Abstract
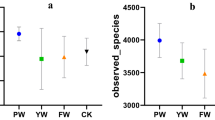
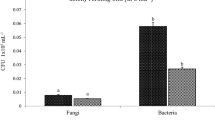
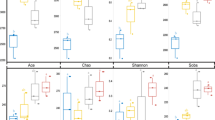
The rhizosphere microbial community is important for plant health and is shaped by numerous environmental factors. This study aimed to unravel the effects of a pesticide/fertilizer mixture on the soil rhizosphere microbiome of field-grown sugarcane. A field trial on sugarcane was conducted in Zhanjian City, Guangdong Province, China, and soil samples from the rhizosphere were collected after clothianidin pesticide and/or organic fertilizer treatments. The effects of pesticide and/or organic fertilizer treatments on the composition, diversity, and predictive function of the rhizosphere microbial communities were examined using 16S rRNA gene and ITS1 amplicon sequencing. Compared with the controls (no pesticide or fertilizer used), the microbial community that resulted from treatment with the pesticide/fertilizer mixture (SPF) had a higher relative bacterial diversity and fungal richness, and contributed more beneficial functions to sugarcane, including xenobiotics biodegradation and metabolism of amino acids. The bacterial and fungal compositions at various taxonomic levels were not significantly different in SPF and SP (pesticide only) treatments compared to treatments without the pesticide, suggesting that the clothianidin addition did not cause a detrimental impact on the soil microbiome. Moreover, five bacterial genera, including Dyella, Sphingomonas, Catenulispora, Mucilaginibacter, and Tumebacillus, were significantly more abundant in the SPF and SP treatments, which could be associated with the pesticide addition. With the addition of organic fertilizers in SPF, the abundances of some soil-beneficial bacteria Bacillus, Paenibacillus, and Brevibacillus were highly increased. Our study provides insights into the interactions between the rhizosphere soil microbiome and pesticide-fertilizer integration, which may help improve the application of pesticide-fertilizer to sugarcane fields.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achorn FP, Wright EB (1982) Production of fertilizer-pesticide mixtures. ASTM Special Technical Publication, USA 764:18
Bokhtiar SM, Sakurai K (2005) Effect of application of inorganic and organic fertilizers on growth, yield and quality of sugarcane. Sugar Tech 7:33–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02942415
Caporaso JG, Lauber CL, Walters WA, Berg-Lyons D, Lozupone CA, Turnbaugh PJ, Fierer N, Knight R (2011) Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(Suppl 1):4516–4522. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1000080107
Cherry R, Mccray M, Sandhu H (2017) Changes in the relative abundance of soil-dwelling insect pests in sugarcane grown in Florida. J Entomol Sci 52:169–176
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Keller K, Brodie EL, Larsen N, Piceno YM, Phan R, Andersen GL (2006) NAST: a multiple sequence alignment server for comparative analysis of 16S rRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res 34(Suppl 2):W394–W399. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkl244
Diez MC, Elgueta S, Rubilar O, Tortella GR, Schalchli H, Bornhardt C, Gallardo F (2017) Pesticide dissipation and microbial community changes in a biopurification system: influence of the rhizosphere. Biodegradation 28:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-017-9804-y
Doolotkeldieva T, Konurbaeva M, Bobusheva S (2018) Microbial communities in pesticide-contaminated soils in Kyrgyzstan and bioremediation possibilities. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:31848–31862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0048-5
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2604
Edgar RC, Haas BJ, Clemente JC, Quince C, Knight R (2011) UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 27:2194–2200. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btr381
Endres L, Oliveira NG, Ferreira VM, Silva JV, Barbosa GV, Sebastião OM (2016) Morphological and physiological response of sugarcane under abiotic stress to neonicotinoid insecticides. Theor Exp Plant Phys 28:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40626-016-0056-8
Franco HCJ, Otto R, Faroni CE, André CV, Emídio CAO, Trivelin PCO (2011) Nitrogen in sugarcane derived from fertilizer under Brazilian field conditions. Field Crop Res 121:29–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2010.11.011
Haney CH, Samuel BS, Bush J et al (2015) Associations with rhizosphere bacteria can confer an adaptive advantage to plants. Nat Plants 1:15051. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2015.51
Hartmann M, Frey B, Mayer J, Mäder P, Widmer F (2015) Distinct soil microbial diversity under long-term organic and conventional farming. ISME J 9:1177. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2014.210
Hirano T, Yanai S, Omotejara T et al (2015) The combined effect of clothianidin and environmental stress on the behavioral and reproductive function in male mice. J Vet Med Sci 77:1207–1215. https://doi.org/10.1292/jvms.15-0188
Huang WJ, Sun DL, Fu JT, Zhao HH, Wang RH, An YX (2020) Effects of continuous sugar beet cropping on rhizospheric microbial communities. Genes 11:13. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11010013
Jin SQ, Zhou F (2018) Zero growth of chemical fertilizer and pesticide use: China’s objectives, progress and challenges. J Res Ecol 9:50–58
Klaine SJ, Hinman ML, Winkelmann DA, Sauser KR, Martin JR, Moore LW (1988) Characterization of agricultural nonpoint pollution: pesticide migration in a West Tennessee watershed. Environ Toxicol Chem 7:609–614. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620070802
Korenblum E, Dong YH, Szymanski J, Panda S, Jozwiak A, Massalha H, Meir S, Rogachev I, Aharoni A (2020) Rhizosphere microbiome mediates systemic root metabolite exudation by root-to-root signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117:3874–3883. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1912130117
Langille MGI, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG et al (2013) Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat Biotechnol 31:814–821. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2676
Li Y, An J, Dang Z, Lv H, Pan W, Gao Z (2018) Treating wheat seeds with neonicotinoid insecticides does not harm the rhizosphere microbial community. PLoS ONE 13:e0205200. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0205200
Martin M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. Embnet J 17:10–12
Nguyen NH, Song Z, Bates ST, Branco S, Tedersoo L, Menke J, Schiling JS, Kennedy PG (2016) FUNGuild: An open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol 20:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2015.06.006
Nilsson RH, Larsson KH, Taylor AFS et al (2019) The UNITE database for molecular identification of fungi: handling dark taxa and parallel taxonomic classifications. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D259–D264. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1022
Prashar P, Shah S (2016) Impact of fertilizers and pesticides on soil microflora in agriculture. In: Lichtfouse E (ed) Sustainable agriculture reviews. Sustainable agriculture reviews, vol 19. Springer, Cham
Schmitz J, Hahn M, Brühl CA (2014) Agrochemicals in field margins—an experimental field study to assess the impacts of pesticides and fertilizers on a natural plant community. Agr Ecosys Environ 193:60–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2014.04.025
Singh NS, Mukherjeem I, Dasm SK, Varghesem E (2018) Leaching of clothianidin in two different Indian soils: effect of organic amendment. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 100:553–559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2290-z
Sun R, Dsouza M, Gilbert JA et al (2016) Fungal community composition in soils subjected to long-term chemical fertilization is most influenced by the type of organic matter. Environ Microbiol 18:5137–5150. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13512
Uneme H (2011) Chemistry of clothianidin and related compounds. J Agric Food Chem 59:2932–2937. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf1024938
Velasco A, Rodríguez J, Castillo R, Ortíz I (2012) Residues of organochlorine and organophosphorus pesticides in sugarcane crop soils and river water. J Environ Sci Heal 47:833–841. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601234.2012.693864
Wintermantel D, Locke B, Andersson GKS et al (2018) Field-level clothianidin exposure affects bumblebees but generally not their pathogens. Nat Commun 9:5446. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07914-3
Xie JJ, Chen YG, Peng DY, Yang CQ, Huang XJ, Wu G, Chen C, Yang JX (2017) Effect of 30% Tiange multifunctional pesticide-fertilizer on sugarcane pests and yield. Asian AgrRes 7:53–56
Xie S, Feng H, Yang F, Zhao Z, Hu X, Wei C, Liang T, Li HT, Geng YB (2019) Does dual reduction in chemical fertilizer and pesticides improve nutrient loss and tea yield and quality? A pilot study in a green tea garden in Shaoxing, Zhejiang Province, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:2464–2476. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3732-1
Xu T, Dyer DG, McConnell LL, Bondarenko S, Allen R, Heinemann O (2016) Clothianidin in agricultural soils and uptake into corn pollen and canola nectar after multiyear seed treatment applications. Environ Toxicol Chem 35:311–321. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.3281
Yang Q, Liu N, Cheng G, Zhang S, Zhou Y, Liang D, Gu Z (2018) Residue and dissipation of clothianidin in rice and soil. Agrochemicals 5:343–346
Yein BR, Singh H, Chhabra HK (2013) Effect of pesticides and fertilizers singly and in combination on the root-knot nematode infesting mung. Indian J Nematol 7:117–122
Zhang P, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Wei Y, Mu W, Liu F (2016) Effects of imidacloprid and clothianidin seed treatments on wheat aphids and their natural enemies on winter wheat. Pest Manag Sci 72:1141–1149. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.4090
Zhang PW, Wang SY, Huang CL et al (2018) Dissipation and residue of clothianidin in granules and pesticide fertilizers used in cabbage and soil under field conditions. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 25:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-7736-4
Zhao LJ, Jia YH, Zhou JT, Li A, Chen JF (2010) Dynamics of augmented soil system containing biphenyl with Dyella ginsengisoli LA-4. J Hazard Mater 179:729–734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.062
Zhu S, Vivanco JM, Manter DK (2016) Nitrogen fertilizer rate affects root exudation, the rhizosphere microbiome and nitrogen-use-efficiency of maize. Appl Soil Ecol 107:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2016.07.009
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by GDAS' Project of Science and Technology Development (2019GDASYL-0103031), National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFD0201103), China Sugar industry Research System (CARS-170306), and Guangdong Provincial Team of Technical System Innovation for Sugarcane Sisal Hemp Industry (2019KJ104-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WH, YA: Designed the work; YL, LC, and DS: Performed the field collections; WH: Performed the laboratory research and analyzed the data; WH, YA: Wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, W., Lu, Y., Chen, L. et al. Impact of pesticide/fertilizer mixtures on the rhizosphere microbial community of field-grown sugarcane. 3 Biotech 11, 210 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02770-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02770-3