.9
Kava R, Greenwood MRC, Johnson PR (1990b) Zucker ( fa/fa ) Rat. ILAR J 32(3):4–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.32.3.4
Kawano K, Hirashima T, Mori S, Natori T (1994) OLETF (Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty) rat: a new NIDDM rat strain. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 24:S317–S320. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-8227(94)90269-0
Kawasaki E, Abiru N, Eguchi K (2004) Prevention of type 1 diabetes: From the view point of β cell damage. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 66(66):S27–S32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2003.09.015
Kim JH, Stewart TP, Zhang W, Kim HY, Nishina PM, Naggert JK (2005) Type 2 diabetes mouse model TallyHo carries an obesity gene on chromosome 6 that exaggerates dietary obesity. Physiol Genomics 22(26):171–181. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00197.2004
Kim TK, Lee JC, Im SH, Lee MS (2020) Amelioration of autoimmune diabetes of NOD mice by immunomodulating probiotics. Front Immunol 11:1832. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01832
King AJ (2012) The use of animal models in diabetes research. Br J Pharmacol 166(3):877–894. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.01911.x
Kocaman N, Kuloğlu T (2020) Expression of asprosin in rat hepatic, renal, heart, gastric, testicular and brain tissues and its changes in a streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus model. Tissue Cell 66:101397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tice.2020.101397
Kong LL, Wu H, Cui WP, Zhou WH, Luo P et al (2013) Advances in murine models of diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/797548
Leiter EH, Reifsnyder PC (2004) Differential levels of diabetogenic stress in two new mouse models of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 53(1):S4-11. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.53.2007.s4
Leiter EH, Strobel M, O’Neill A, Schultz D, Schile A, Reifsnyder PC (2013) Comparison of two new mouse models of polygenic type 2 diabetes at the Jackson Laboratory, NONcNZO10Lt/J and TALLYHO/JngJ. J Diabetes Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/165327
Lenzen S (2008) The mechanisms of alloxan- and streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Diabetologia 51(2):216–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-007-0886-7
Lenzen S, Munday R (1991) Thiol-group reactivity, hydrophilicity and stability of alloxan, its reduction products and its N-methyl derivatives and a comparison with ninhydrin. Biochem Pharmacol 42(7):1385–1391. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(91)90449-F
Li S, Huang Q, Zhang L, Qiao X, Zhang Y, Tang F, Li Z (2019) Effect of CAPE-pNO2 against type 2 diabetes mellitus via the AMPK/GLUT4/ GSK3β/PPARα pathway in HFD/STZ-induced diabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol 853:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.03.027
Lutz TA, Woods SC (2012) Overview of animal models of obesity. Curr Protoc Pharmacol 58(1):5–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471141755.ph0561s58
Masiello P, Broca C, Gross R, Roye M, Manteghetti M et al (1998) Experimental NIDDM: development of a new model in adult rats administered streptozotocin and nicotinamide. Diabetes 47(2):224–229. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.47.2.224
Melanitou E, Devendra D, Liu E, Miao D, Eisenbarth GS (2004) Early and quantal (by litter) expression of insulin autoantibodies in the nonobese diabetic mice predict early diabetes onset. J Immunol 173(11):6603–6610. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.173.11.6603
Minokoshi Y, Kahn CR, Kahn BB (2003) Tissue-specific ablation of the GLUT4 glucose transporter or the insulin receptor challenges assumptions about insulin action and glucose homeostasis. J Biol Chem 278(36):33609–33612
Mordes JP, Poussier P, Rossini AA, Blankenhorn EP, Greiner DL (2007) Rat models of type 1 diabetes: genetics, environment, and autoimmunity. Anim Model Diabetes Second Ed Front Res https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.45.3.278
Muhlhausler B, Smith SR (2009) Early-life origins of metabolic dysfunction: role of the adipocyte. Trends Endocrinol Metab 20(2):51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2008.10.006
Munday R (1988) Dialuric acid autoxidation. Biochem Pharmacol 37(3):409–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/0006-2952(88)90207-9
Murakawa Y, Zhang W, Pierson CR, Brismar T, Östenson CG, Sima AAF (2002) Impaired glucose tolerance and insulinopenia in the GK-rat causes peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 18(6):473–483. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.326
Naderi A, Zahed R, Aghajanpour L, Amoli FA, Lashay A (2019) Long term features of diabetic retinopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic Wistar rats. Exp Eye Res 184:213–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2019.04.025
Nakajima S, Hira T, Hara H (2015) Postprandial glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion is increased during the progression of glucose intolerance and obesity in high-fat/high-sucrose diet-fed rats. Br J Nutr 113(9):1477–1488. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114515000550
Nakamura M, Yamada K (1967) Studies on a diabetic (KK) strain of the mouse. Diabetologia 3:212–221. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01222198
Nayak Y, Hillemane V, Daroji VK, Ayashree BSJ, Unnikrishnan MK (2014) Antidiabetic activity of benzopyrone analogues in nicotinamide-streptozotocin induced type 2 diabetes in rats. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/854267
Nazir N, Muhammad J, Ghaffar R, Nisar M, Zahoor M, Uddin F, Ullah R, Alotaibi A (2021) Phytochemical profiling and antioxidant potential of Daphne mucronata Royle and action against paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity in rabbits. Saudi J Biol Sci 28(9):5290–5301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.05.051
Obasi DC, Ogugua VN (2021) GC-MS analysis, pH and antioxidant effect of Ruzu herbal bitters on alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Biochem Biophys Reports 27:101057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.101057
Oguntibeju OO, Aboua GY, Omodanisi EI (2020) Effects of Moringa oleifera on oxidative stress, apoptotic and inflammatory biomarkers in streptozotocin-induced diabetic animal model. South African J Bot 129:354–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2019.08.039
Onyibe PN, Edo GI, Nwosu LC, Ozgor E (2021) Effects of vernonia amygdalina fractionate on glutathione reductase and glutathione-S-transferase on alloxan induced diabetes wistar rat. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 36:102118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102118
Oraby MA, El-Yamany MF, Safar MM, Assaf N, Ghoneim HA (2019) Dapagliflozin attenuates early markers of diabetic nephropathy in fructose-streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 109:910–920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.100
Östenson CG, Efendic S (2007) Islet gene expression and function in type 2 diabetes; studies in the Goto–Kakizaki rat and humans. Diabetes, Obes Metab 9(Suppl 2):180–186
Oyadomari S, Araki E, Mori M (2002) Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in pancreatic β cells. Apoptosis 7(4):335–345. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1463-1326.2007.00787.x
Pak CY, Mcarthur RG, Eun HM, Yoon JW (1988) Association of cytomegalovirus infection with autoimmune type 1 diabetes. Lancet 332(8601):1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(88)92941-8
Park EY, Kim HJ, Kim YK, Park SU, Choi JE et al (2012) Increase in insulin secretion induced by panax ginseng berry extracts contributes to the amelioration of hyperglycemia in streptozotocin induced diabetic mice. J Ginseng Res 36(2):153–160. https://doi.org/10.5142/jgr.2012.36.2.153
Peterson RG, Jackson CV, Zimmerman K, De Winter W, Huebert N, Hansen MK (2015) Characterization of the ZDSD rat: a translational model for the study of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/487816
Portha B, Levacher C, Picon L, Rosselin G (1974) Diabetogenic effect of streptozotocin in the rat during the perinatal period. Diabetes 23(11):889–895. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.23.11.889
Portha B, Lacraz G, Kergoat M, Homo-Delarche F, Giroix MH et al (2009) The GK rat beta-cell: a prototype for the diseased human beta-cell in type 2 diabetes? Mol Cell Endocrinol 297(1–2):73–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2008.06.013
Pozzilli P, Signore A, Williams AJK, Beales PE (1993) NOD mouse colonies around the world- recent facts and figures. Immunol Today 14(5):193–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-5699(93)90160-M
Raafat K, Aboul-Ela M, El-Lakany A (2021) Alloxan-induced diabetic thermal hyperalgesia, prophylaxis and phytotherapeutic effects of Rheum ribes L. in mouse model. Arch Pharm Res 44(8):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-014-0372-y
Radenković M, Stojanović M, Prostran M (2016) Experimental diabetes induced by alloxan and streptozotocin: the current state of the art. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 78:13–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vascn.2015.11.004
Reed MJ, Meszaros K, Entes LJ, Claypool MD, Pinkett JG et al (2000) A new rat model of type 2 diabetes: the fat-fed, streptozotocin-treated rat. Metabolism 49(11):1390–1394
Reusser F (1971) Mode of action of streptozotocin. J Bacteriol 105(2):580–588. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.105.2.580-588.1971
Rewers M, Ludvigsson J (2016) Environmental risk factors for type 1 diabetes. Lancet 387(10035):2340–2348. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30507-4
Roep BO, Atkinson M (2004) Animal models have little to teach us about Type 1 diabetes: 1. In support of this proposal. Diabetologia 47(10):1650–1656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-004-1517-1
Rossini AA, Like AA, Chick WL, Appel MC, Cahill GF (1977) Studies of streptozotocin induced insulitis and diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74(6):2485–2489. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.74.6.248
Saliu TP, Yazawa N, Hashimoto K, Miyata K, Kudo A (2022) Serum amyloid a3 promoter-driven luciferase activity enables visualization of diabetic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci 23(2):899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23020899
Schwartz MW, Niswender KD (2004) Adiposity signaling and biological defense against weight gain: Absence of protection or central hormone resistance? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(12):5889–5897. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2004-0906
Sergeys J, Etienne I, Van Hove I, Lefevere E, Stalmans I et al (2019) Longitudinal in vivo characterization of the streptozotocin-induced diabetic mouse model: Focus on early inner retinal responses. Investig Ophthalmol vis Sci 60(2):807–822. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.18-25372
Skovsø S (2014) Modeling type 2 diabetes in rats using high fat diet and streptozotocin. J Diabetes Investig 5(4):349–358. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.12235
Slieker LJ, Sundell KL, Heath WF, Osborne HE, Bue J et al (1992) Glucose transporter levels in tissues of spontaneously diabetic Zucker fa/fa rat (ZDF/drt) and viable yellow mouse (A(vy)/a). Diabetes 41(2):187–193. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.41.2.187
Sole SS, Srinivasan BP (2012) Aqueous extract of tamarind seeds selectively increases glucose transporter-2, glucose transporter-4, and islets’ intracellular calcium levels and stimulates β-cell proliferation resulting in improved glucose homeostasis in rats with streptozotocin-induce. Nutr Res 32(8):626–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2012.06.015
Solikhah TI, Solikhah GP (2021) Effect of Muntingia calabura L. Leaf Extract on blood glucose levels and body weight of alloxan-induced diabetic mice. Pharmacogn J 13(6):1450–1455. https://doi.org/10.5530/PJ.2021.13.184
Sone H, Kawakami Y, Okuda Y, Sekine Y, Honmura S et al (1997) Ocular vascular endothelial growth factor levels in diabetic rats are elevated before observable retinal proliferative changes. Diabetologia 40(6):726–730. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001250050740
Souza-Mello V, Gregorio BM, Cardoso-de-Lemos FS, de Carvalho L, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2010) Comparative effects of telmisartan, sitagliptin and metformin alone or in combination on obesity, insulin resistance, and liver and pancreas remodelling in C57BL/6 mice fed on a very high-fat diet. Clin Sci 119(6):239–250. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20100061
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL, Ramarao P (2005) Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose streptozotocin-treated rat : A model for type 2 diabetes and pharmacological screening. Pharmacological Res 52:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2005.05.004
Steiner H, Oelz O, Zahnd G, Froesch ER (1970) Studies on islet cell regeneration, hyperplasia and intrainsular cellular interrelations in long lasting streptozotocin diabetes in rats. Diabetologia 6(6):558–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00418221
Sun C De, Zhang B, Zhang JK, Xu CJ, Wu YL et al (2012) Cyanidin-3-glucoside-rich extract from Chinese bayberry fruit protects pancreatic β cells and ameliorates hyperglycemia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J Med Food 15(3):288–298. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2011.1806
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K et al (2022) IDF diabetes atlas: global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 183:109119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
Surguchov A (2020) Caveolin: a new link between diabetes and AD. Cell Mol Neurobiol 40(7):1059–1066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-020-00796-4
Tabatabaie PS, Yazdanparast R (2017) Teucrium polium extract reverses symptoms of streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats via rebalancing the Pdx1 and FoxO1 expressions. Biomed Pharmacother 93:1033–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.06.082
Tiano JP, Mauvais-Jarvis F (2012) Importance of oestrogen receptors to preserve functional β-cell mass in diabetes. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8(6):342–351
Toda C, Diano S (2014) Mitochondrial UCP2 in the central regulation of metabolism. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 28(5):757–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2014.02.006
Udumula MP, Mangali S, Kalra J, Dasari D, Goyal S et al (2021) High fructose and streptozotocin induced diabetic impairments are mitigated by Indirubin-3-hydrazone via downregulation of PKR pathway in Wistar rats. Sci Rep 11(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-92345-2
Ueda H, Ikegami H, Yamato E, Fu J, Fukuda M et al (1995) The NSY mouse: a new animal model of spontaneous NIDDM with moderate obesity. Diabetologia 38(5):503–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00400717
Von Herrath M, Nepom GT (2009) Animal models of human type 1 diabetes. Nat Immunol 10(2):129–132. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni0209-129
Wallis RH, Wang K, Marandi L, Hsieh E, Ning T et al (2009) Type 1 diabetes in the BB rat: a polygenic disease. Diabetes 58(4):1007–1017. https://doi.org/10.2337/db08-1215
Wang Z, Gleichmann H (1998) GLUT2 in pancreatic islets: crucial target molecule in diabetes induced with multiple low doses of streptozotocin in mice. Diabetes 47(1):50–56. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.47.1.50
Wang RN, Kliippel G, Bouwens L, Jette C (1995) Duct- to islet-cell differentiation and islet growth in the pancreas of duct-ligated adult rats. Diabetologia 38:1405–1411. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00400600
Wang ZH, Hsu CC, Lin HH, Chen JH (2014) Antidiabetic effects of carassius auratus complex formula in high fat diet combined streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Evid-Based Complement Altern Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/628473
Weaver DC, McDaniel ML, Naber SP, Barry CD, Lacy PE (1978) Alloxan stimulation and inhibition of insulin release from isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Diabetes 27(12):1205–1214. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.27.12.1205
Wickramasinghe ASD, Kalansuriya P, Attanayake AP (2021) Herbal medicines targeting the improved β -cell functions and β -cell regeneration for the management of diabetes mellitus. Evidence-Based Complement Altern Med 2021:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2920530
Wilson RD, Islam MS (2012) Fructose-fed streptozotocin-injected rat: an alternative model for type 2 diabetes. Pharmacol Rep 64(1):129–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1734-1140(12)70739-9
Wszola M, Klak M, Kosowska A, Tymicki G, Berman A et al (2021) Streptozotocin-induced diabetes in a mouse model (balb/c) is not an effective model for research on transplantation procedures in the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Biomedicines 9(12):1790. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121790
Xu M, Sun B, Li D, Mao R, Li H et al (2017) Beneficial effects of small molecule oligopeptides isolated from Panax ginseng meyer on pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction and death in diabetic rats. Nutrients 9(10):1061. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101061
Yamagami T, Miwa A, Takasawa S, Yamamoto H, Okamoto H (1985) Induction of rat pancreatic B cell tumors by the combined administration of streptozotocin or alloxan and poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) synthetase inhibitors. Cancer Res 45(4):1845–1849
Yadav KS, Yadav NP, Shanker K, Thomas SC, Srivastav S et al (2013) Assessment of antidiabetic potential of Cissampelos pareira leaf extract in streptozotocin–nicotinamide induced diabetic mice. J Pharm Res 6(8):874–878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jopr.2013.06.027
Yao HW, Ling P, Chen SH, Tung YY, Chen SH (2012) Factors affecting herpes simplex virus reactivation from the explanted mouse brain. Virology 433(1):116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2012.07.018
Yokoi N, Namae M, Fuse M, Wang HY, Hirata T et al (2003) Establishment and characterization of the Komeda diabetes-prone rat as a segregating inbred strain. Exp Anim 52(4):295–301. https://doi.org/10.1538/expanim.52.295
Yoon JW, Ko W, Bae YS, Pak CY, Amano K et al (1988) Identification of antigenic differences between the diabetogenic and non-diabetogenic variants of encephalomyocarditis virus using monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol 69(5):1085–1090. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-69-5-1085
Yu J, Sharma P, Girgis CM, Gunton JE (2022) Vitamin D and beta cells in type 1 diabetes: a systematic review. Int J Mol Sci 23(22):14434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232214434
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Yanni J, Qureshi MA, Logantha S et al (2019) Electrical conduction system remodeling in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus rat heart. Front Physiol 10:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00826
Zhou C, Pridgen B, King N, Xu J, Breslow JL (2011) Hyperglycemic Ins2AkitaLdlr–/– mice show severely elevated lipid levels and increased atherosclerosis: a model of type 1 diabetic macrovascular disease. J Lipid Res 52(8):1483–1493. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M014092
Zhuge F, Ni Y, Wan C, Liu F, Fu Z (2021) Anti-diabetic effects of astaxanthin on an stz-induced diabetic model in rats. Endocr J 68(4):451–459. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrjEJ20-0699
Ziv E, Shafrir E, Kalman R, Galer S, Bar-On H (1999) Changing pattern of prevalence of insulin resistance in Psammomys obesus, a model of nutritionally induced type 2 diabetes. Metab Clin Exp 48(12):1549–1554. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0026-0495(99)90244-5
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr A.P. Pawar, Principal, PCP, BVDU, for providing the necessary facilities to prepare the manuscript. Graphical abstract was prepared by Biorender.The authors would like to acknowledge BANRF, India for supporting Ms Rashmi Patil.
Funding
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical statement
Not applicable (review article).
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rashmi, P., Urmila, A., Likhit, A. et al. Rodent models for diabetes. 3 Biotech 13, 80 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03488-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03488-0