Abstract
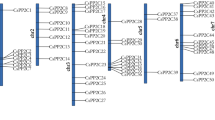
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase (SHMT) is a pyridoxal phosphate-dependent enzyme that plays crucial roles in the photorespiration and one-carbon metabolism of plants. In the present research, we conducted a systematic analysis of the SHMT gene family in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L). Results show that a total of 6 SHMT members were identified from the cucumber genome database. CsSHMT1 and CsSHMT2 participate in a fragment duplication event, indicating that CsSHMTs may complete the expansion of family members through fragment duplication. Gene structure analysis found that the number of exons of CsSHMTs ranges from 4 to 15. Members with the same number of exons are classified into the same class in the phylogenetic analysis. Each class reflects its subcellular distribution. Expression and function analysis reveals that CsSHMTs express in a variety of plant tissues, indicating that SHMT gene expression pattern is not organ-specific. qRT-PCR analysis found that CsSHMT3 and CsSHMT5 positively respond to abscisic acid (ABA), and CsSHMT2-6 are induced by indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) and methyl jasmonate (MeJA). Abiotic stress analysis shows that CsSHMT3 is significantly induced by drought and salt stress. These results may provide useful information for further function and evolution analysis of cucumber SHMT genes.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barkla BJ, Vera-Estrella R, Miranda-Vergara MC, Pantoja O (2014) Quantitative proteomics of heavy metal exposure in Arabidopsis thaliana reveals alterations in one-carbon metabolism enzymes upon exposure to zinc. J Proteomics 111:128–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2014.03.006
Bauwe H, Kolukisaoglu U (2003) Genetic manipulation of glycine decarboxylation. J Exp Bot 54:1523–1535. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erg171
Benedito VA, Torres-Jerez I, Murray JD, Andriankaja A, Allen S, Kakar K, Wandrey M, Verdier J, Zuber H, Ott T, Moreau S, Niebel A, Frickey T, Weiller G, He J, Dai X, Zhao PX, Tang Y, Udvardi MK (2008) A gene expression atlas of the model legume Medicago truncatula. Plant J 55:504–513. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03519.x
Camejo D, Romero-Puertas Mdel C, Rodriguez-Serrano M, Sandalio LM, Lazaro JJ, Jimenez A, Sevilla F (2013) Salinity-induced changes in S-nitrosylation of pea mitochondrial proteins. J Proteom 79:87–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2012.12.003
Cannon SB, Mitra A, Baumgarten A, Young ND, May G (2004) The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 4:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-4-10
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y, Thomas HR, Frank MH, He Y, Xia R (2020) TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol Plant 13:1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Fang C, Zhang P, Li L, Yang L, Mu D, Yan X, Li Z, Lin W (2020) Serine hydroxymethyltransferase localised in the endoplasmic reticulum plays a role in scavenging H2O2 to enhance rice chilling tolerance. BMC Plant Biol 20:236. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-02446-9
Gardeström P, Edwards GE, Henricson D, Ericson I (1985) The localization of serine hydroxymethyltransferase in leaves of C3 and C4 species. Physiol Plant 64:29–33
Ho CL, Saito K (2001) Molecular biology of the plastidic phosphorylated serine biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana. Amino Acids 20:243–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s007260170042
Hu B, Jin J, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo J, Gao G (2015) GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene features visualization server. Bioinformatics 31:1296–1297. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
Huang S, Li R, Zhang Z, Li L, Gu X, Fan W, Lucas WJ, Wang X, Xie B, Ni P, Ren Y, Zhu H, Li J, Lin K, Jin W, Fei Z, Li G, Staub J, Kilian A, van der Vossen EA, Wu Y, Guo J, He J, Jia Z, Ren Y, Tian G, Lu Y, Ruan J, Qian W, Wang M, Huang Q, Li B, Xuan Z, Cao J, Asan WuZ, Zhang J, Cai Q, Bai Y, Zhao B, Han Y, Li Y, Li X, Wang S, Shi Q, Liu S, Cho WK, Kim JY, Xu Y, Heller-Uszynska K, Miao H, Cheng Z, Zhang S, Wu J, Yang Y, Kang H, Li M, Liang H, Ren X, Shi Z, Wen M, Jian M, Yang H, Zhang G, Yang Z, Chen R, Liu S, Li J, Ma L, Liu H, Zhou Y, Zhao J, Fang X, Li G, Fang L, Li Y, Liu D, Zheng H, Zhang Y, Qin N, Li Z, Yang G, Yang S, Bolund L, Kristiansen K, Zheng H, Li S, Zhang X, Yang H, Wang J, Sun R, Zhang B, Jiang S, Wang J, Du Y, Li S (2009) The genome of the cucumber, Cucumis sativus L. Nat Genet 41:1275–1281. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.475
Kito K, Tsutsumi K, Rai V, Theerawitaya C, Cha-Um S, Yamada-Kato N, Sakakibara S, Tanaka Y, Takabe T (2017) Isolation and functional characterization of 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase involved in salt responses in sugar beet. Protoplasma 254:2305–2313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1127-7
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones SJ, Marra MA (2009) Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res 19:1639–1645. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.092759.109
Lakhssassi N, Patil G, Piya S, Zhou Z, Baharlouei A, Kassem MA, Lightfoot DA, Hewezi T, Barakat A, Nguyen HT, Meksem K (2019) Genome reorganization of the GmSHMT gene family in soybean showed a lack of functional redundancy in resistance to soybean cyst nematode. Sci Rep 9:1506. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37815-w
Laloum T, Martin G, Duque P (2018) Alternative splicing control of abiotic stress responses. Trends Plant Sci 23:140–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2017.09.019
Liu S, Kandoth PK, Warren SD, Yeckel G, Heinz R, Alden J, Yang C, Jamai A, El-Mellouki T, Juvale PS, Hill J, Baum TJ, Cianzio S, Whitham SA, Korkin D, Mitchum MG, Meksem K (2012) A soybean cyst nematode resistance gene points to a new mechanism of plant resistance to pathogens. Nature 492:256–260. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11651
Liu S, Kandoth PK, Lakhssassi N, Kang J, Colantonio V, Heinz R, Yeckel G, Zhou Z, Bekal S, Dapprich J, Rotter B, Cianzio S, Mitchum MG, Meksem K (2017) The soybean GmSNAP18 gene underlies two types of resistance to soybean cyst nematode. Nat Commun 8:14822. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14822
Liu Y, Mauve C, Lamothe-Sibold M, Guerard F, Glab N, Hodges M, Jossier M (2019) Photorespiratory serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 activity impacts abiotic stress tolerance and stomatal closure. Plant Cell Environ 42:2567–2583. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13595
Matas AJ, Yeats TH, Buda GJ, Zheng Y, Chatterjee S, Tohge T, Ponnala L, Adato A, Aharoni A, Stark R, Fernie AR, Fei Z, Giovannoni JJ, Rose JK (2011) Tissue- and cell-type specific transcriptome profiling of expanding tomato fruit provides insights into metabolic and regulatory specialization and cuticle formation. Plant Cell 23:3893–3910. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.111.091173
Mentch SJ, Locasale JW (2016) One-carbon metabolism and epigenetics: understanding the specificity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1363:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12956
Mishra P, Mishra V, Takabe T, Rai V, Singh NK (2016) Elucidation of salt-tolerance metabolic pathways in contrasting rice genotypes and their segregating progenies. Plant Cell Rep 35:1273–1286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-1959-1
Nogues I, Tramonti A, Angelaccio S, Ruszkowski M, Sekula B, Contestabile R (2020) Structural and kinetic properties of serine hydroxymethyltransferase from the halophytic cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica provide a rationale for salt tolerance. Int J Biol Macromol 159:517–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.081
Palmieri MC, Lindermayr C, Bauwe H, Steinhauser C, Durner J (2010) Regulation of plant glycine decarboxylase by S-nitrosylation and glutathionylation. Plant Physiol 152:1514–1528. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.152579
Pan S, Fan M, Liu Z, Li X, Wang H (2021) Serine, glycine and one carbon metabolism in cancer (review). Int J Oncol 58:158–170. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2020.5158
Prabhu V, Chatson KB, Abrams GD, King J (1996) 13C nuclear magnetic resonance detection of interactions of serine hydroxymethyltransferase with C1-tetrahydrofolate synthase and glycine decarboxylase complex activities in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 112:207–216. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.1.207
Ros R, Munoz-Bertomeu J, Krueger S (2014) Serine in plants: biosynthesis, metabolism, and functions. Trends Plant Sci 19:564–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2014.06.003
Ruszkowski M, Sekula B, Ruszkowska A, Dauter Z (2018) Chloroplastic serine hydroxymethyltransferase from Medicago truncatula: a structural characterization. Front Plant Sci 9:584. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00584
Schirch V, Szebenyi DM (2005) Serine hydroxymethyltransferase revisited. Curr Opin Chem Biol 9:482–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2005.08.017
Schulze S, Westhoff P, Gowik U (2016) Glycine decarboxylase in C3, C4 and C3–C4 intermediate species. Curr Opin Plant Biol 31:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2016.03.011
Vandepoele K, Quimbaya M, Casneuf T, De Veylder L, Van de Peer Y (2009) Unraveling transcriptional control in Arabidopsis using cis-regulatory elements and coexpression networks. Plant Physiol 150:535–546. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.136028
Voll LM, Jamai A, Renne P, Voll H, McClung CR, Weber AP (2006) The photorespiratory Arabidopsis shm1 mutant is deficient in SHM1. Plant Physiol 140:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.071399
Waditee-Sirisattha R, Sittipol D, Tanaka Y, Takabe T (2012) Overexpression of serine hydroxymethyltransferase from halotolerant cyanobacterium in Escherichia coli results in increased accumulation of choline precursors and enhanced salinity tolerance. FEMS Microbiol Lett 333:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02597.x
Wang Y, Tang H, Debarry JD, Tan X, Li J, Wang X, Lee TH, Jin H, Marler B, Guo H, Kissinger JC, Paterson AH (2012) MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res 40:e49. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr1293
Wang D, Liu H, Li S, Zhai G, Shao J, Tao Y (2015) Characterization and molecular cloning of a serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 (OsSHM1) in rice. J Integr Plant Biol 57:745–756. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.12336
Wei G, Tian P, Zhang F, Qin H, Miao H, Chen Q, Hu Z, Cao L, Wang M, Gu X, Huang S, Chen M, Wang G (2016) Integrative analyses of nontargeted volatile profiling and transcriptome data provide molecular insight into VOC diversity in cucumber plants (Cucumis sativus). Plant Physiol 172:603–618. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01051
Wu XY, Zhou GC, Chen YX, Wu P, Liu LW, Ma FF, Wu M, Liu CC, Zeng YJ, Chu AE, Hang YY, Chen JQ, Wang B (2016) Soybean cyst nematode resistance emerged via artificial selection of duplicated serine hydroxymethyltransferase genes. Front Plant Sci 7:998. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00998
Xu C, Huang B (2010) Differential proteomic response to heat stress in thermal Agrostis scabra and heat-sensitive Agrostis stolonifera. Physiol Plant 139:192–204. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2010.01357.x
Xu G, Guo C, Shan H, Kong H (2012) Divergence of duplicate genes in exon–intron structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:1187–1192. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1109047109
Yu Z, Duan X, Luo L, Dai S, Ding Z, Xia G (2020) How plant hormones mediate salt stress responses. Trends Plant Sci 25:1117–1130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2020.06.008
Zhang Y, Sun K, Sandoval FJ, Santiago K, Roje S (2010) One-carbon metabolism in plants: characterization of a plastid serine hydroxymethyltransferase. Biochem J 430:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20100566
Zhang J, Li M, Bryan AC, Yoo CG, Rottmann W, Winkeler KA, Collins CM, Singan V, Lindquist EA, Jawdy SS, Gunter LE, Engle NL, Yang XH, Barry K, Tschaplinski TJ, Schmutz J, Pu YQ, Ragauskas AJ, Tuskan GA, Muchero W, Chen JG (2019) Overexpression of a serine hydroxymethyltransferase increases biomass production and reduces recalcitrance in the bioenergy crop Populus. Sustain Energy Fuels 3:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8se00471d
Brengi SH, Khedr AAEM, Abouelsaad IA (2022) Effect of melatonin or cobalt on growth, yield and physiological responses of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) plants under salt stress. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 21(1):51–60. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2021.06.012
Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2007) Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat Protoc 2(4):953–971. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.131
Mishra P, Jain A, Takabe T, Tanaka Y, Negi M, Singh N, Jain N, Mishra V, Maniraj R, Krishnamurthy SL, Sreevathsa R, Singh NK, Rai V (2019) Heterologous expression of serine hydroxymethyltransferase-3 from rice confers tolerance to salinity stress in E. coli and Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 10:217. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00217
Wu JX, Zhang ZG, Zhang Q, Han X, Gu XF, Lu TG (2015) The molecular cloning and clarification of a photorespiratory mutant, oscdm1, using enhancer trapping. Front Genet 6:226. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2015.00226
Yu CS, Chen YC, Lu CH, Hwang JK (2006) Prediction of protein subcellular localization. Protein Struct Funct Bioinf 64:643–651. https://doi.org/10.1002/prot.21018
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Professor Sanwen Huang (Institute of Vegetables and Flowers, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China) and Professor Chunhua Chen (State Key Laboratory of Crop Biology, Shandong Collaborative Innovation Center of Fruit & Vegetable Quality and Efficient Production, Tai’an, People’s Republic of China) for providing us cucumber seeds.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program (2018YFD1000800); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31160398, 31560563, 31860568, 32072559 and 32102370); Key Research and Development Program of Gansu Province, China (No. 21YF5WA096); the Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province, China (Nos. 1606RJZA073 and 1606RJZA077); the Research Fund of Higher Education of Gansu, China (No. 2018C-14 and 2019B-082).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WBL conceived of the study. RG wrote the manuscript and WBL, CLW revised the manuscript. RG, YYL, XJP performed the experiments and contributed to data analysis. All authors reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical statements
This manuscript is original and has not been published or presented elsewhere in part or in entirety and is not under consideration by another journal. We have read and understood your journal’s policies, and we believe that neither the manuscript nor the study violates any of these. There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, R., Luo, Y., Pan, X. et al. Genome-wide identification of SHMT family genes in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) and functional analyses of CsSHMTs in response to hormones and abiotic stresses. 3 Biotech 12, 305 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03378-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03378-x