Abstract
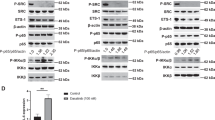
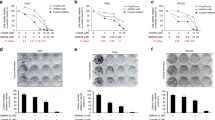
Combination of docetaxel, cisplatin and 5-FU, known as TPF, is an FDA-approved treatment for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Acquired chemo-resistance to TPF, a primary reason for non-responsiveness to the treatment and relapse of tumor is a major concern for treatment failure, especially in elder patients. In this study, we investigated the role of Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases (IRAK) mediated Toll-like receptor (TLR)—signaling in chemo-resistance using a cell line-based in-vitro TPF-resistant HNSCC model of laryngeal origin. TPF chemo-resistant state showed over-expression and phosphorylation of the active downstream kinases IRAK-1 and IRAK-4 along with enhanced proliferative potential, survival, stemness and metastatic capability as compared to the parent cell line. Pharmacological inhibition of IRAK-1 and -4 had a cytostatic effect on chemo-resistant cells and re-sensitized them to chemotherapy. The treatment also decreased the pro-oncogenic effects of the chemo-resistant cells. Our study provides insights into the pro-oncogenic role of amplified IRAK-1 and-4 mediated TLR signaling in TPF-resistant HNSCC. Pharmacological inhibition of IRAK-1 and-4 signaling is a promising therapeutic strategy for TPF-resistant HNSCC. It can also be used as a combination therapy or a chemo-drug sparing regimen in HNSCC.

Source: UALCAN browser






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data will be available on request to corresponding author.
Abbreviations
- HNSCC:
-
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- HPV:
-
Human papillomavirus
- 5-FU:
-
5-Fluorouracil
- PD1:
-
Programmed cell death 1
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- FDA:
-
Food and drugs administration
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- TLR:
-
Toll-like receptor
- PAMPs:
-
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- DAMPs:
-
Damage-associated molecular patterns
- IRAK:
-
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase
- TNBC:
-
Triple-negative breast cancer
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- PDAC:
-
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- CRC:
-
Colorectal carcinoma
- NPC:
-
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- IC:
-
Inhibitory concentration
- Bcl-2:
-
B cell lymphoma-2
- Bcl-xL:
-
B cell lymphoma extra large
- MMP-2:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-2
- ALDH1:
-
Aldehyde dehydrogenase-1
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- S.D.:
-
Standard deviation
- FSC:
-
Forward scatter
- SSC:
-
Side scatter
- CSCs:
-
Cancer stem cells
- MFI:
-
Mean fluorescence intensity
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
References
Abaurrea A, Araujo AM, Caffarel MM (2021) The role of the IL-6 cytokine family in epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer progression. Int J Mol Sci 22(15):8334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158334
Adams AK, Bolanos LC, Dexheimer PJ et al (2015) IRAK1 is a novel DEK transcriptional target and is essential for head and neck cancer cell survival. Oncotarget 6(41):43395–43407. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6028
Agliano F, Karlinsey KS, Ragazzi M et al (2020) A benzimidazole inhibitor attenuates sterile inflammation induced in a model of systemic autoinflammation in female mice. Sci Rep 10(1):1–1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-68985-1
Cao Z, Henzel WJ, Gao X (1996) IRAK: a kinase associated with the interleukin-1 receptor. Science 271(5252):1128–1131. https://www.science.org/doi/https://doi.org/10.1126/science.271.5252.1128
Chandrashekar DS, Karthikeyan SK, Korla PK, Patel H, Shovon AR, Athar M et al (2022) UALCAN: an update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 25:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2022.01.001
Cheng BY, Lau EY, Leung HW et al (2018) IRAK1 augments cancer stemness and drug resistance via the AP-1/AKR1B10 signaling cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res 78(9):2332–2342. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2445
Cognetti DM, Weber RS, Lai SY (2008) Head and neck cancer: an evolving treatment paradigm. Cancer 113(7 Suppl):1911–1932. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.23654
Cohen MH, Chen H, Shord S et al (2013) Approval summary: Cetuximab in combination with cisplatin or carboplatin and 5-fluorouracil for the first-line treatment of patients with recurrent locoregional or metastatic squamous cell head and neck cancer. Oncologist 18(4):460–466. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0458
Cohen EE, Bell RB, Bifulco CB et al (2019) The Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer consensus statement on immunotherapy for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (HNSCC). J Immunother Cancer 7(1):1–31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-019-0662-5
Elliott DA, Nabavizadeh N, Hiluf K, Holland JM (2017) Head and neck cancer. Controversies in radiation oncology. Springer, Cham, pp 137–157. https://doi.org/10.1007/174_2017_47
El-Zayat SR, Sibaii H, Mannaa FA (2019) Toll-like receptors activation, signaling, and targeting: an overview. Bull Natl Res Cent 43(1):1–2. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42269-019-0227-2
Fayette J, Fontaine-Delaruelle C, Ambrun A et al (2016) Neoadjuvant modified TPF (docetaxel, cisplatin, fluorouracil) for patients unfit to standard TPF in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a study of 48 patients. Oncotarget 7(24):37297–37304. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8934
Ferrari D, Ghi MG, Franzese C, Codecà C, Gau M, Fayette J (2020) The slippery role of induction chemotherapy in head and neck cancer: myth and reality. Front Oncol 10:7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.00007
Foda HD, Zucker S (2001) Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Drug Discov Today 6(9):478–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1359-6446(01)01752-4
Gao J, Zhao S, Halstensen TS (2016) Increased interleukin-6 expression is associated with poor prognosis and acquired cisplatin resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 35(6):3265–3274. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.4765
Govindan SV, Kulsum S, Pandian RS et al (2015) Establishment and characterization of triple drug resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Mol Med Rep 12(2):3025–3032. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3768
Ilie SM, Ruginescu I, Saada E et al (2012) The tolerance of TPF chemotherapy regime standard or modified in head neck cancer patients over 65 years old. Ann Oncol 23:ix341. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0923-7534(20)33597-3
Kaczanowska S, Joseph AM, Davila E (2013) TLR agonists: our best frenemy in cancer immunotherapy. J Leukoc Biol 93(6):847–863. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.1012501
Kawamura Y, Saijo K, Imai H, Ishioka C (2021) Inhibition of IRAK1/4 enhances the antitumor effect of lenvatinib in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. Cancer Sci 112:4711–4721. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.15095
Kawasaki T, Kawai T (2014) Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Front Immunol 5:461. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00461
Kim R, Hahn S, Shin J et al (2016) The effect of induction chemotherapy using docetaxel, cisplatin, and fluorouracil on survival in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis. Cancer Res Treat 48(3):907–916. https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2015.359
Krysko DV, Garg AD, Kaczmarek A et al (2012) Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 12(12):860–875. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3380
Li S, Li Q (2014) Cancer stem cells and tumor metastasis. Int J Oncol 44(6):1806–1812. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2014.2362
Li Q, Chen Y, Zhang D et al (2019) IRAK4 mediates colitis-induced tumorigenesis and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. JCI Insight 4(19):e130867. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.130867
Liu L, Liu S, Deng P et al (2021) Targeting the IRAK1-S100A9 axis overcomes resistance to paclitaxel in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Res 81(5):1413–1425. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-20-2125
Lorch JH, Goloubeva O, Haddad RI et al (2011) Induction chemotherapy with cisplatin and fluorouracil alone or in combination with docetaxel in locally advanced squamous-cell cancer of the head and neck: long-term results of the TAX 324 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 12(2):153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70279-5
Meng DF, Sun R, Liu GY et al (2020) S100A14 suppresses metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by inhibition of NF-kB signaling through degradation of IRAK1. Oncogene 39(30):5307–5322. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-1363-8
Muhaxheri G, Gabrić D, Vučićević Boras V (2015) Epidemiology and aetiology of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Libri Oncologici: Croat J Oncol 43(1–3):75–81
Pandolfi F, Altamura S, Frosali S, Conti P (2016) Key role of DAMP in inflammation, cancer, and tissue repair. Clin Ther 38(5):1017–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.02.028
Sato Y, Goto Y, Narita N, Hoon DS (2009) Cancer cells expressing toll-like receptors and the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Microenviron Suppl 1(Suppl 1):205–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-009-0022-y
Sher DJ, Schwartz DL, Nedzi L et al (2016) Comparative effectiveness of induction chemotherapy for oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: a population-based analysis. Oral Oncol 54:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.12.008
Shibue T, Weinberg RA (2017) EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14(10):611–629. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.44
Srivastava R, Geng D, Liu Y et al (2012) Augmentation of therapeutic responses in melanoma by inhibition of IRAK-1,-4. Cancer Res 72(23):6209–6216. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0337
Stanciu AE, Zamfir-Chiru-Anton A, Stanciu MM et al (2017) Imbalance between matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases promotes invasion and metastasis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Lab 63(10):1613–1620. https://doi.org/10.7754/Clin.Lab.2017.170339
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Uz U, Eskiizmir G (2021) Association between interleukin-6 and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a systematic review. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol 14(1):50–60. https://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2019.00906
van der Heijden M, Essers PB et al (2020) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is a prognostic marker for patient outcome in advanced stage HNSCC patients treated with chemoradiotherapy. Radiother Oncol 147:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radonc.2020.05.013
Vermorken JB, Remenar E, van Herpen C et al (2007) Cisplatin, fluorouracil, and docetaxel in unresectable head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med 357(17):1695–1704. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa071028
Wang X, Zhu Y, Ma Y et al (2013) The role of cancer stem cells in cancer metastasis: new perspective and progress. Cancer Epidemiol 37(1):60–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canep.2012.07.007
Wee ZN, Yatim SM, Kohlbauer VK et al (2015) IRAK1 is a therapeutic target that drives breast cancer metastasis and resistance to paclitaxel. Nat Commun 6(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9746
Xu X, Wang Y, Chen Z et al (2005) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 contributes to cancer cell migration on collagen. Cancer Res 65(1):130–136
Yadav A, Kumar B, Datta J et al (2011) IL-6 promotes head and neck tumor metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the JAK-STAT3-SNAIL signaling pathway. Mol Cancer Res 9(12):1658–1667. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0271
Zhang D, Li L, Jiang H et al (2017) Constitutive IRAK4 activation underlies poor prognosis and chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 23(7):1748–1759. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1121
Zhong Q, Fang J, Huang Z et al (2018) A response prediction model for taxane, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy in hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Sci Rep 8(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31027-y
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by a grant from Gujarat State Biotechnology Mission (GSBTM) under the Financial Assistance Programme (Project ID-1393) to Ratika Srivastava. Humayara Khan was supported by research scholarships from The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, GSBTM and SHODH, Education Department, Govt. of Gujarat (Ref. ID-201901720067). Authors acknowledge The Department of Microbiology and Biotechnology Centre, The Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, Gujarat, India and The Seeding labs, USA for infrastructure and instrumentation facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RS conceptualization, funding acquisition, methodology, visualization, project administration, data curation, resources, supervision, validation, writing-original draft, writing-review and editing. SNP and AM TCGA data mining analysis. HK investigation, validation, writing-original draft.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Research involving human participants and animals
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, H., Pandey, S.N., Mishra, A. et al. Suppression of TLR signaling by IRAK-1 and -4 dual inhibitor decreases TPF-resistance-induced pro-oncogenic effects in HNSCC. 3 Biotech 13, 14 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03420-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03420-y