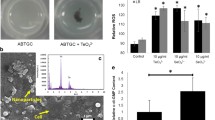
Abstract
Biofilms represent a protective survival mode in which bacteria adapt themselves to the natural environment for survival purposes. Biofilm formation is regulated by 3,5-cyclic diguanylic acid (c-di-GMP), which is a universal second messenger molecule in bacteria. Diguanylate cyclase (DGC) catalyses c-di-GMP intracellular synthesis, which plays important roles in bacterial adaptation to the natural environment. In this study, the DGC gene was first cloned from Antarctic Rhodococcus sp. NJ-530. DGC contained 948 nucleotides and encoded 315 amino acids with a molecular weight of 34.6 KDa and an isoelectric point of 5.58. qRT–PCR demonstrated that the DGC expression level was significantly affected by lower salinity and temperature. Consistently, more biofilm formation occurred under the same stress. It has been shown that Rhodococcus sp. NJ-530 can adapt to the extreme environment in Antarctica, which is closely related to biofilm formation. These results provide an important reference for studying the adaptive mechanism of Antarctic microorganisms to this extreme environment.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
An ML, Zheng Z, Qu CF, Wang XX, Chen H, Shi CL, Miao JL (2018) The first (6–4) photolyase with DNA damage repair activity from the Antarctic microalga Chlamydomonas sp. ICE-L. Mutat Res 809:13–19
Azevedo NF, Pinto AR, Reis NM, Vieira MJ, Keevil CW (2006) Shear stress, temperature, and inoculation concentration influence the adhesion of water-stressed Helicobacter pylori to stainless steel 304 and polypropylene. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(4):2936–2941
Bazire A, Diab F, Jebbar M, Haras D (2007) Influence of high salinity on biofilm formation and benzoate assimilation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34(1):5–8
Berlanga M, Guerrero R (2016) Living together in biofilms: the microbial cell factory and its biotechnological implications. Microb Cell Fact 15(1):165–175
Bolter M (2004) Ecophysiology of psychrophilic and psychrotolerant microorganisms. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-Grand, France) 50(5):563–573
Cady NC, McKean KA, Behnke J, Kubec R, Mosier AP, Kasper SH, Burz DS, Musah RA (2012) Inhibition of biofilm formation, quorum sensing and infection in Pseudomonas aeruginosa by natural products-inspired organosulfur compounds. PLoS ONE 7(6):e38492
Castro M, Deane SM, Ruiz L, Rawlings DE, Guiliani N (2015) Diguanylate cyclase null mutant reveals that C-Di-GMP pathway regulates the motility and adherence of the extremophile bacterium Acidithiobacillus caldus. PLoS ONE 10(2):e0116399
Christen B, Christen M, Paul R, Schmid F, Folcher M, Jenoe P, Meuwly M, Jenal U (2006) Allosteric control of cyclic di-GMP signaling. J Biol Chem 281(42):32015–32024
Dessi-Fulgheri F (2013) Antarctic ecosystems: an extreme environment in a changing world. Front Biogeogr 5(1):2215–2232
Doll K, Jongsthaphongpun KL, Stumpp NS, Winkel A, Stiesch M (2016) Quantifying implant-associated biofilms: Comparison of microscopic, microbiologic and biochemical methods. J Microbiol Methods 130:61–68
Donlan RM (2002) Biofilms: microbial life on surfaces. Emerg Infect Dis 8(9):881–890
Fazli M, Rybtke M, Steiner E, Weidel E, Berthelsen J, Groizeleau J, Bin W, Zhi BZ, Yaming Z, Kaever V, Givskov M, Hartmann RW, Eberl L, Tolker-Nielsen T (2017) Regulation of Burkholderia cenocepacia biofilm formation by RpoN and the c-di-GMP effector BerB. Microbiologyopen 6(1483):e00480
Gjermansen M, Nilsson M, Yang L, Tolker-Nielsen T (2010) Characterization of starvation-induced dispersion in Pseudomonas putida biofilms: genetic elements and molecular mechanisms. Mol Microbiol 75(4):815–826
Głowacki R, Strek P, Zagórska-Swiezy K, Składzień J, Oleś K, Hydzik-Sobocińska K, Miodoński A (2008) Biofilm from patients with chronic rhinosinusitis morphological SEM studies. Otolaryngol Pol 62(3):305–310
Gompelman M, van Asten SAV, Peters EJG (2016) Update on the role of infection and biofilms in wound healing: pathophysiology and treatment. Plast Reconstr Surg 138(3):61S-70S
Gupta K, Liao J, Petrova OE, Cherny KE, Sauer K (2014) Elevated levels of the second messenger c-di-GMP contribute to antimicrobial resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 92(3):488–506
Ha DG, O’Toole GA (2015) C-di-GMP and its effects on biofilm formation and dispersion: a pseudomonas aeruginosa review. Microbiol Spectr. https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.MB-0003-2014
Hachulla EV, Gressin L, Guillevin PD, Groote J, Cabane P, Carpentier C, Francès A (2004) Bacterial biofilms: from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rev Microbiol 2(2):95–108
Hall-Stoodley L, Costerton JW, Stoodley P (2004) Bacterial biofilms:from the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat Rew Microbiol 2:95–108
He YY, Wang YB, Zheng Z, Liu FM, An ML, He XD, Qu CF, Li LL, Miao JL (2017) Cloning and stress-induced expression analysis of calmodulin in the antarctic alga Chlamydomonas sp. ICE-l Curr Microbiol 74(8):921–929
He YY, Qu CF, Zhang LP, Miao JL (2021) DNA photolyase from Antarctic marine bacterium Rhodococcus sp. NJ-530 can repair DNA damage caused by ultraviolet. 3 Biotech. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02660-8
Hengge R (2016) Trigger phosphodiesterases as a novel class of c-di-GMP effector proteins. Philosoph Trans Royal Soc B Biol Sci 371(1707):20150498
Jakobsen TH, Tolker-Nielsen T, Givskov M (2017) Bacterial biofilm control by perturbation of bacterial signaling processes. Int J Mol Sci 18(9):1970
Jenal U, Reinders A, Lori C (2017) Cyclic di-GMP: second messenger extraordinaire. Nat Rev Microbiol 15(5):271–284
Jones CJ, Wozniak DJ (2017) Congo Red Stain Identifies Matrix Overproduction and Is an Indirect Measurement for c-di-GMP in Many Species of Bacteria. Methods Mol Biol 1657:147–156
Kaplan JB (2010) Biofilm dispersal: mechanisms, clinical implications, and potential therapeutic uses. J Dent Res 89:205–218
Kasim WA, Gaafar RM, Abou-Ali RM, Omar MN, Hewait HM (2016) Effect of biofilm forming plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on salinity tolerance in barley. Ann Agric Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2016.07.003
Lee K, Yoon SS (2017) Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm, a programmed bacterial life for fitness. J Microbiol Biotechnol 27(6):1053–1064
Li C, Ma L, Mou SL, Wang YB, Zheng Z, Liu FM, Qi XQ, An ML, Chen H, Miao JL (2015) Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers photolyase from extremophilic microalga: remarkable UVB resistance and efficient DNA damage repair. Mutat Res 773:37–42
Li LL, An ML, Qu CF, Zheng Z, Wang YB, Liu FM, He YY, He XD, Miao JL (2017) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of major intrinsic protein gene in Chlamydomonas sp. ICE-L from Antarctica. Extremophiles 21(4):817–827
Liu YJ, Xie J, Zhao LJ, Qian YF, Zhao Y, Liu X (2015) Biofilm formation characteristics of pseudomonas lundensis isolated from meat. J Food Sci 80(12):2904–2910
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2002) Analysis of relative gene expression using different real-time quantitative PCR. Methods 25(4):402–408
Ma Q, Yang Z, Pu M, Peti W, Wood TK (2010) Engineering a novel c-di-GMP-binding protein for biofilm dispersal. Environ Microbiol 13(3):631–642
Marshall SH, Gómez FA, Ramírez R, Nilo L, Henríquez V (2012) Biofilm generation by Piscirickettsia salmonis under growth stress conditions: a putative in vivo survival/persistence strategy in marine environments. Res Microbiol 163(8):557–566
Mei X, Xing D, Yang Y, Liu Q, Zhou H, Guo C, Ren N (2017) Adaptation of microbial community of the anode biofilm in microbial fuel cells to temperature. Bioelectrochemistry 117:29–33
Mou SL, Zhang X, Ye NH, Dong M, Liang C, Liang Q, Miao JL, Xu D, Zheng Z (2012) Cloning and expression analysis of two different LhcSR genes involved in stress adaptation in an Antarctic microalga, Chlamydomona sp. ICE-L. Extremophiles 16(2):193–203
Nagar V, Godambe LP, Bandekar JR, Shashidhar R (2017) Biofilm formation by Aeromonas strains under food-related environmental stress conditions. J Food Process Preserv. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.13182
Opoku-Temeng C, Sintim HO (2017) Targeting c-di-GMP Signaling, Biofilm Formation, and Bacterial Motility with Small Molecules. Methods Mol Biol 1657:419–430
Qian W, Ma L, Gu L, Zhang L (2017) Preface for special issue on biofilm and c-di-GMP–Microbial society, c-di-GMP regulation, and new research techniques. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao 33(9):1351–1356
Rice SA, Koh KS, Queck SY, Labbate M, Lam KW, Kjelleberg S (2005) Biofilm formation and sloughing in Serratia marcescens are controlled by quorum sensing and nutrient cues. J Bacteriol 187(10):3477–3485
Römling U, Galperin MY, Gomelsky M (2013) Cyclic di-GMP: the first 25 years of a universal bacterial second messenger. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77(1):1–52
Schirmer T, Jenal U (2009) Structural and mechanistic determinants of c-di-GMP signalling. Nat Rev Microbiol 7(10):724–735
Shikuma NJ, Yildiz FH (2009) Identification and characterization of OscR, a transcriptional regulator involved in osmolarity adaptation in Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol 191(13):4082–4096
Simm R, Morr M, Kader A, Nimtz M, Römling U (2004) GGDEF and EAL domains inversely regulate cyclic di-GMP levels and transition from sessility to motility. Mol Microbiol 53(4):1123–1134
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729
Townsley L, Yildiz FH (2015) Temperature affects c-di-GMP signalling and biofilm formation in Vibrio cholerae. Environ Microbiol 17(11):4290–4305
Townsley YFA (2015) The role of temperature in the environmental survival and transmission of Vibrio cholerae. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/104933v8
Ueda A, Wood TK (2009) Connecting quorum sensing, c-di-GMP, pel polysaccharide, and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through tyrosine phosphatase TpbA (PA3885). PLoS Pathog 5(6):e1000483
Vásquez-Ponce F, Higuera-Llantén S, Pavlov MS, Ramírez-Orellana R, Marshall SH, Olivares-Pacheco J (2017) Alginate overproduction and biofilm formation by psychrotolerant Pseudomonas mandelii depends on temperature in Antarctic marine sediments. Electron J Biotechnol 28(C):27–34
Xu Z, Liang Y, Lin S, Chen D, Li B, Li L, Deng Y (2016) Crystal violet and XTT assays on staphylococcus aureus biofilm quantification. Curr Microbiol 73(4):474–482
Yang CY, Chin KH, Chuah ML, Liang ZX, Wang AH, Chou SH (2011) The structure and inhibition of a GGDEF diguanylate cyclase complexed with (c-di-GMP)(2) at the active site. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 67(12):997–1008
Zogaj X, Wyatt GC, Klose KE (2012) Cyclic di-GMP stimulates biofilm formation and inhibits virulence of Francisella novicida. Infect Immun 80(12):4239–4247
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant no: 2018YFD0900705, Jinlai Miao, Basic Scientific Fund for National Public Research Institutes of China, grant no: 2020Q02, Changfeng Qu, Natural Science Foundation of China, grant no: 32000074, Changfeng Qu, grant no: 42176130, Jinlai Miao, Natural Science Foundation of Shandong, grant no: ZR2019BD023, Changfeng Qu, grant no: ZR2021MD044, Jinlai Miao,Tai Mountain Industry Leading Talent of Shan Dong, grant no: 2019TSCYCX-06, Jinlai Miao, Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangxi, grant no: AA21196002, Jinlai Miao
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
No conflict of interest is associated with this work.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., He, Y., Deng, Y. et al. A diguanylate cyclase regulates biofilm formation in Rhodococcus sp. NJ-530 from Antarctica. 3 Biotech 12, 27 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-03093-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-03093-z