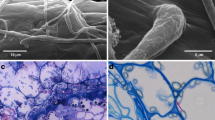
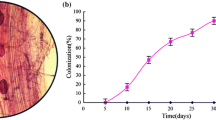
Abstract
Pisolithus albus is a ubiquitous ectomycorrhizal fungus that establishes symbiosis with a wide range of woody plants around the globe. The symbiotic association of this fungus plays a crucial role in the nutrient cycling of their host plants and enables them to thrive in adverse environmental conditions. Based on its ecological importance and lack of genomic studies, whole-genome sequencing was carried out to analyze P. albus sequences through an Illumina HiSeq X system. The functional annotations were performed against various databases to explore genomic patterns and traits possibly attributing to its specialization. Comparative genomics of P. albus with phylogenetically related Pisolithus microcarpus and Pisolithus tinctorius (only available genomes of Pisolithus at NCBI till now) led to the identification of their unique and shared basic functional and stress adaptation capabilities. The de novo assembled genome of 56.15 Mb with 91.8% BUSCO completeness is predicted to encode 23,035 genes. The study is aimed to generate solid genomic data resources for P. albus, forming the theoretical basis for future transcriptomic, proteomic and metabolomic studies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available in the GenBank repository by the corresponding author.
References
Aggangan NS, Aggangan BJS (2012) Selection of ectomycorrhizal fungi and tree species for rehabilitation of Cu mine tailings in the Philippines. J Environ Sci Manag 15:59–71
Allen GC, Flores-Vergara MA, Krasynanski S, Kumar S, Thompson WF (2006) A modified protocol for rapid DNA isolation from plant tissues using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide. Nat Protoc 1:2320–2325. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.384
Ameri A, Ghadge C, Vaidya JG, Deokule SS (2011) Anti-Staphylococcus aureus activity of Pisolithus albus from Pune, India. J Med Plants Res 5:527–532
Anderson IC, Chambers SM, Cairney JWG (1998) Use of molecular methods to estimate the size and distribution of mycelial individuals of the ectomycorrhizal basidiomycete Pisolithus tinctorius. Mycol Res 102:295–300. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756297004954
Andrews S (2010) FastQC—a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Babraham Bioinformatics. http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/. Accessed 12 Jan 2021
Baker DN, Langmead B (2019) Dashing: fast and accurate genomic distances with HyperLogLog. Genome Boil 20:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-019-1875-0
Basso V, Kohler A, Miyauchi S, Singan V, Guinet F, Šimura J, Novák O, Barry KW, Amirebrahimi M, Block J, Daguerre YNH, Grigoriev IV, Martin F, Veneault-Fourrey C (2020) An ectomycorrhizal fungus alters sensitivity to jasmonate, salicylate, gibberellin, and ethylene in host roots. Plant Cell Environ 43:1047–1068. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13702
Bisht V, Purwar S, Kumar D, Kumar B, Upadhayay V (2022) Effect of different spacings of eucalyptus plantation on biomass production of wheat cultivars in Northern India. Pharm Innov 11:135–139
Blin K, Shaw S, Kloosterman AM, Charlop-Powers Z, Van Wezel GP, Medema MH, Weber T (2021) AntiSMASH 6.0: improving cluster detection and comparison capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res 49:W29–W35. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab335
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Bougher NL, Syme K (1998) Fungi of southern Australia. University of Western Australia Press, Perth
Boutet E, Lieberherr D, Tognolli M, Schneider M, Bansal P, Bridge AJ et al (2016) UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot, the manually annotated section of the UniProt KnowledgeBase: how to use the entry view. Plant bioinformatics. Humana Press, New York, pp 23–54. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3167-5_2
Brzostek ER, Dragoni D, Brown ZA, Phillips RP (2015) Mycorrhizal type determines the magnitude and direction of root-induced changes in decomposition in a temperate forest. New Phytol 206:1274–1282. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13303
Chan PP, Lin BY, Mak AJ, Lowe TM (2019) tRNAscan-SE 2.0: improved detection and functional classification of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 49:9077–9096. https://doi.org/10.1101/614032
Chikhi R, Medvedev P (2014) Informed and automated k-mer size selection for genome assembly. Bioinformatics 30:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt310
Díez J (2005) Invasion biology of Australian ectomycorrhizal fungi introduced with eucalypt plantations into the Iberian Peninsula. Biol Invasions 7:3–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-004-9624-y
Gadgil RL, Gadgil PD (1971) Mycorrhiza and litter decomposition. Nature 233:133–133. https://doi.org/10.1038/233133a0
Hodge A (2017) Accessibility of inorganic and organic nutrients for mycorrhizas. Mycorrhizal mediation of soil. Elsevier, pp 129–148
Jackman SD, Vandervalk BP, Mohamadi H, Chu J, Yeo S, Hammond SA, Jahesh G, Khan H, Coombe L, Warren RL, Birol I (2017) ABySS 2.0: Resource-efficient assembly of large genomes using a Bloom filter. Genome Res 27:768–777. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.214346.116
Jackson O, Quilliam RS, Stott A, Grant H, Subke JA (2019) Rhizosphere carbon supply accelerates soil organic matter decomposition in the presence of fresh organic substrates. Plant Soil 440:473–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04072-3
Jourand P, Ducousso M, Loulergue-Majorel C, Hannibal L, Santoni S, Prin Y, Lebrun M (2010) Ultramafic soils from New Caledonia structure Pisolithus albus in ecotype. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 72:238–249. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2010.00843.x
Jourand P, Hannibal L, Majorel C, Mengant S, Ducousso M, Lebrun M (2014) Ectomycorrhizal Pisolithus albus inoculation of Acacia spirorbis and Eucalyptus globulus grown in ultramafic topsoil enhances plant growth and mineral nutrition while limits metal uptake. J Plant Physiol 171:164–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2013.10.011
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Kawashima S, Okuno Y, Hattori M (2004) The KEGG resource for deciphering the genome. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D277–D280. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh063
Kaur A, Monga R (2021) Eucalyptus trees plantation: a review on suitability and their beneficial role. Int J Bio-Resour Stress Manag 12:16–25. https://doi.org/10.23910/1.2020.2174
Keller NP (2019) Fungal secondary metabolism: regulation, function and drug discovery. Nat Rev Microbiol 17:167–180. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0121-1
Kohler A, Kuo A, Nagy L, Mori E, Barry KW, Buscot F et al (2015) Convergent losses of decay mechanisms and rapid turnover of symbiosis genes in mycorrhizal mutualists. Nat Genet 47:410–415. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3223
Li W, Jaroszewski L, Godzik A (2002) Tolerating some redundancy significantly speeds up clustering of large protein databases. Bioinformatics 18:77–82. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/18.1.77
Li L, Stoeckert CJ, Roos DS (2003) OrthoMCL: identification of ortholog groups for eukaryotic genomes. Genome Res 13:2178–2189. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1224503
Majorel C, Hannibal L, Soupe ME, Carriconde F, Ducousso M, Lebrun M, Jourand P (2012) Tracking nickel-adaptive biomarkers in Pisolithus albus from New Caledonia using a transcriptomic approach. Mol Ecol 21:2208–2223. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05527.x
Maltz MR, Chen Z, Cao J, Arogyaswamy K, Shulman H, Aronson EL (2019) Inoculation with Pisolithus tinctorius may ameliorate acid rain impacts on soil microbial communities associated with Pinus massoniana seedlings. Fungal Ecol 40:50–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2018.11.011
Marçais G, Delcher AL, Phillippy AM, Coston R, Salzberg SL, Zimin A (2018) MUMmer4: a fast and versatile genome alignment system. PLoS Comput Biol 14:1005944–8. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005944
Martin F, Duplessis S, Ditengou F, Lagrange H, Voiblet C, Lapeyrie F (2001) Developmental cross talking in the ectomycorrhizal symbiosis: signals and communication genes. New Phytol 151:145–154. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.2001.00169.x
Martin F, Díez J, Dell B, Delaruelle C (2002) Phylogeography of the ectomycorrhizal Pisolithus species as inferred from nuclear ribosomal DNA ITS sequences. New Phytol 153:345–357. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.0028-646X.2001.00313.x
Martino E, Morin E, Grelet GA et al (2018) Comparative genomics and transcriptomics depict ericoid mycorrhizal fungi as versatile saprotrophs and plant mutualists. New Phytol 217:1213–1229. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14974
Marx DH (1977) Tree host range and world distribution of the ectomycorrhizal fungus Pisolithus tinctorius. Can J Microbiol 23:217–223. https://doi.org/10.1139/m77-033
Melin E (1953) Physiology of mycorrhizal relations in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 4:325–346. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pp.04.060153.001545
Mikheenko A, Prjibelski A, Saveliev V, Antipov D, Gurevich A (2018) Versatile genome assembly evaluation with QUAST-LG. Bioinformatics 34:142–150. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty266
Mohanta TK, Bae H (2015) The diversity of fungal genome. Biol Proced Online 17:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12575-015-0020-z
Ondov BD, Treangen TJ, Melsted P, Mallonee AB, Bergman NH, Koren S et al (2016) Mash: fast genome and metagenome distance estimation using MinHash. Genome Biol 17:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-0997-x
Phosri C, Martin MP, Suwannasai N, Sihanonth P, Watling R (2012) Pisolithus: a new species from southeast Asia and a new combination. Mycotaxon 120:195–208. https://doi.org/10.5248/120.195
Plassard C, Becquer A, Garcia K (2019) Phosphorus transport in mycorrhiza: how far are we? Trends Plant Sci 24:794–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2019.06.004
Ravita RS, Ginwal HS, Barthwal S (2022) Screening of salt tolerant Eucalyptus clones based on physio-morphological and biochemical responses using grey relational analysis. J Sustain For 18:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/10549811.2022.2045508
Read DJ (1991) Mycorrhizas in ecosystems. Experientia 47:376–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972080
Reddy MS, Kour M, Aggarwal S, Ahuja S, Marmeisse R, Fraissinet-Tachet L (2016) Metal induction of a Pisolithus albus metallothionein and its potential involvement in heavy metal tolerance during mycorrhizal symbiosis. Environ Microbiol 18:2446–2454. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13149
Rog I, Rosenstock NP, Körner C, Klein T (2020) Share the wealth: trees with greater ectomycorrhizal species overlap share more carbon. Mol Ecol 29:2321–2333. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.15351
Sebastiana M, Pereira VT, Alcântara A, Pais MS, Silva AB (2013) Ectomycorrhizal inoculation with Pisolithus tinctorius increases the performance of Quercus suber L. (cork oak) nursery and field seedlings. New For 44:937–949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-013-9386-4
Shi L, Deng X, Yang Y, Jia Q, Wang C, Shen Z, Chen Y (2019) A Cr(VI)-tolerant strain, Pisolithus sp1, with a high accumulation capacity of Cr in mycelium and highly efficient assisting Pinus thunbergii for phytoremediation. Chemosphere 224:862–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.015
Simão FA, Waterhouse RM, Ioannidis P, Kriventseva EV, Zdobnov EM (2015) BUSCO: Assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics 31:3210–3212. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btv351
Singh V, Raj A, Jhariya MK, Thakur S (2022) Economic evaluation of agroforestry and non-agroforestry systems in Eastern Uttar Pradesh, India. Vegetos. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-022-00348-9
Singla S, Reddy MS, Marmeisse R, Gay G (2004) Genetic variability and taxonomic position of ectomycorrhizal fungus Pisolithus from India. Microbiol Res 159:203–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2004.03.003
Smith SE, Read DJ (2010) Mycorrhizal symbiosis, 3rd edn. Academic Press, New York, p 137
Sousa NR, Franco AR, Oliveira RS, Castro PML (2012) Ectomycorrhizal fungi as an alternative to the use of chemical fertilisers in nursery production of Pinus pinaster. J Environ Manag 95:S269–S274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.07.016
Suzek BE, Wang Y, Huang H, McGarvey PB, Wu CH, UniProt Consortium (2015) UniRef clusters: a comprehensive and scalable alternative for improving sequence similarity searches. Bioinformatics 31:926–932. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu739
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38:3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
Tatusov RL, Galperin MY, Natale DA, Koonin EV (2000) The COG database: a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res 28:33–36. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.33
Ter-Hovhannisyan V, Lomsadze A, Chernoff YO, Borodovsky M (2008) Gene prediction in novel fungal genomes using an ab initio algorithm with unsupervised training. Genome Res 18:1979–1990. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.081612.108
UniProt Consortium (2009) The universal protein resource (UniProt) 2009. Nucleic Acids Res 37:D169–D174. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn664
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Elsevier, pp 315–322
Xu L, Dong Z, Fang L, Luo Y, Wei Z, Guo H, Zhang G, Gu YQ, Coleman-Derr D, Xia Q, Wang Y (2019) OrthoVenn2: a web server for whole-genome comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res 47:W52–W58. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz333
Yu F, Song J, Liang J, Wang S, Lu J (2020) Whole genome sequencing and genome annotation of the wild edible mushroom, Russula griseocarnosa. Genomics 112:603–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2019.04.012
Zhang H, Yohe T, Huang L, Entwistle S, Wu P, Yang Z et al (2018) dbCAN2: a meta server for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 46:W95–W101. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky418
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Thapar Institute of Engineering and Technology for providing the facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
EC performed the whole analysis and wrote the first draft. PS curated and mentored bioinformatics analysis. KMM and MSR supervised the project. PS, KMM and MSR proofread the manuscript before all the authors agreed to the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chot, E., Suravajhala, P., Medicherla, K.M. et al. Characterization and genome-wide sequence analysis of an ectomycorrhizal fungus Pisolithus albus, a potential source for reclamation of degraded lands. 3 Biotech 13, 58 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03483-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-023-03483-5