Abstract
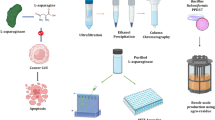
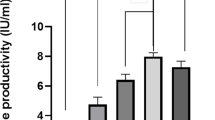
With the emergence of multiple side effects on the usage of commercial L-asparaginase formulations, keen interest is provoked to investigate new sources of L-asparaginases that possess antileukemic properties with minimal side effects. The present study reports the cost-effective bench-scale production, homogeneity purification and apoptosis induction potential of a new L-asparaginase preparation from Bacillus indicus against human leukemia cells. The enzyme is highly specific toward the natural substrate L-asparagine. The study initiated with the enzyme production using cost-effective substrates in which a 3.28-fold enhancement of enzyme activity was achieved in comparison with an unoptimized medium using the central composite experimental design approach. The scale-up of the process in a 3.7-L batch bioreactor resulted in 16.42 ± 0.17 IU/mL of L-asparaginase activity in 24 h. The crude extracellular enzyme was purified to homogeneity using anion exchange chromatography followed by gel filtration chromatography. A single band of approximately 35 kDa molecular weight was obtained on SDS-PAGE, while native PAGE analysis confirmed it to be a tetramer of four identical subunits. The circular dichroism spectroscopic study revealed the α + β mixed type of secondary structure with 38.7% α-helices and 27.4% β pleated sheets. The antitumor toxicity exhibited on the MOLT-4 leukemia cells by the new L-asparaginase was revealed using the MTT assay and acridine orange/propidium iodide dual staining for live/dead cells. The flow cytometry analysis established the potential of the purified L-asparaginase to induce the apoptotic cell death mechanism in MOLT-4 leukemia cells. Conclusively, the L-asparaginase of Bacillus indicus is a highly promising candidate that can be introduced as a new enzyme therapeutic against various leukemia disorders.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Abakumova OY, Podobed OV, Karalkin PA, Kondakova LI, Sokolov NN (2012) Antitumor activity of L-asparaginase from Erwinia carotovora against different human and animal leukemic and solid tumor cell lines. Biochem (mosc) Suppl B 6:307–316. https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990750812040026
Bank HL (1988) Rapid assessment of islet viability with acridine orange and propidium iodide. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 24:266–273. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02628826
Cecconello DK, Magalhães MRD, Werlang ICR, Lee MLDM, Michalowski MB, Daudt LE (2020) Asparaginase: an old drug with new questions. Hematol Transfus Cell Ther 42:275–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.htct.2019.07.010
Costa IM, Custódio Moura D, Meira Lima G, Pessoa A, Oresco dos Santos C, de Oliveira MA, Monteiro G (2022) Engineered asparaginase from Erwinia chrysanthemi enhances asparagine hydrolase activity and diminishes enzyme immunoreactivity-a new promise to treat acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 97:228–239. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.6933
Doriya K, Kumar DS (2016) Isolation and screening of L-asparaginase free of glutaminase and urease from fungal sp. 3 Biotech 6:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-016-0544-1
El-Naggar NEA, Deraz SF, Soliman HM, El-Deeb NM, El-Ewasy SM (2016) Purification, characterization, cytotoxicity and anticancer activities of L-asparaginase, anti-colon cancer protein, from the newly isolated alkaliphilic Streptomyces fradiae NEAE-82. Sci Rep 6:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32926
Erdem Ö, Gültekin-Özgüven M, Berktaş I, Erşan S, Tuna HE, Karadağ A, Özçelik B, Güneş G, Cutting SM (2014) Development of a novel synbiotic dark chocolate enriched with Bacillus indicus HU36, maltodextrin and lemon fiber: optimization by response surface methodology. LWT - Food Sci Technol 56:187–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2013.10.020
Ferrari M, Fornasiero MC, Isetta AM (1990) MTT colorimetric assay for testing macrophage cytotoxic activity in vitro. J Immunol Methods 131:165–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(90)90187-Z
Fonseca MHG, da Silva FT, de Morais SB, Trevizani R (2021) Circumventing the side effects of L-asparaginase. Biomed Pharmacother 139:111616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111616
Friedman M (2003) Chemistry, biochemistry, and safety of acrylamide. A review. J Agric Food Chem 51:4504–4526. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf030204+
Fung MKL, Chan GCF (2017) Drug-induced amino acid deprivation as strategy for cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol Pharm 10:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-017-0509-9
Gallagher SR (1995) One-dimensional electrophoresis using nondenaturing conditions. Curr Protoc Protein Sci 1:10–13. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471140864.ps1003s00
Garcia-Bermudez J, Williams RT, Guarecuco R, Birsoy K (2020) Targeting extracellular nutrient dependencies of cancer cells. Mol Metab 33:67–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2019.11.011
Golbabaie A, Nouri H, Moghimi H, Khaleghian A (2020) L-asparaginase production and enhancement by Sarocladium strictum: In vitro evaluation of anti-cancerous properties. J Appl Microbiol 129:356–366. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.14623
Hendriksen HV, Kornbrust BA, Østergaard PR, Stringer MA (2009) Evaluating the potential for enzymatic acrylamide mitigation in a range of food products using an asparaginase from Aspergillus oryzae. J Agric Food Chem 57:4168–4176. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf900174q
Hong H, Huang JM, Khaneja R, Hiep L, Urdaci M, Cutting S (2008) The safety of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus indicus as food probiotics. J Appl Microbiol 105:510–520. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03773.x
Husain I, Sharma A, Kumar S, Malik F (2016) Purification and characterization of glutaminase free asparaginase from Enterobacter cloacae: in-vitro evaluation of cytotoxic potential against human myeloid leukemia HL-60 cells. PLoS One 11:e0148877. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0148877
Jiang J, Batra S, Zhang J (2021) Asparagine: a metabolite to be targeted in cancers. Metabolites 11:402. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060402
Kenari SLD, Alemzadeh I, Maghsodi V (2011) Production of l-asparaginase from Escherichia coli ATCC 11303: Optimization by response surface methodology. Food Bioprod Process 89:315–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2010.11.002
Kumar S, Darnal S, Patial V, Kumar V, Kumar V, Kumar S, Singh D (2022) Molecular cloning, characterization, and in-silico analysis of L-asparaginase from Himalayan Pseudomonas sp. PCH44. 3 Biotech 12:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03224-0
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685. https://doi.org/10.1038/227680a0
Liu FS, Zajic JE (1972) L-asparaginase synthesis by Erwinia aroideae. Appl Microbiol 23:667–668. https://doi.org/10.1128/am.23.3.667-668.1972
Lubkowski J, Wlodawer A (2021) Structural and biochemical properties of L-asparaginase. FEBS J 288:4183–4209. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.16042
Mascotti K, McCullough J, Burger SR (2000) HPC viability measurement: trypan blue versus acridine orange and propidium iodide. Transfusion 40:693–696. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1537-2995.2000.40060693.x
Métayer LE, Brown RD, Carlebur S, Burke GA, Brown GC (2019) Mechanisms of cell death induced by arginase and asparaginase in precursor B-cell lymphoblasts. Apoptosis 24:145–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-018-1506-3
Mihooliya KN, Nandal J, Swami L, Verma H, Chopra L, Sahoo DK (2017) A new pH indicator dye-based method for rapid and efficient screening of L-asparaginase producing microorganisms. Enzyme Microb Technol 107:72–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enzmictec.2017.08.004
Nguyen HA, Su Y, Zhang JY, Antanasijevic A, Caffrey M, Schalk AM, Liu L, Rondelli D, Oh A, Mahmud DL, Bosland MC (2018) A novel l-asparaginase with low l-glutaminase coactivity is highly efficacious against both T-and B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias in vivo. Cancer Res 78:1549–1560. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2106
Reddy PRM, Ramesh B, Mrudula S, Reddy G, Seenayya G (2003) Production of thermostable β-amylase by Clostridium thermosulfurogenes SV2 in solid-state fermentation: optimization of nutrient levels using response surface methodology. Process Biochem 39:267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(02)00193-0
Sanjeeviroyar A, Rajendran A, Muthuraj M, Basha KM, Thangavelu V (2010) Sequential optimization and kinetic modeling of L-asparaginase production by Pectobacterium carotovorum in submerged fermentation. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 5:743–755. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.401
Shakambari G, Sumi BM, Ashokkumar B, Palanivelu P, Varalakshmi P (2015) Industrial effluent as a substrate for glutaminase free L-asparaginase production from Pseudomonas plecoglossicida strain RS1; media optimization, enzyme purification and its characterization. RSC Adv 5:48729–48738. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA05507E
Sharma D, Mishra A (2021) L-asparaginase production in solid-state fermentation using Aspergillus niger: process modeling by artificial neural network approach. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2021.1972426
Sharma D, Singh K, Singh K, Mishra A (2019) Insights into the microbial L-Asparaginases: from production to practical applications. Curr Protein Pept Sci 20:452–464. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389203720666181114111035
Shifrin S, Parrott CL (1974) In vitro assembly of L-asparaginase subunits. J Biol Chem 249:4175–4180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9258(19)42499-X
Shrivastava A, Khan AA, Khurshid M, Kalam MA, Jain SK, Singhal PK (2016) Recent developments in l-asparaginase discovery and its potential as anticancer agent. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 100:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.01.002
Sindhu R, Manonmani HK (2018) L-Asparaginase induces intrinsic mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in human gastric adenocarcinoma cells and impedes tumor progression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:2393–2399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.167
Singh Y, Gundampati RK, Jagannadham MV, Srivastava SK (2013) Extracellular L-asparaginase from a protease-deficient Bacillus aryabhattai ITBHU02: purification, biochemical characterization, and evaluation of antineoplastic activity in vitro. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 171:1759–1774. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-013-0455-0
Singh K, Sharma D, Mishra A (2021) Mahua flowers (Madhuca sp.) utilization as a carbon-rich natural substrate for the cost-effective bench-scale production of fumaric acid. SN Appl Sci 3:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-021-04176-5
Strzelczyk P, Zhang D, Dyba M, Wlodawer A, Lubkowski J (2020) Generalized enzymatic mechanism of catalysis by tetrameric L-asparaginases from mesophilic bacteria. Sci Rep 10:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-74480-4
Uber JB, Bulka NR, Nogueira BB, Martim DB, Bueno PS, Barbosa-Tessmann IP (2022) Bioprospection of L-asparaginase producing microorganisms and cloning of the L-asparaginase type II gene from a Pseudomonas putida species group isolate. Biologia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-022-01072-0
Ueno T, Ohtawa K, Mitsui K, Kodera Y, Hiroto M, Matsushima A, Inada Y, Nishimura H (1997) Cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of leukemia cells induced by L-asparaginase. Leukemia 11:1858–1861. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2400834
Vala AK, Sachaniya B, Dudhagara D, Panseriya HZ, Gosai H, Rawal R, Dave BP (2018) Characterization of L-asparaginase from marine-derived Aspergillus niger AKV-MKBU, its antiproliferative activity and bench scale production using industrial waste. Int J Biol Macromol 108:41–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.114
Van Engeland M, Nieland LJ, Ramaekers FC, Schutte B, Reutelingsperger CP (1998) Annexin V-affinity assay: a review on an apoptosis detection system based on phosphatidylserine exposure. Cytometry 31:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0320(19980101)31:1%3c1::AID-CYTO1%3e3.0.CO;2-R
Vander Heiden MG (2011) Targeting cancer metabolism: a therapeutic window opens. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:671–684. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3504
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reutellingsperger C (1995) A novel assay for apoptosis flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled annexin V. J Immunol Methods 184:39–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(95)00072-I
Willis RC, Woolfolk CA (1974) Asparagine utilization in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 118:231–241. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.118.1.231-241.1974
Yaacob MA, Hasan WANW, Ali MSM, Rahman RNZRA, Salleh AB, Basri M, Leow TC (2014) Characterisation and molecular dynamic simulations of J15 asparaginase from Photobacterium sp. strain J15. Acta Biochim Pol. https://doi.org/10.18388/abp.2014_1840
Zhang J, Fan J, Venneti S, Cross JR, Takagi T, Bhinder B, Djaballah H, Kanai M, Cheng EH, Judkins AR, Pawel B (2014) Asparagine plays a critical role in regulating cellular adaptation to glutamine depletion. Mol Cell 56:205–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.018
Acknowledgements
We thank School of Biochemical engineering, Indian Institute of Technology BHU Varanasi, India, for providing us the infrastructure and facilities for conducting research work.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by DS and AM. The first draft of the manuscript was written by DS, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not required.
Informed consent
Not applicable as the study did not involve human participants.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, D., Mishra, A. Apoptosis induction in leukemic cells by L-asparaginase preparation from Bacillus indicus: bench-scale production, purification and therapeutic application. 3 Biotech 13, 21 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03440-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03440-8