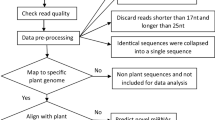
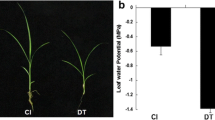
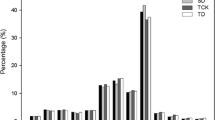
Abstract
Drought is a major factor which reduces cane growth and productivity. In the present study, we sequenced drought susceptible (V1) and drought tolerant (V2) sugarcane varieties using high-throughput miRNA deep sequencing method to study the regulation of gene expression by miRNAs during drought stress in sugarcane. A total of 1224 conserved miRNAs which belong to 89 miRNA families were identified and 38% of the differentially regulated miRNAs were common for both varieties. Additionally 435 novel miRNAs were also identified from four small RNA libraries. We identified 145 miRNAs that were differentially expressed in susceptible variety (V1–31) and 143 miRNAs differentially expressed in the tolerant variety (V2–31). Target prediction revealed that the genes mainly encoded transcription factors, proteins, phosphatase and kinases involved in signal transduction pathways, integral component of membrane and inorganic ion transport metabolism, enzymes involved in carbohydrate transport and metabolism and drought-stress-related proteins involved in defense mechanisms. Pathway analysis of targets revealed that “General function prediction only” was the most significant pathway observed in both tolerant and susceptible genotypes followed by “signal transduction mechanisms”. Functional annotation of the transcripts revealed genes like calcium-dependent protein kinase, respiratory burst oxidase, caffeic acid 3-O-methyltransferase, peroxidase, calmodulin, glutathione S-transferase and transcription factors like MYB, WRKY that are involved in drought tolerant pathways. qRT-PCR was used to verify the expression levels of miRNAs and their potential targets obtained from RNA sequencing results.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data supporting the results of this article are given in the paper and in additional files. The sequencing reads have been submitted as sequence read archive (SRA) in NCBI with the BioProject ID—PRJNA593909.
Change history
19 July 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02916-3
References
Akdogan G, Tufekci ED, UranbeyS UT (2016) MiRNA-based drought regulation in wheat. Funct Integr Genomics 16:221–233
Aravind J, Rinku S, Pooja B, Shikha M, Kaliyugam S, Mallikarjuna MG, Kumar A, Rao AR, Nepolean T (2017) Identification, characterization, and functional validation of drought-responsive MicroRNAs in subtropical maize inbreds. Front Plant Sci 8:941. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00941
Axtell MJ (2013) Classification and comparison of small RNAs from plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:137–159
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Bertolini E, Verelst W, Horner DS, Gianfranceschi L, Piccolo V, Inze D, Pe ME, Mica E (2013) Addressing the role of microRNAs in reprogramming leaf growth during drought stress in Brachypodium distachyon. Mol Plant 6(2):423–443
Borges F, Martienssen RA (2015) The expanding world of small RNAs in plants. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16:727–741. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm4085
Cheah BH, Nadarajah K, Divate MD, Wickneswari R (2015) Identification of four functionally important microRNA families with contrasting differential expression profiles between drought-tolerant and susceptible rice leaf at vegetative stage. BMC Genomics 16:692. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-015-1851-3
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, Lao KQ, Livak KJ, Guegler KJ (2005) Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem–loop RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 33(20):1–9
Chen Q, Li M, Zhang Z, Tie W, Chen X, Jin L, Zhai N, Zheng Q, Zhang J, Wang R, Xu G, Zhang H, Liu P, Zhou H (2017) Integrated mRNA and microRNA analysis identifies genes and small miRNA molecules associated with transcriptional and post-transcriptional-level responses to both drought stress and re-watering treatment in tobacco. BMC Genomics 18:62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-016-3372-0
Chen P, Chen J, Sun M, Yan H, Feng G, Wu B, Zhang X, Wang X, Huang L (2020) Comparative transcriptome study of switch grass (Panicum virgatum L.) homologous autopolyploid and its parental amphidiploids responding to consistent drought. Biotechnol Biofuels 13:170
Companhia Nacional de Abastecimento [CONAB] (2017) Acompanhamento da safrabrasileira de cana-de-açúcar, v.4 – SAFRA 2017/2018 n.1 – PrimeiroLevantamento
Czech B, Munafo M, Ciabrelli F, Eastwood EL, Fabry MH, Kneuss E et al (2018) piRNA-guided genome defense: from biogenesis to silencing. Annu Rev Genet 52:131–157. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-120417-031441
Devi K, Gomathi R, Arun Kumar R, Manimekalai R, Selvi A (2018) Field tolerance and recovery potential of sugarcane varieties subjected to drought. Indian J Plant Physiol 23(1):271–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-018-0367-7
Devi K, Prathima PT, Gomathi R, Manimekalai R, Lakshmi K, Selvi A (2019) Gene expression profiling in sugarcane genotypes during drought stress and rehydration. Sugar Tech 21(5):717–733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12355-018-0687-y
Ding Y, Ye Y, Jiang Z, Wang Y, Zhu C (2016) MicroRNA390 is involved in cadmium tolerance and accumulation in rice. Front Plant Sci 7:235. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00235
Dong OX, Yu S, Jain R, Zhang N, Duong PQ, Butler C, Li Y, Lipzen A, Martin JA, Barry KW, Schmutz J, Tian L, Ronald PC (2020) Marker-free carotenoid-enriched rice generated through targeted gene insertion using CRISPR-Cas9. Nat Commun 11:1178. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14981-y
Fahlgren N, Howell MD, Kasschau KD, Chapman EJ, Sullivan CM et al (2007) High-throughput sequencing of Arabidopsis microRNAs: evidence for frequent birth and death of MiRNA genes. PLoS ONE 2:e219
Fantao Z, Yuan L, Meng Z, Yi Z, Hongping C, Biaolin H, Jiankun X (2018) Identification and characterization of drought stress responsive novel microRNAs in Dongxiang wild rice. Rice Sci 25(4):175–184
Farooq M, Wahid A, Kobayashi N, Fujita D, Basra SMA (2009) Plant drought stress: effects, mechanisms and management. Agron Sustain Dev 29:185–212
Ferreira TH, Gentile A, Vilela RD, Costa GGL, Dias LI, Endres L et al (2012) MicroRNAs associated with drought response in the bioenergy crop sugarcane (Saccharum spp.). PLoS ONE 7:e46703. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046703
Gao F, Wang N, Li H, Liu J, Fu C, Xiao Z, Wei C, Lu X, Fen J, Zhou Y (2016) Identification of drought responsive microRNAs and their targets in Ammopiptanthus mongolicus using highthroughput sequencing. Sci Rep 6:34601. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep34601
Gentile A, Ferreira TH, Mattos RS, Dias LI, Hoshino AA, Carneiro MS, Souza GM, Calsa T Jr, Nogueira RM, Endres L, Menossi M (2013) Effects of drought on the microtranscriptome of field-grown sugarcane plants. Planta 237(3):783–798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1795-7
Gentile A, Dias LI, Mattos RS, Ferreira TH, Menossi M (2015) MicroRNAs and drought responses in sugarcane. Front Plant Sci 6:1–13
Glazinska P, Wojciechowski W, Wilmowicz E, Zienkiewicz A, Frankowski K, Kopcewicz J (2013) The involvement of InMIR167 in the regulation of expression of its target gene InARF8, and their participation in the vegetative and generative development of Ipomoea nil plants. J Plant Physiol 171:225–234
Golldack D, Li C, Mohan H, Probst N (2014) Tolerance to drought and salt stress in plants: unraveling the signaling networks. Front Plant Sci 5:151
Guirao RS, Yi H, San Segundo B (2018) The polycistronic miR166k-166h positively regulates rice immunity via post-transcriptional control of EIN2. Front Plant Sci 9:337. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.00337
Guo Y, Zhao S, Zhu C, Chang X, Yue C, Wang Z, Lin Y, Lai Z (2017) Identification of drought-responsive miRNAs and physiological characterization of tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.) under drought stress. BMC Plant Biol 17:211. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1172-6
Hamza NB, Sharma N, Tripathi A, Mishra NS (2016) MicroRNA expression profiles in response to drought stress in Sorghum bicolor. Gene Expr Patterns 20(2):88–98
Hua Y, Zhang C, Shi W, Chen H (2019) High-throughput sequencing reveals microRNAs and their targets in response to drought stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 33(1):465–471. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2019.1586586
Huang SC, Lu GH, Tang CY, Ji YJ, Tan GS, Hu DQ, Cheng J, Wang GH, Qi JL, Yang YH (2018) Identification and comparative analysis of aluminum-induced microRNAs conferring plant tolerance to aluminum stress in soybean. Biol Plant 62(1):97–108
Jin W, Li N, Zhang B, Wu F, Li W, Guo A, Deng Z (2008) Identification and verification of microRNA in wheat (Triticum aestivum). J Plant Res 121:351–355
Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP (2004) Computational identification of plant microRNAs and their targets, including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol Cell 14:787–799
Katiyar A, Smita S, Muthusamy SK, Chinnusamy V, Pandey DM, Bansal KC (2015) Identification of novel drought-responsive microRNAs and trans-acting siRNAs from Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench by high-throughput sequencing analysis. Front Plant Sci 6:506. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00506
Khraiwesh B, Zhu JK, Zhu JH (2012) Role of miRNAs and siRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses of plants. Biochem Biophys Acta 1819(2):137–148
Lakshmanan P, Robinson N (2014) Stress physiology: abiotic stresses. In: Moore PH, Botha FC (eds) Sugarcane: physiology, biochemistry, and functional biology. John Wiley & Sons Inc, Chichester, pp 411–434
Li F, Pignatta D, Bendix C, Brunkard JO, Cohn MM, Tung J et al (2012) MicroRNA regulation of plant innate immune receptors. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 109:1790–1795. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1118282109
Li Y, Wan L, Bi S, Wan X, Li Z, Cao J, Tong Z, Xu H, He F, Li X (2017) Identification of drought-responsive microRNAs from roots and leaves of alfalfa by high-throughput sequencing. Genes 8:119
Liu M, YuH ZG, Huang Q, Lu Y, Ouyang B (2017) Profiling of drought-responsive microRNA and mRNA in tomato using high-throughput sequencing. BMC Genomics 18:481. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-3869-1
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lorenz R, Bernhart SH, Höner zu Siederdissen C, Tafer H, Flamm C, Stadler PF, Hofacker IL (2011) ViennaRNA package 2.0. Algorithm Mol Biol 6:26
Machado RS, Ribeiro RV, Eduardo P, Marchiori R (2009) Biometric and physiological responses to water-deficit in sugarcane at different phonological stages. Pesqui Agropecu Bras 44(12):1575–1582
Mutum RD, Kumar S, Balyan S, Kansal S, Mathur S, Raghuvanshi S (2016) Identification of novel miRNAs from drought tolerant rice variety Nagina 22. Sci Rep 6:30786. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30786
Namwongsa J, Jongrungklang N, Songsri P (2019) Genotypic variation in root distribution and physiological responses of sugarcane induced by drought stress. SABRAO J Breed Genet 51(4):470–493
OECD-FAO (2019) OECD-FAO agricultural outlook 2019–2028, chapter 5: sugar. OECD-FAO, Paris, pp 1–326
Osakabe Y, Osakabe K, Shinozaki K, Tran LSP (2014) Response of plants to water stress. Front Plant Sci 5:86. https://doi.org/10.3389/Fpls.2014.00086
Pagliarani C, Vitali M, Ferrero M, Vitulo N, Incarbone M, Lovisolo C, Valle G, Schubert A (2017) The accumulation of miRNAs differentially modulated by drought stress is affected by grafting in grapevine. Plant Physiol 173:2180–2195
Pei HX, Ma N, Chen JW, Zheng Y, Tian J, Li J, Zhang S, Fei ZJ, Gao JP (2013) Integrative analysis of miRNA and mRNA profiles in response to ethylene in rose petals during flower opening. PLoS ONE 8(5):e64290
Rampino P, Pataleo S, Gerardi C, Mita G, Perrotta C (2006) Drought stress response in wheat: physiological and molecular analysis of resistant and sensitive genotypes. Plant Cell Environ 29:2143–2152
Rogers K, Chen XM (2013) Biogenesis, turnover, and mode of action of plant MicroRNAs. Plant Cell 25:2383–2399. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.113159
Sailaja B, Voleti SR, Subrahmanyam D, Sarla N, Prasanth VV, Bhadana VP, Mangrauthia SK (2014) Prediction and expression analysis of miRNAs associated with heat stress in Oryzasativa. Rice Sci 21(1):3–12
Selvi A, Devi K, Manimekalai R, Prathima PT (2020) Comparative analysis of drought responsive transcriptomes of sugarcane genotypes with differential tolerance to drought. 3 Biotech 10(6):236
Shriram V, Kumar V, Devarumath RM, Khare TS, Wani SH (2016) MicroRNAs as potential targets for abiotic stress tolerance in plants. Front Plant Sci 7:817
Silva RGd, Rosa-Santos TM, Franca SdC, Kottapalli P, Kottapalli KR, Zingaretti SM (2019) Microtranscriptome analysis of sugarcane cultivars in response to aluminum stress. PLoS ONE 14(11):e0217806. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217806
Singh KB, Foley RC, Onate-Sanchez L (2002) Transcription factors in plant defense and stress responses. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:430–436
Smoczynska A, Pacak AM, Nuc P, Swida-Barteczka A, Kruszka K, KarlowskiArturJarmolowski WM, Szweykowska-Kulinska Z (2020) A functional network of novel barley microRNAs and their targets in response to drought. Genes 11:488. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11050488
Su Y, Zhang Y, Huang N, Liu F, Su W, Xu L, Ahmad W, Wu Q, Guo J, Que Y (2017) Small RNA sequencing reveals a role for sugarcane miRNAs and their targets in response to Sporisorium scitamineum infection. BMC Genomics 18:325. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-3716-4
Sunkar R (2010) MicroRNAs with macro-effects on plant stress responses. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21(8):805–811
Sunkar R, Li YF, Jagadeeswaran G (2012) Functions of microRNAs in plant stress responses. Trends Plant Sci 17(4):196–203
Tang ZH, Zhang LP, Xu CG, Yuan SH, Zhang FT, Zheng YL et al (2012) Uncovering small RNA-mediated responses to cold stress in a wheat thermosensitive genic male-sterile line by deep sequencing. Plant Physiol 159:721–738
Thiebaut F, Grativol C, Carnavale-Bottino M, Rojas CA, Tanurdzic LOS, Farinelli L, Martienssen RA, Hemerly AS, Ferreira PC (2012) Computational identification and analysis of novel sugarcane microRNAs. BMC Genomics 13:290. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-290
Valliyodan B, Nguyen HT (2006) Understanding regulatory networks and engineering for enhanced drought tolerance in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9(2):189–195
Varkonyi-Gasic E, Rongmei Wu, Wood M, Walton EF, Hellens RP (2007) Protocol: a highly sensitive RT-PCR method for detection and quantification of microRNAs. Plant Methods 3:12
Vasudevan S, Tong Y, Steitz JA (2007) Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate translation. Science 318:1931–1934
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-003-1105-5
Wei L, Zhang D, Xiang F, Zhang Z (2009) Differentially expressed miRNAs potentially involved in the regulation of defense mechanism to drought stress in maize seedlings. Int J Plant Sci 170:979–989
Xia XJ, Zhou YH, Shi K, Zhou J, Foyer CH, Yu JQ (2015) Interplay between reactive oxygen species and hormones in the control of plant development and stress tolerance. J Exp Bot 66(10):2839–2856
Yan Q, Cui X, Lin S, Gan S, Xing H, Dou D (2016) GmCYP82A3, a soybean cytochrome P450 family gene involved in the jasmonic acid and ethylene signaling pathway, enhances plant resistance to biotic and abiotic stresses. PLoS ONE 11:9
Yang C, Liu J, Dong X, Cai Z, Tian W, Wang X (2014) Short-term and continuing stresses differentially interplay with multiple hormones to regulate plant survival and growth. Mol Plant 7(5):841–855
Yang Y, Zhang X, Su Y, Zou J, Wang Z, Xu L, Que Y (2017) miRNA alteration is an important mechanism in sugarcane response to low temperature environment. BMC Genomics 18:833. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-4231-3
Zhang JW, Long Y, Xue MD, Xiao XG, Pei XW (2017) Identification of microRNAs in response to drought in common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) shoots and roots. PLoS ONE 12(1):e0170330. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170330
Zhao Y, Cheng X, Liu X, Wu H, Bi H, Xu H (2018) The wheat MYB transcription factor TaMYB31 is involved in drought stress responses in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 9:1426
Zhou L, Liu Y, Liu Z, Kong D, Duan M, Luo L (2010) Genome-wide identification and analysis of drought-responsive microRNAs in Oryza sativa. J Exp Bot 61(15):4157–4168
Zhu Y, Weng M, Yang Y, Zhang C, Li Z, Shen WH, Dong A (2011) Arabidopsis homologues of the histone chaperone ASF1 are crucial for chromatin replication and cell proliferation in plant development. Plant J 66:443–455
Zhu L, Ow DW, Dong ZC (2018) Transfer RNA-derived small RNAs in plants. Sci China Life Sci 61:155–161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-017-9167-5
Zhuang J, Zhang J, Hou XL, Wang F, Xiong AS (2014) Transcriptomic, proteomic, metabolomic and functional genomic approaches for the study of abiotic stress in vegetable crops. Crit Rev Plant Sci 33(2–3):225–237
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi under the research project PI-14/1.2.35. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support and facilities provided by the Director, ICAR-Sugarcane Breeding Institute, Coimbatore and also thank Genotypic Technology Pvt. Ltd., Bangalore for small RNA sequencing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AS: conceptualization, project administration, data analysis and interpretation of the data, supervision, writing, review and editing. KD: laboratory experiments, validation, writing and review. RM: methodology for RNA Seq, analysis and interpretation of the data. PTP: data analysis, methodology for validation, review and editing. VPR: methodology for validation and expression analysis. KL: data analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in this publication.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selvi, A., Devi, K., Manimekalai, R. et al. High-throughput miRNA deep sequencing in response to drought stress in sugarcane. 3 Biotech 11, 312 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02857-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02857-x