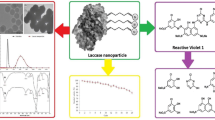
Abstract
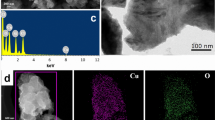
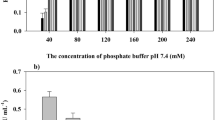
In the present study, Tricholoma giganteum AGHP laccase was immobilized on amino-functionalized cadmium oxide nanoparticles (CdO NPs) which was carried out by glutaraldehyde. The synthesized CdO NPs were characterized by using transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Energy dispersive X-ray analysis (EDXA) and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis which reflected the NPs had an average size of 35 nm with hexagonal and irregular shapes. Fourier transform infra-red (FTIR) study of laccase with amino-functionalized CdO (lac-CdO) NPs confirmed the crosslinking of laccase with CdO NPs. With immobilized laccase, a shift in pH (5.5) and temperature (35 ℃) optima was observed, when compared to free laccase (pH 4.5, 30 ℃). Lac-CdO NPs displayed 1.15 times higher stability (90 ± 0.47%) than free laccase (78 ± 0.69%) at optimum pH of 5.5. Immobilized laccase showed 1.19-fold improvement in thermal stability and 2.25-fold increment in half-life after 3 h of incubation at 50 ℃ as compared to free laccase. Recycling capability study demonstrated that lac-CdO NPs were able to retain 85 ± 0.68% of relative activity at the end of 20th 2,2-azinobis-3-ethylbenzthiozoline-6-sulfonic acid (ABTS) oxidation cycle. In addition, lac-CdO NPs showed remarkable reusability in catalysing various organic synthesis reactions even after several cycle of catalysis. Furthermore, the interactions of organic synthesis reactions and interacted residues were observed by assessing the molecular docking poses of T. giganteum laccase with substrates. The obtained results would be advantageous to develop a biocatalyst over a chemical catalyst for effective synthesis of potent organics having industrial importance.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Data and required material will be provided on request.
Abbreviations
- ABTS:
-
2,2-Azinobis-3-ethylbenzthiozoline-6-sulfonic acid
- CdO NPs:
-
Cadmium oxide nanoparticles
- lac-CdO NPs:
-
Laccase amino-functionalized CdO NPs
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- EDXA:
-
Energy dispersive x-ray analysis
- FTIR:
-
Fourier-transform infra-red spectroscopy
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
References
Ardao I, Alvaro G, Benaiges MD (2011) Reversible immobilization of rhamnulose-1-phosphate aldolase for biocatalysis: enzyme loading optimization and aldol addition kinetic modeling. Biochem Eng J 56(3):190–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2011.06.007
Asgher M, Noreen S, Bilal M (2017) Enhancement of catalytic, reusability, and long-term stability features of Trametes versicolor IBL-04 laccase immobilized on different polymers. Int J Biol Macromol 95:54–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.11.012
Bayramoğlu G, Yilmaz M, Arica MY (2010) Reversible immobilization of laccase to poly (4-vinylpyridine) grafted and Cu (II) chelated magnetic beads: biodegradation of reactive dyes. Bioresour Technol 101(17):6615–6621. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.03.088
Borhade AV, Uphade BK, Gadhave AG (2015) Efficient, solvent-free synthesis of acridinediones catalyzed by CdO nanoparticles. Res Chem Intermediat 41(3):1447–1458. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-013-1284-z
Chakraborty M, McConville D, Niu Y, Tessier C, Youngs W (1998) Reactions of primary and secondary amines with substituted hydroquinones: nuclear amination, side-chain amination, and indolequinone formation. J Org Chem 63:7563. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo980541v
Cichewicz RH, Kouzi SA (2002) Resveratrol oligomers: structure, chemistry, and biological activity. Stud Nat Prod Chem 26:507–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1572-5995(02)80014-X
Corvini PF, Shahgaldian P (2010) LANCE: Laccase-nanoparticle conjugates for the elimination of micropollutants (endocrine disrupting chemicals) from wastewater in bioreactors. Rev Environ Sci Bio 9(1):23–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-009-9182-y
da Silva V, Amatto I, Gonsales da Rosa-Garzon N, de Oliveira A, Simoes F, Santiago F, da Silva P, Leite N, Raspante Martins J, Cabral H (2022) Enzyme engineering and its industrial applications. Biotechnol Appl Bioc 69(2):389–409. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.2117
Datta S, Christena LR, Rajaram YRS (2013) Enzyme immobilization: an overview on techniques and support materials. 3 Biotech 3(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-012-0071-7
Gahlout M, Rudakiya DM, Gupte S, Gupte A (2017) Laccase-conjugated amino-functionalized nanosilica for efficient degradation of Reactive Violet 1 dye. Int Nano Lett 7(3):195–208. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40089-017-0215-1
Gao Y, Shah K, Kwok I, Wang M, Rome LH, Mahendra S (2022) Immobilized fungal enzymes: innovations and potential applications in biodegradation and biosynthesis. Biotechnol Adv. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.107936
Hommes G, Gasser CA, Howald CB, Goers R, Schlosser D, Shahgaldian P, Corvini PF-X (2012) Production of a robust nanobiocatalyst for municipal wastewater treatment. Bioresource Technol 115:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.129
Hongyan L, Zexiong Z, Shiwei X, He X, Yinian Z, Haiyun L, Zhongsheng Y (2019) Study on transformation and degradation of bisphenol A by Trametes versicolor laccase and simulation of molecular docking. Chemosphere 224:743–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.02.143
Hou J, Dong G, Ye Y, Chen V (2014) Laccase immobilization on titania nanoparticles and titania-functionalized membranes. J Membrane Sci 452:229–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2013.10.019
Huang J, Xiao H, Li B, Wang J, Jiang D (2006) Immobilization of Pycnoporus sanguineus laccase on copper tetra-aminophthalocyanine–Fe3O4 nanoparticle composite. Biotechnology Appl Bioc 44(2):93–100. https://doi.org/10.1042/BA20050213
Huang W, Zhang W, Gan Y, Yang J, Zhang S (2022) Laccase immobilization with metal-organic frameworks: current status, remaining challenges and future perspectives. Crit Rev Env Sci Tech 52(8):1282–1324. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2020.1854565
Hudson R, Li C-J, Moores A (2012) Magnetic copper–iron nanoparticles as simple heterogeneous catalysts for the azide–alkyne click reaction in water. Green Chem 14(3):622–624. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2GC16421C
Jain D, Kachhwaha S, Jain R, Srivastava G, Kothari SL (2010) Novel microbial route to synthesize silver nanoparticles using spore crystal mixture of Bacillus thuringiensis. Indian J Exp Biol 48(11):1152–1156
Jaiswal N, Pandey VP, Dwivedi UN (2016) Immobilization of papaya laccase in chitosan led to improved multipronged stability and dye discoloration. Int J Biol Macromol 86:288–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.01.079
Ji C, Hou J, Chen V (2016) Cross-linked carbon nanotubes-based biocatalytic membranes for micro-pollutants degradation: performance, stability, and regeneration. J Membrane Sci 520:869–880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2016.08.056
Kahane SV, Sasikala R, Vishwanadh B, Sudarsan V, Mahamuni S (2013) CdO–CdS nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic activity for hydrogen generation from water. Int J Hydrogen Energ 38(35):15012–15018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.09.077
Kantam ML, Redddy PV, Srinivas P, Venugopal A, Bhargava S, Nishina Y (2013) Nanocrystalline magnesium oxide-stabilized palladium (0): the Heck reaction of heteroaryl bromides in the absence of additional ligands and base. Cat Sci Tec 3(10):2550–2554. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00404J
Kara F, Demirel G, Tümtürk H (2006) Immobilization of urease by using chitosan–alginate and poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid)/κ-carrageenan supports. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 29(3):207–211. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-006-0073-0
Khatami SH, Vakili O, Movahedpour A, Ghesmati Z, Ghasemi H, Taheri-Anganeh M (2022) Laccase: various types and applications. Biotechnol Appl Bioc. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.2313
Kim M, Park JM, Um HJ, Lee DH, Lee KH, Kobayashi F, Iwasaka Y, Hong CS, Min J, Kim YH (2010) Immobilization of cross-linked lipase aggregates onto magnetic beads for enzymatic degradation of polycaprolactone. J Basic Microb 50(3):218–226. https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.200900099
Lisboa CS, Santos VG, Vaz BG, Lucas NC et al (2011) C-H functionalization of 1,4-naphthoquinone by oxidative coupling with anilines in the presence of a catalytic quantity of copper (II) acetate. J Org Chem 76:5264–5273. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo200354u
Liu Y, Zeng Z, Zeng G, Tang L, Pang Y, Li Z, Liu C, Lei X, Wu M, Ren P (2012) Immobilization of laccase on magnetic bimodal mesoporous carbon and the application in the removal of phenolic compounds. Bioresource Technol 115:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.11.015
Lowry O, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall R (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Makas YG, Kalkan NA, Aksoy S, Altinok H, Hasirci N (2010) Immobilization of laccase in κ-carrageenan based semi-interpenetrating polymer networks. J Biotechnol 148(4):216–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2010.05.011
Meena J, Gupta A, Ahuja R, Singh M, Panda AK (2021) Recent advances in nano-engineered approaches used for enzyme immobilization with enhanced activity. J Mol Liq 338:116602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2021.116602
Mohajershojaei K, Mahmoodi NM, Khosravi A (2015) Immobilization of laccase enzyme onto titania nanoparticle and decolorization of dyes from single and binary systems. Biotechnol Bioproc E 20(1):109–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-014-0196-0
Mohammadi ZB, Zhang F, Kharazmi MS, Jafari SM (2022) Nano-biocatalysts for food applications; immobilized enzymes within different nanostructures. Crit Rev Food Sci. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2092719
Mou J, Gao G, Chen C, Liu J, Gao J, Liu Y, Pei D (2017) Highly efficient one-pot three-component Betti reaction in water using reverse zinc oxide micelles as a recoverable and reusable catalyst. RSC Adv 7(23):13868–13875. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA28599F
Niku-Paavola M-L, Karhunen E, Kantelinen A, Viikari L, Lundell T, Hatakka A (1990) The effect of culture conditions on the production of lignin modifying enzymes by the white-rot fungus Phlebia radiata. J Biotechnol 13(2–3):211–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-1656(90)90106-L
Olga M, Jana M, Anna M, Irena K, Jan M, Alena Č (2022) Antimicrobial properties and applications of metal nanoparticles biosynthesized by green methods. Biotechnol Adv. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2022.107905
Palmer T, Bonner PL (2007) Enzymes: biochemistry, biotechnology, clinical chemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Pang S, Wu Y, Zhang X, Li B, Ouyang J, Ding M (2016) Immobilization of laccase via adsorption onto bimodal mesoporous Zr-MOF. Process Biochem 51(2):229–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.11.033
Patel H, Gupte A (2016) Optimization of different culture conditions for enhanced laccase production and its purification from Tricholoma giganteum AGHP. Bioresour Bioprocess 3(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-016-0088-6
Patel SK, Kalia VC, Choi JH, Haw JR, Kim IW, Lee JK (2014) Immobilization of laccase on SiO2 nanocarriers improves its stability and reusability. J Microbiol Biotechn 24(5):639–647. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1401.01025
Qiu H, Xu C, Huang X, Ding Y, Qu Y, Gao P (2008) Adsorption of laccase on the surface of nanoporous gold and the direct electron transfer between them. J Phys Chem C 112(38):14781–14785. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp805600k
Rana S, Velázquez JJ, Jonnalagadda SB (2022) Highly active reduced graphene oxide supported Ni nanoparticles for C-S coupling reactions. Nanoscale Adv 4(15):3131–3135. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2NA00316C
Rudakiya DM, Patel SH, Narra M (2019) Structural insight into the fungal β-glucosidases and their interactions with organics. Int J Biol Macromol 138:1019–1028. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.07.177
Rudakiya DM, Patel DH, Gupte A (2020) Exploiting the potential of metal and solvent tolerant laccase from Tricholoma giganteum AGDR1 for the removal of pesticides. Int J Biol Macromol 144:586–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.068
Sakai S, Liu Y, Yamaguchi T, Watanabe R, Kawabe M, Kawakami K (2010) Immobilization of Pseudomonas cepacia lipase onto electrospun polyacrylonitrile fibers through physical adsorption and application to transesterification in nonaqueous solvent. Biotechnol Lett 32(8):1059–1062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0279-8
Sassolas A, Blum LJ, Leca-Bouvier BD (2012) Immobilization strategies to develop enzymatic biosensors. Biotechnol Adv 30(3):489–511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.09.003
Sheldon RA (2016) Engineering a more sustainable world through catalysis and green chemistry. J Roy Soc Interface 13(116):20160087. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2016.0087
Song T, Zhou B, Peng GW, Zhang QB, Wu LZ, Liu Q, Wang Y (2014) Aerobic oxidative coupling of resveratrol and its analogues by visible light using mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride (mpg-C3N4) as a bioinspired catalyst. Chem Eur J 20(3):678–682. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201303587
Tavares AP, Silva CG, Dražić G, Silva AM, Loureiro JM, Faria JL (2015) Laccase immobilization over multi-walled carbon nanotubes: kinetic, thermodynamic and stability studies. J Colloid Interf Sci 454:52–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.04.054
Thema F, Beukes P, Gurib-Fakim A, Maaza M (2015) Green synthesis of Monteponite CdO nanoparticles by Agathosma betulina natural extract. J Alloy Compd 646:1043–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.05.279
Thovhogi N, Park E, Manikandan E, Maaza M, Gurib-Fakim A (2016) Physical properties of CdO nanoparticles synthesized by green chemistry via Hibiscus Sabdariffa flower extract. J Alloy Compd 655:314–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.09.063
Velu SS, Buniyamin I, Ching LK, Feroz F, Noorbatcha I, Gee LC et al (2008) Regio-and stereoselective biomimetic synthesis of oligostilbenoid dimers from resveratrol analogues: influence of the solvent, oxidant, and substitution. Chem Eur J 14(36):11376–11384. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200801575
Verma S, Mungse HP, Kumar N, Choudhary S, Jain SL, Sain B, Khatri OP (2011) Graphene oxide: an efficient and reusable carbocatalyst for aza-Michael addition of amines to activated alkenes. Chem Commun 47(47):12673–12675. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CC15230K
Vignali E, Gigli M, Cailotto S, Pollegioni L, Rosini E, Crestini C (2022) The laccase lig multienzymatic multistep system in lignin valorization. Chemsuschem. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202201147
Witayakran S, Ragauskas AJ (2007) One-pot synthesis of 1,4-naphthoquinones and related structures with laccase. Green Chem 9:475–480. https://doi.org/10.1039/B606686K
Xu R, Tang R, Zhou Q, Li F, Zhang B (2015) Enhancement of catalytic activity of immobilized laccase for diclofenac biodegradation by carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng J 262:88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.09.072
Yamamoto T, Sekine Y (1984) Condensation of thiophenols with aryl halides using metallic copper as a reactant. Intermediation of cuprous thiophenolates. Can J Chem 62(8):1544–1547. https://doi.org/10.1139/v84-263
Zahirinejad S, Hemmati R, Homaei A, Dinari A, Hosseinkhani S, Mohammadi S, Vianello F (2021) Nano-organic supports for enzyme immobilization: scopes and perspectives. Colloid Surf B 204:111774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2021.111774
Zhu Y, Kaskel S, Shi J, Wage T, van Pée K-H (2007) Immobilization of Trametes versicolor laccase on magnetically separable mesoporous silica spheres. Chem Mater 19(26):6408–6413. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm071265g
Acknowledgements
The authors also wish to acknowledge SICART, V.V. Nagar, Gujarat, for providing the necessary instrumentation facilities.
Funding
The authors are thankful to the Department of Biotechnology (DBT sanction no. BT/PR5859/PID/6/696/2012) and Ministry of Science and Technology, New Delhi, for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: HP, AG. Formal analysis and investigation: HP, DR. Writing-Original draft preparation: HP, DR. Supervision: AG.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declares no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patel, H., Rudakiya, D.M. & Gupte, A. Utilization of laccase immobilized CdO nanoparticles in synthesis of industrially potent organics and their molecular docking studies. 3 Biotech 13, 6 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03413-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03413-x