Abstract
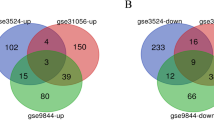
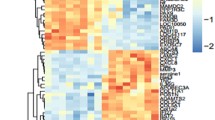
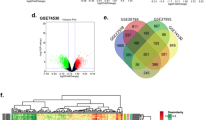
Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is one of the leading cancers with poor disease survival rate. Herein, we explored molecular basis, in silico identification and in vitro verification of genes associated with OSCC. Five gene expression series including, GSE30784, GSE13601, GSE9844, GSE23558 and GSE37991 were screened for differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways were enriched by cluster Profiler. Further, protein–protein interaction network was analysed and hub genes were verified. A total of 6476 (up-regulated: 2848; down-regulated: 3628) DEGs were identified among OSCC patients and healthy controls. Gene Ontology analysis indicated DEGs enrichment in cellular motility, invasion and adhesion processes. KEGG analysis revealed enrichment of PI3K-Akt signalling, focal adhesion and regulation of actin cytoskeleton pathways. Subsequently, nine DEGs including APP, EHMT1, ACACB, PCNA, PLAU, FST, HMGA2, LAMC2 and SPP1 were correlated with TCGA expression data along with significant association towards patient’s survival, recognized as hub genes. This dysregulated mRNA signature of genes was validated in two OSCC cell lines with an anti-cancer agent, fisetin. Fisetin inhibited the expression of APP, EHMT1, PCNA, PLAU, FST, HMGA2, LAMC2, SPP1 and upregulated the expression of ACACB gene which were associated with growth inhibition of both the OSCC cell lines. The regulatory effect of fisetin supported crucial role of nine hub genes identified in OSCC. This study signified that hub genes and pathways might influence the aggressiveness of OSCC. Thus, the proposed hub genes could be potential diagnostic biomarker and drug targets for OSCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal S, Nayek A, Pradhan D et al (2017) dbGAPs: a comprehensive database of genes and genetic markers associated with psoriasis and its subtypes. Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2017.10.003
Altman R (2016) Current progress in bioinformatics 2016. Brief Bioinform 17:1–1. https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bbv105
Ambatipudi S, Gerstung M, Pandey M et al (2012) Genome-wide expression and copy number analysis identifies driver genes in gingivobuccal cancers. Genes Chromosom Cancer 51:161–173. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.20940
Ambatipudi S, Bhosale PG, Heath E et al (2013) Downregulation of keratin 76 expression during oral carcinogenesis of human, hamster and mouse. PLoS ONE 8:e70688. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070688
Bader GD, Hogue CW (2003) An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinform 4:2. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-4-2
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P et al (2013) NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets–update. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D991-995. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1193
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H et al (2009) ClueGO: a Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 25:1091–1093. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp101
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I et al (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68:394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Camarda R, Zhou Z, Kohnz RA et al (2016) Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation as a therapy for MYC-overexpressing triple-negative breast cancer. Nat Med 22:427–432. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4055
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya SAH et al (2017) UALCAN: a portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia 19:649–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002
Chen C, Méndez E, Houck J et al (2008) Gene expression profiling identifies genes predictive of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer EpidemiolBiomarkPrev 17:2152–2162. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-2893
Chiu Y-W, Liou L-Y, Chen P-T et al (2016) Tyrosine 397 phosphorylation is critical for FAK-promoted Rac1 activation and invasive properties in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Lab Invest 96:296–306. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2015.151
Choi HS, Kim Y-K, Yun P-Y (2019) Upregulation of MDR- and EMT-related molecules in cisplatin-resistant human oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Int J MolSci 20:3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20123034
Choudhari AS, Mandave PC, Deshpande M et al (2020) Phytochemicals in cancer treatment: from preclinical studies to clinical practice. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01614
Cline MS, Smoot M, Cerami E et al (2007) Integration of biological networks and gene expression data using Cytoscape. Nat Protoc 2:2366–2382. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2007.324
Ding Y, Liu P, Zhang S et al (2018) Screening pathogenic genes in oral squamous cell carcinoma based on the mRNA expression microarray data. Int J Mol Med 41:3597–3603. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3514
Estilo CL, O-charoenrat P, Talbot S et al (2009) Oral tongue cancer gene expression profiling: identification of novel potential prognosticators by oligonucleotide microarray analysis. BMC Cancer 9:11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-9-11
He F, Chen H, Probst-Kepper M et al (2012) PLAU inferred from a correlation network is critical for suppressor function of regulatory T cells. MolSystBiol 8:624. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb.2012.56
Hou Y, Li H, Huo W (2020) THBS4 silencing regulates the cancer stem cell-like properties in prostate cancer via blocking the PI3K/Akt pathway. Prostate 80:753–763. https://doi.org/10.1002/pros.23989
Janik S, Bekos C, Hacker P et al (2019) Follistatin impacts tumor angiogenesis and outcome in thymic epithelial tumors. Sci Rep 9:17359. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53671-8
Klintman M, Buus R, Cheang MCU et al (2016) Changes in expression of genes representing key biologic processes after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer, and prognostic implications in residual disease. Clin Cancer Res 22:2405–2416. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1488
Lee C-H, Chang JS-M, Syu S-H et al (2015) IL-1β promotes malignant transformation and tumor aggressiveness in oral cancer. J Cell Physiol 230:875–884. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24816
Li Y, Jia S, Dai W (2020) Fisetin modulates human oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation by blocking pak4 signaling pathways. Drug Des DevelTher 14:773–782. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S229270
Liang Y, Kong D, Zhang Y et al (2020) Fisetin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via JAK/STAT3 signaling pathways in human thyroid TPC 1 cancer cells. BiotechnolBioproc E 25:197–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0326-9
Lin C-Y, Chin C-H, Wu H-H et al (2008) Hubba: hub objects analyzer—a framework of interactome hubs identification for network biology. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W438–W443. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn257
Lyons AJ, Jones J (2007) Cell adhesion molecules, the extracellular matrix and oral squamous carcinoma. Int J Oral MaxillofacSurg 36:671–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijom.2007.04.002
Nagao T, Warnakulasuriya S (2020) Screening for oral cancer: future prospects, research and policy development for Asia. Oral Oncol 105:104632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104632
Naghizadeh S, Mansoori B, Mohammadi A et al (2019) Effects of HMGA2 gene downregulation by siRNA on lung carcinoma cell migration in A549 cell lines. J Cell Biochem 120:5024–5032. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27778
Park B-S, Choi N-E, Lee JH et al (2019) Crosstalk between fisetin-induced apoptosis and autophagy in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer 10:138–146. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.28500
Petryszak R, Burdett T, Fiorelli B et al (2014) Expression Atlas update—a database of gene and transcript expression from microarray- and sequencing-based functional genomics experiments. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D926–D932. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1270
Piñero J, Ramírez-Anguita JM, Saüch-Pitarch J et al (2020) The DisGeNET knowledge platform for disease genomics: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res 48:D845–D855. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz1021
Sabarwal A, Agarwal R, Singh RP (2017) Fisetin inhibits cellular proliferation and induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human gastric cancer cells. MolCarcinog 56:499–514. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.22512
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2019) Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 69:7–34. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21551
Silva-Carvalho AÉ, Alencar APD, Resende MR et al (2020) Epigenetic priming by EHMT1/EHMT2 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia induces TP53 and TP73 overexpression and promotes cell death. Toxicol In Vitro 69:104992. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2020.104992
Stott-Miller M, Houck JR, Lohavanichbutr P et al (2011) Tumor and salivary matrix metalloproteinase levels are strong diagnostic markers of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer EpidemiolBiomarkPrev 20:2628–2636. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-11-0503
Stuelten CH, Parent CA, Montell DJ (2018) Cell motility in cancer invasion and metastasis: insights from simple model organisms. Nat Rev Cancer 18:296–312. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2018.15
Sun C, Yuan Q, Wu D et al (2017) Identification of core genes and outcome in gastric cancer using bioinformatics analysis. Oncotarget 8:70271–70280. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20082
Wang H, Cai J, Du S et al (2020a) LAMC2 modulates the acidity of microenvironments to promote invasion and migration of pancreatic cancer cells via regulating AKT-dependent NHE1 activity. Exp Cell Res 391:111984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111984
Wang J, Wang Y, Kong F et al (2020b) Identification of a six-gene prognostic signature for oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Cell Physiol 235:3056–3068. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29210
Wu X, Chen S, Lu C (2020a) Amyloid precursor protein promotes the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells by regulating the MAPK signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med 45:162–174. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2019.4404
Wu X, Chen Y, Kong W, Zhao Z (2020b) Amyloid precursor protein regulates 5-fluorouracil resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. J Zhejiang UnivSci B 21:234–245. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1900413
Xu X, Wang Y, Deng H et al (2018) HMGA2 enhances 5-fluorouracil chemoresistance in colorectal cancer via the Dvl2/Wnt pathway. Oncotarget 9:9963–9974. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.24133
Yang Y, Shen J, Yan D et al (2018a) Euchromatic histone lysine methyltransferase 1 regulates cancer development in human gastric cancer by regulating E-cadherin. OncolLett 15:9480–9486. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8506
Yang Y, Zhong Z, Ding Y et al (2018b) Bioinformatic identification of key genes and pathways that may be involved in the pathogenesis of HBV-associated acute liver failure. Genes Dis 5:349–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2018.02.005
Yang J, Nie J, Ma X, Wei Y, Peng Y, Wei X et al (2019) Targeting PI3K in cancer: mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Mol Cancer 18:26–26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-0954-x
Ye H, Yu T, Temam S et al (2008) Transcriptomic dissection of tongue squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Genomics 9:69. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-69
Yuan J, Kensler KH, Hu Z et al (2020) Integrative comparison of the genomic and transcriptomic landscape between prostate cancer patients of predominantly African or European genetic ancestry. PLoS Genet 16:e1008641. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008641
Zeng B, Zhou M, Wu H, Xiong Z (2018) SPP1 promotes ovarian cancer progression via Integrin β1/FAK/AKT signaling pathway. Onco Targets Ther 11:1333–1343. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S154215
Zhang P, Ruan Y, Xiao J et al (2018) Association of serum follistatin levels with histological types and progression of tumor in human lung cancer. Cancer Cell Int 18:162. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-018-0664-2
Zhang H, Schaefer A, Wang Y et al (2020) Gain-of-function RHOA mutations promote focal adhesion kinase activation and dependency in diffuse gastric cancer. CancerDiscov 10:288–305. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0811
Zhao X, Liu Z, Ren Z et al (2020) Triptolide inhibits pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration via down-regulating PLAU based on network pharmacology of Tripterygiumwilfordii Hook F. Eur J Pharmacol 880:173225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173225
Zhong P, Liu L, Shen A et al (2019) Five extracellular matrix-associated genes upregulated in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: an integrated bioinformatics analysis. OncolLett 18:5959–5967. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10982
Zhou H, Huang T, Xiong Y et al (2018) The prognostic value of proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in colorectal cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000013752
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to CIF, JNU and ICMR-AIIMS Computational Genomics Centre, New Delhi for helping in present work.
Funding
The work is supported by DPRP, Department of Science and Technology (DST), India, and DST-PURSE, UGC-RN, UPE-2 from Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi. M.Y. is supported by a fellowship from DST-INSPIRE (IF160971), New Delhi, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Execution of research method, bioinformatics analysis, result interpretation, experimental validation, and original draft preparation were performed by Monika Yadav. Dr. Pradhan has done bioinformatics analysis, result interpretation, and visualization. Conceptualization, supervision, reviewing, and final editing of manuscript were accomplished by Dr. Singh.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not include any human or animal samples.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, M., Pradhan, D. & Singh, R.P. Integrated analysis and identification of nine-gene signature associated to oral squamous cell carcinoma pathogenesis. 3 Biotech 11, 215 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02737-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02737-4